Executive Summary
DeFi runs on credit. To achieve the scale of traditional fixed-income markets, control over rate and duration is needed. Borrowers and lenders should be able to lock in rate and tenor upfront, making costs, income, and liquidity predictable.
Today, most onchain lending relies on variable-rate, utilization-based, perpetual loans, which make rate stability infeasible. Size addresses this with a term-structure order book. It offers fixed-term, fixed-rate credit, enabling better risk management by letting borrowers and lenders forecast costs and income.
For institutions to confidently deploy large amounts of capital onchain, they need to be able to rely on tools that let them lock rate and duration upfront to match assets and liabilities. Variable, perpetual loans that float rates based on unpredictable supply and demand can’t do that. Size’s term-structure order book (TSOB) was designed exactly to fix this issue: by making time a first-class market dimension, participants post limit orders that specify size, rate(s), maturity date(s), and accepted collateral.
Key Takeaways
- Time Becomes Tradable: Size prices funding by date, not pool utilization, via a term-structure order book. Lenders and borrowers trade dated claims they can hold, hedge, or transfer.
- Tenor Fragmentation Fix: One quote can target multiple maturities and serve multiple assets through Collateral Sets and haircuts. Depth concentrates where demand is, instead of being fragmented across multiple thinner pools with discrete tenors or collateral assets.
- Predictable Cash Flows: Fixed terms lock both rate and maturity, aligning inflows with obligations and letting participants budget predictably and confidently. Order book exits provide pre‑maturity flexibility.
- Earn Layer Automation: The Earn product places and maintains term offers, using managed Collateral Sets and per-pair Rate Providers; while actively waiting for a match, deposits earn a variable rate in Very Liquid Vaults.
- Capital Efficiency: Deposits keep working in liquid vaults, accruing variable yield while pending fixed-rate matches. Exposure is capped within instantly withdrawable capacity to allow the book to settle fills on demand.
- Term-Driven Strategies: By turning loans into dated, tradable claims, Size unlocks strategies variable-rate pools can’t, such as structured rate trades, long-horizon funding, and tighter asset‑liability management.
Market Context & Positioning
Institutions need three things from DeFi credit: a known term, size at a date, and a way out. In utilization-based floating-rate pools, all time preferences mix in one venue. Makers can’t target a date, and borrowers can’t source size at a precise maturity. At the same time, attempts to imitate tenors (wrappers, tranches, separate pools) result in capital fragmentation across multiple thin markets (different maturities and collateral assets) and still don’t produce a clean curve.
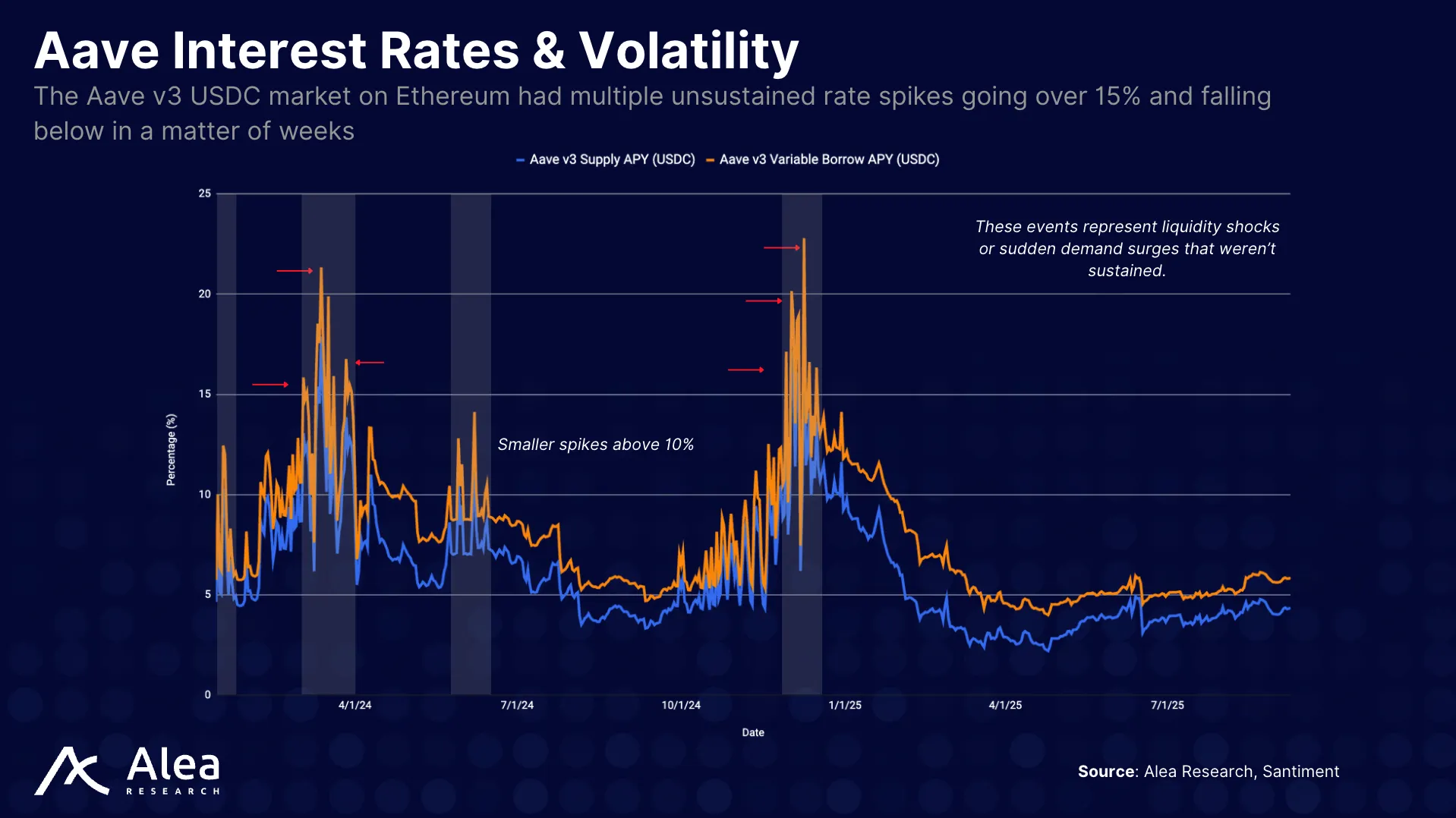
Utilization-based variable-rate pools are attractive because of their seemingly frictionless UX (easy to join and exit when utilization is moderate) and continuous price discovery. Since the floating rate tracks usage, it’s easy to algorithmically auto-adjust market behavior. However, when utilization spikes from liquidations, news, or yield rotations, the subsequent rate hikes don’t instantly attract offsetting deposits.
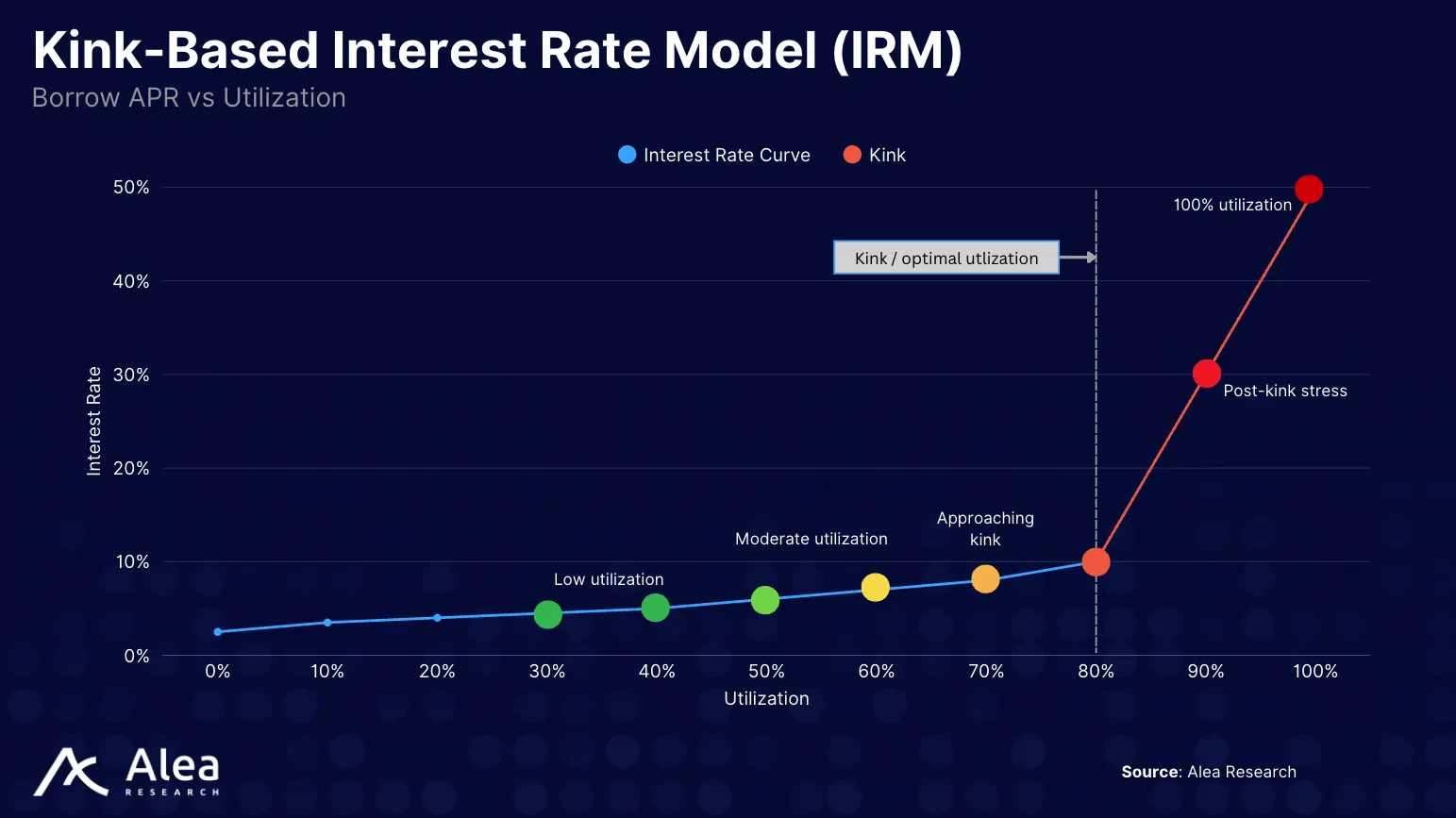
Contrast this with TradFi’s fixed income, where fixed-rates are prevalent and allow participants to lock their borrowing costs for a set term at loan origination. This enables duration management, pricing across a yield curve, and term premium (higher compensation for longer maturities).
Market stability and favorable conditions for efficient risk management require financial instruments that let their participants accurately predict their costs over a specified period. Sophisticated strategies and institutions demand time certainty, date‑specific size, and a clean secondary‑market exit. Size delivers all three.
- Known term: Makers quote by exact maturity; borrowers lock the rate and cost at execution.
- Size at a date: Maker quotes determine capacity per tenor.
- Early exit: Positions are tradable claims. Lenders sell the claim; borrowers prepay or roll by crossing the book.
In Size, makers deploy once and reach many assets; borrowers see deeper books at key maturities without hunting per-asset pools. A single quote can fund multiple collateral types (within defined haircuts) and, as a result, liquidity concentrates where demand is instead of being split across bespoke pools. This results in tighter spreads with a well-defined yield curve for price discovery and a more reliable term structure.
Protocol Overview
In Size’s term-structure order book (TSOB) orders are matched like in any other order book, with the live stack of bids and offers forming a tradable yield curve. Thus, price discovery moves from “what the pool will pay today” to “what the market will pay for this tenor,” letting participants plan, hedge, or exit early by executing trades on either side of the book.
In addition to lending and borrowing, users can actively trade and speculate on rates by buying and selling credit for any maturity, or by placing orders at rates significantly above or below the current bid-ask spread on the yield curve, such as at two or three times the width of the spread.
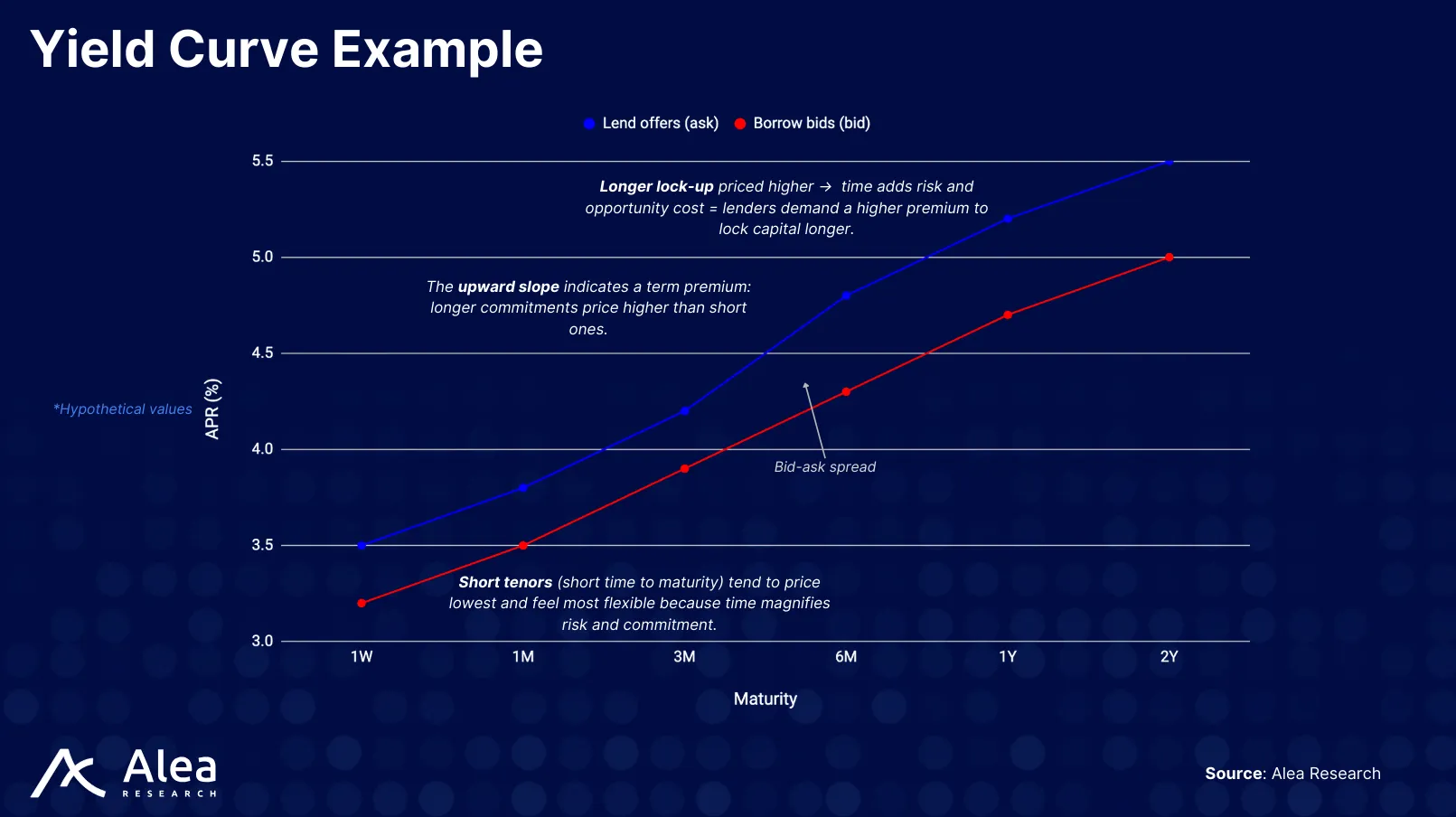
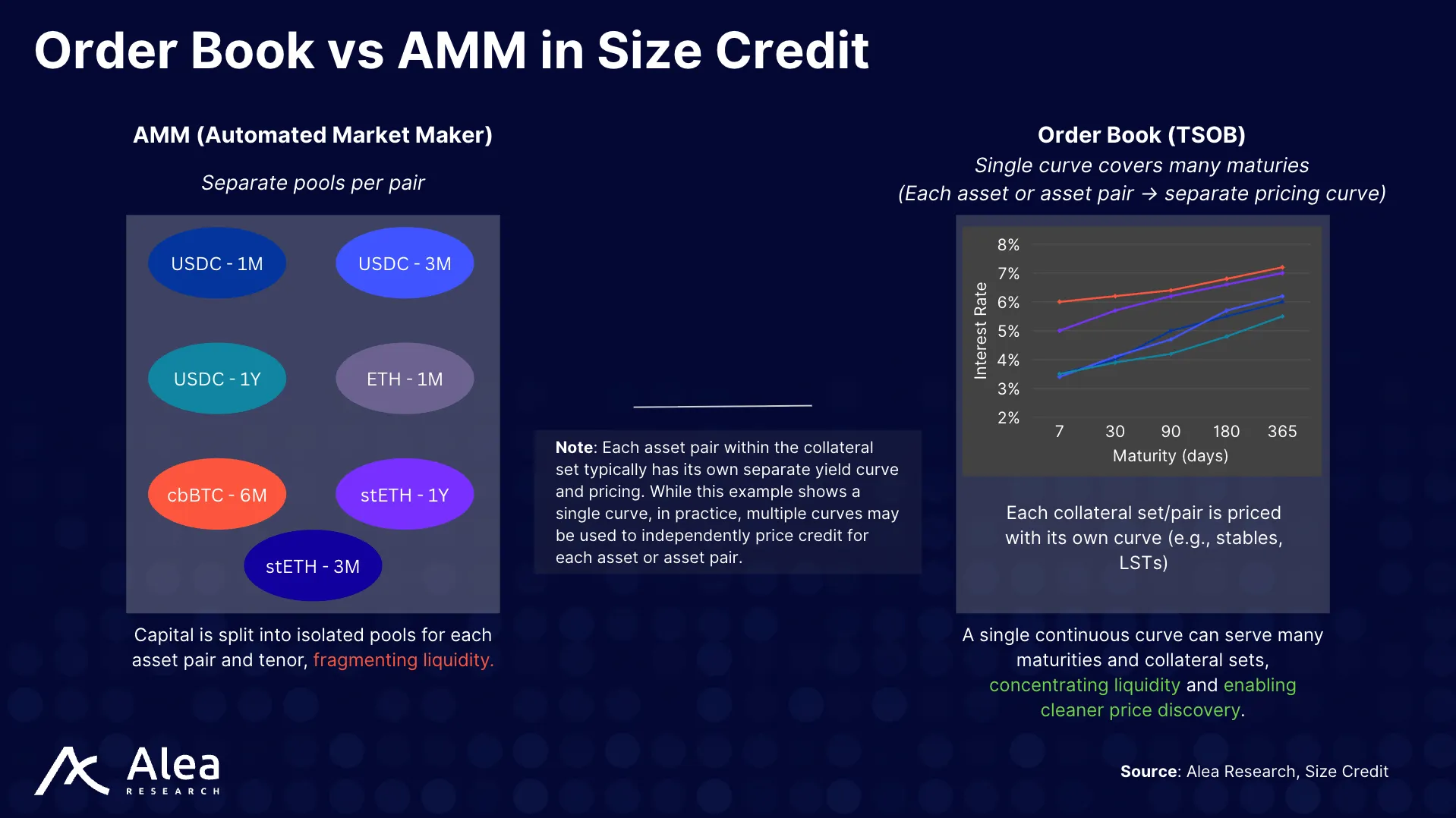
Size concentrates liquidity across tenors and collateral, optimizing for those points on the curve where demand appears. Across tenors: makers quote multiple maturities from the same balance sheet. Across pairs: a single offer can be written against a set of collateral assets (e.g., stables, $ETH-staking derivatives, $BTC wrappers). When a borrower fills an order with any asset from a collateral set, Size does not treat all assets equally. Instead, it discounts each asset’s value using predefined haircuts that reflect its risk profile. For example, $1,000 of $USDC might count fully, while $1,000 of $wstETH might be recognized as only $950 of collateral. In addition, Size supports multiple markets for the same asset pair, each with its own LLTVs and risk parameters. This means collateral requirements, haircuts, and overall risk exposures can be isolated and managed on a per-market basis, rather than universally across the protocol.
How the Term-structure Order Book (TSOB) Works
Size’s TSOB is a 2D order book: time on the x-axis and rate on the y-axis. Lenders and borrowers post limit orders across maturities. When these acceptable rates (minimum for lenders, maximum for borrowers) are aggregated into best‑bid and best‑ask term structures, the engine produces a live, tradable yield curve.
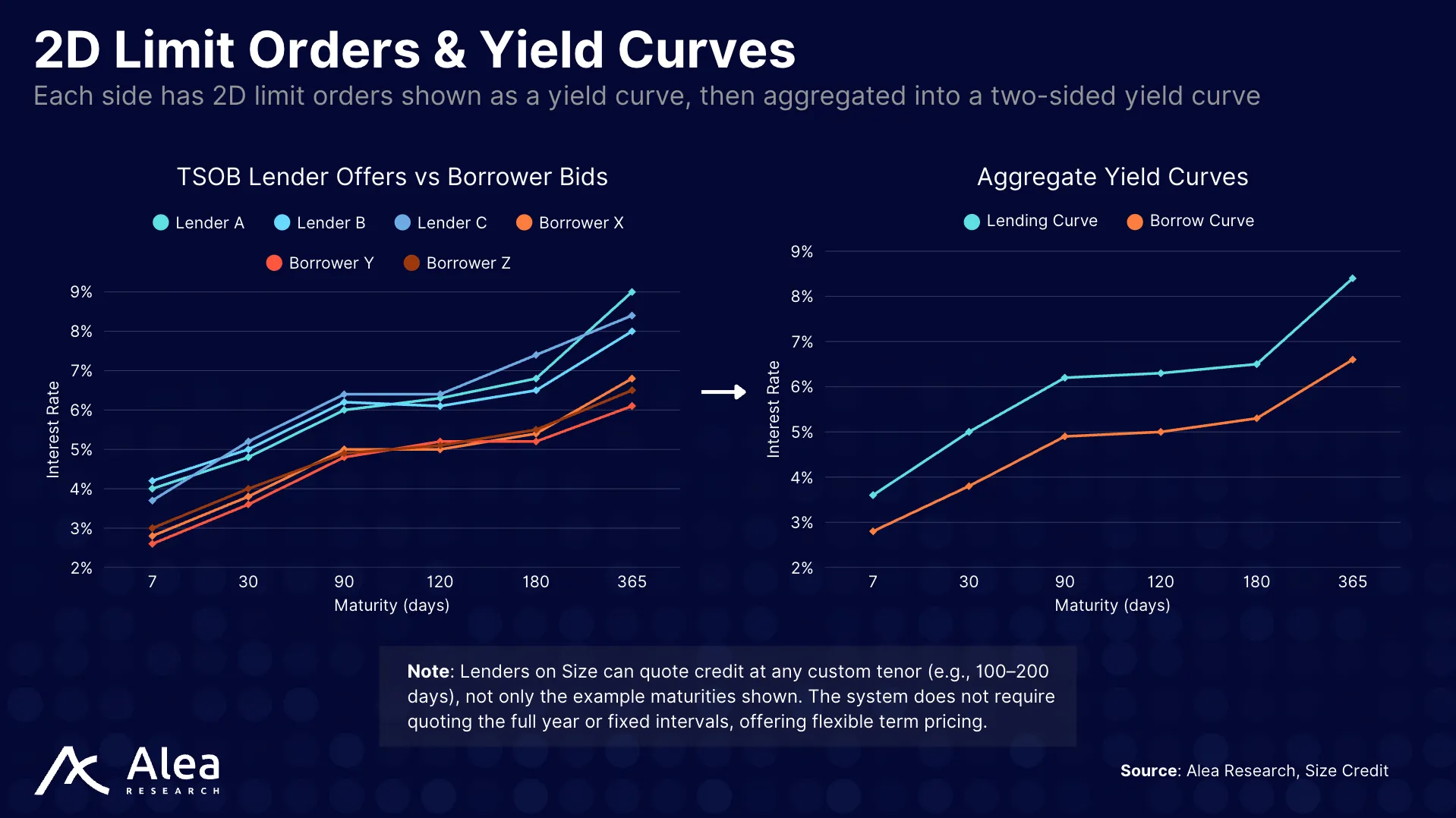
Orders are symmetric and granular. For example, a maker can submit a curve with anchors at 7D, 30D, 90D, and 180D, each with its own rate and size. The book supports partial fills at any of those points. To keep quoting simple while keeping the curve dense, Size uses interpolation between anchors (typically piecewise linear): if demand appears at 45D and only 30D/90D are quoted, the engine computes the implied 45D rate from the posted curve. Makers cover more tenors with fewer updates, while takers see continuous pricing.
Size’s matching engine is run offchain, using price-time priority: best rate fills first; ties go to the oldest. The deliberate choice to use an order book, instead of an AMM, is key for sharing liquidity across pairs and maturities. An AMM would fragment capital per tenor and asset, whereas Size’s TSOB makes it possible for a single yield curve to accept fills from a defined collateral set (e.g., yield-bearing stables, LSTs, LRTs, RWAs, etc).
Earn Product
Earn is designed for passive lenders who want to put deposits to work without manually managing lending strategies. Most lenders don’t have the time or resources to monitor term quotes, optimize maturities, and track multiple collateral types. Lenders set their preferences (target maturity, minimum rate, collateral set), and the protocol automates the rest by actively refreshing orders, filling them with best-fit borrowers, and converting deposits into fixed-term claims that earn yield until maturity.
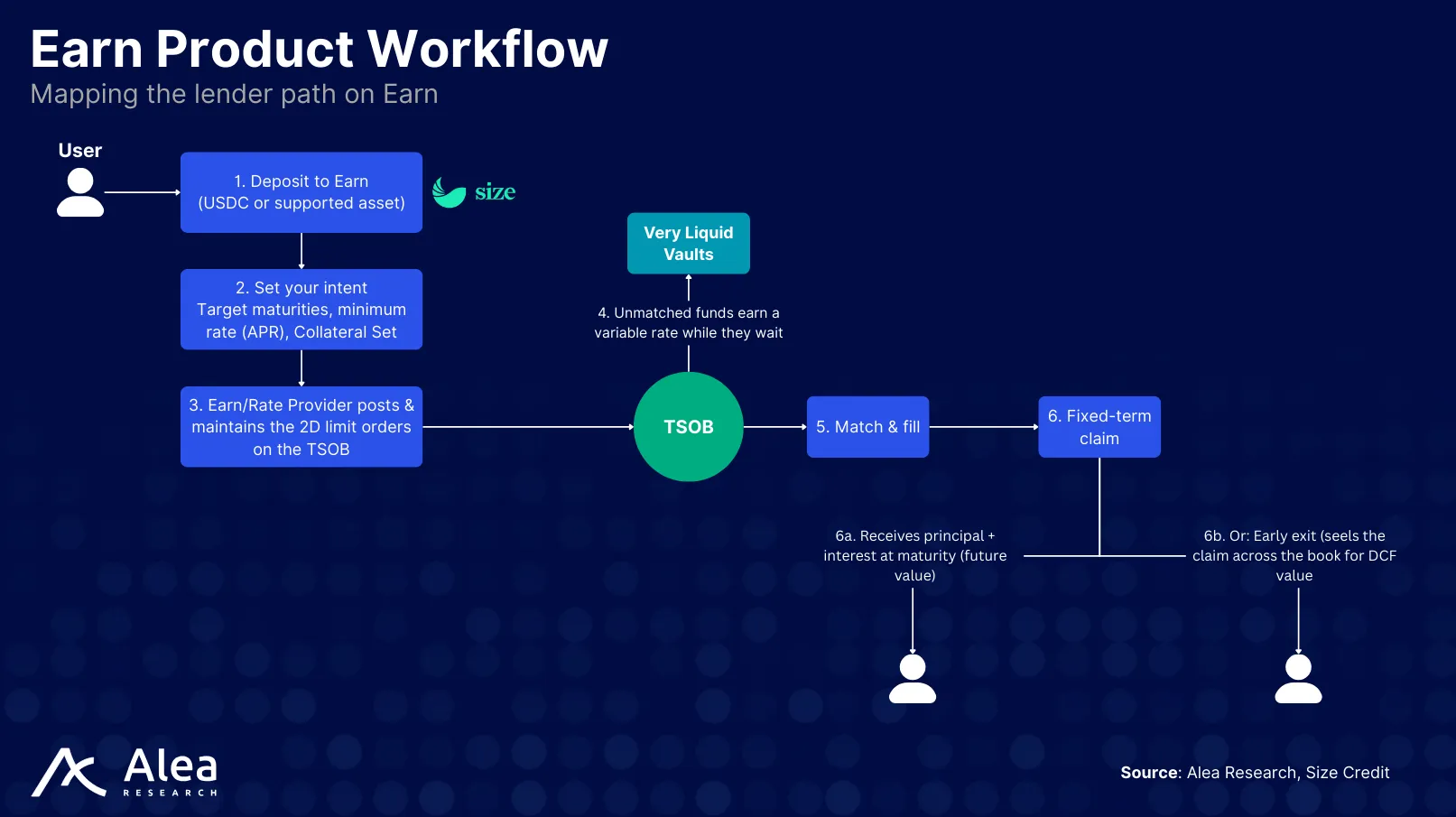
Earn removes the need for manual order management and micro-managing quotes by maintaining rate curves, rolling maturities, and efficiently sourcing yield across different collateral types. Managed Collateral Sets determine eligible assets (e.g., yield-bearing stablecoins, LSTs, $BTC wrappers, altcoins) along with their haircuts, which are discounts applied to collateral value to protect lenders against volatility or liquidity risk.
Each set can appoint a different Rate Provider for each lending pair. A Rate Provider is an independent party or module responsible for determining and updating interest rate rules based on market conditions and asset risk. Rate Providers set quoting logic for the pool, and Earn automatically generates, refreshes, and updates orders according to these rules.
It’s also worth noting that unmatched deposits don’t sit idle on Earn. Before a fixed-rate match, deposits earn an optimized variable return in Very Liquid Vaults (VLVs).
Very Liquid Vaults: the Underlying Liquidity Engine
Earn deposits first sit in Very Liquid Vaults (VLVs), which act as the parking place for lender capital. While waiting to be matched on the TSOB, these funds are allocated across short-term strategies (e.g., Aave) to earn a variable return, staying productive even before being locked into fixed-rate loans.
When a borrower takes a fixed-term loan, liquidity is pulled directly from the VLVs and settled on Size, meaning it is converted into a fixed-term credit position for the lender, with principal plus interest due at maturity. If the lender later chooses to exit early or when the loan matures, repayment flows back into the VLVs where it becomes liquid again.
The design of VLVs guarantees that a portion of assets can be instantly withdrawn at all times. This makes funds available both for borrowers who need fixed-rate capital and for lenders who may want to withdraw or reallocate without delay.
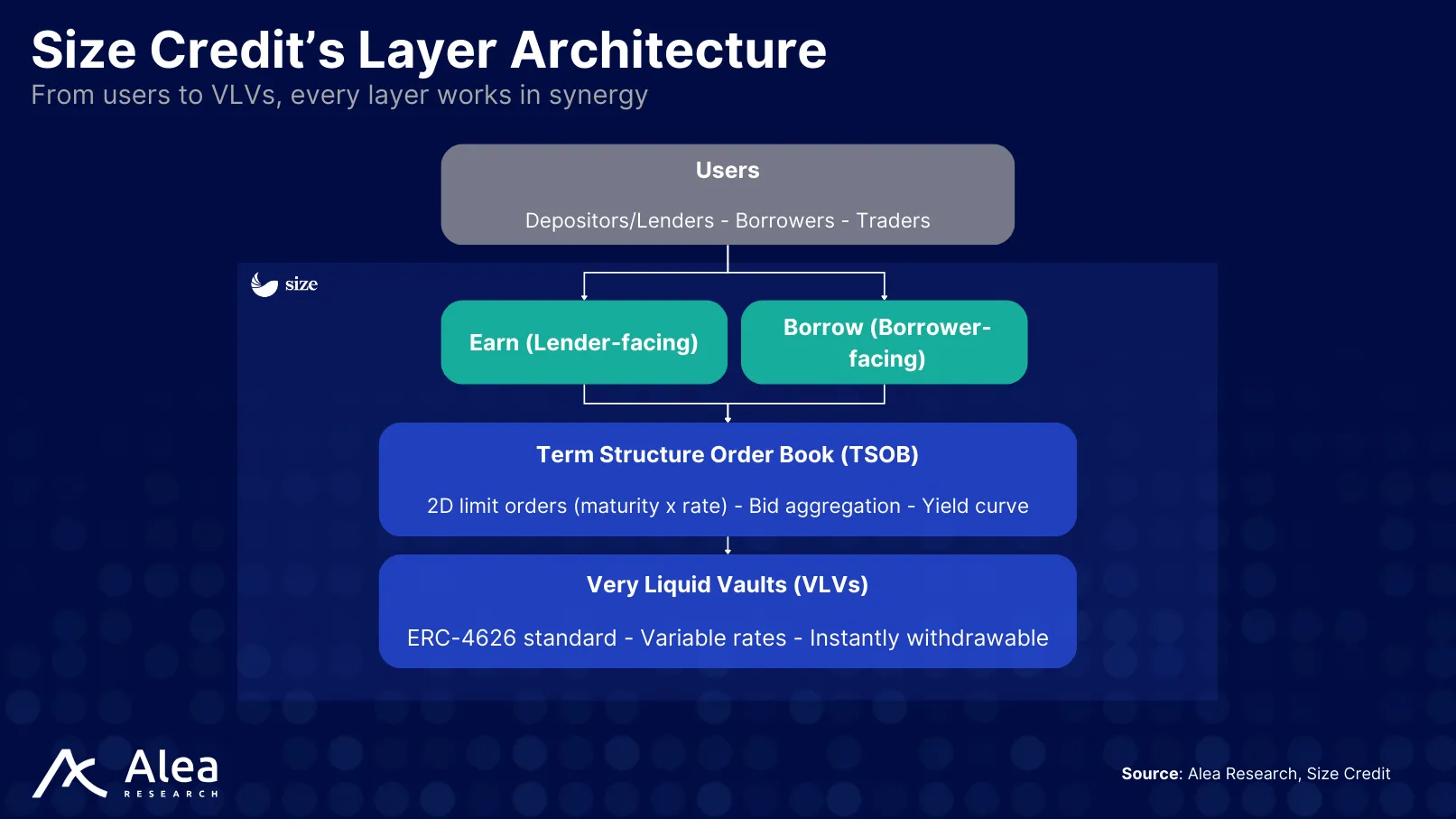
VLVs are ERC-4626 tokens (e.g., yield-bearing tokenized vaults) that allocate capital to a series of whitelisted strategies. Each vault can allocate any amount to underlying protocols such as Aave, Morpho, or Euler, and actively manages liquidity in each venue. They set limits and rebalance funds to make sure withdrawals are always satisfied on demand.
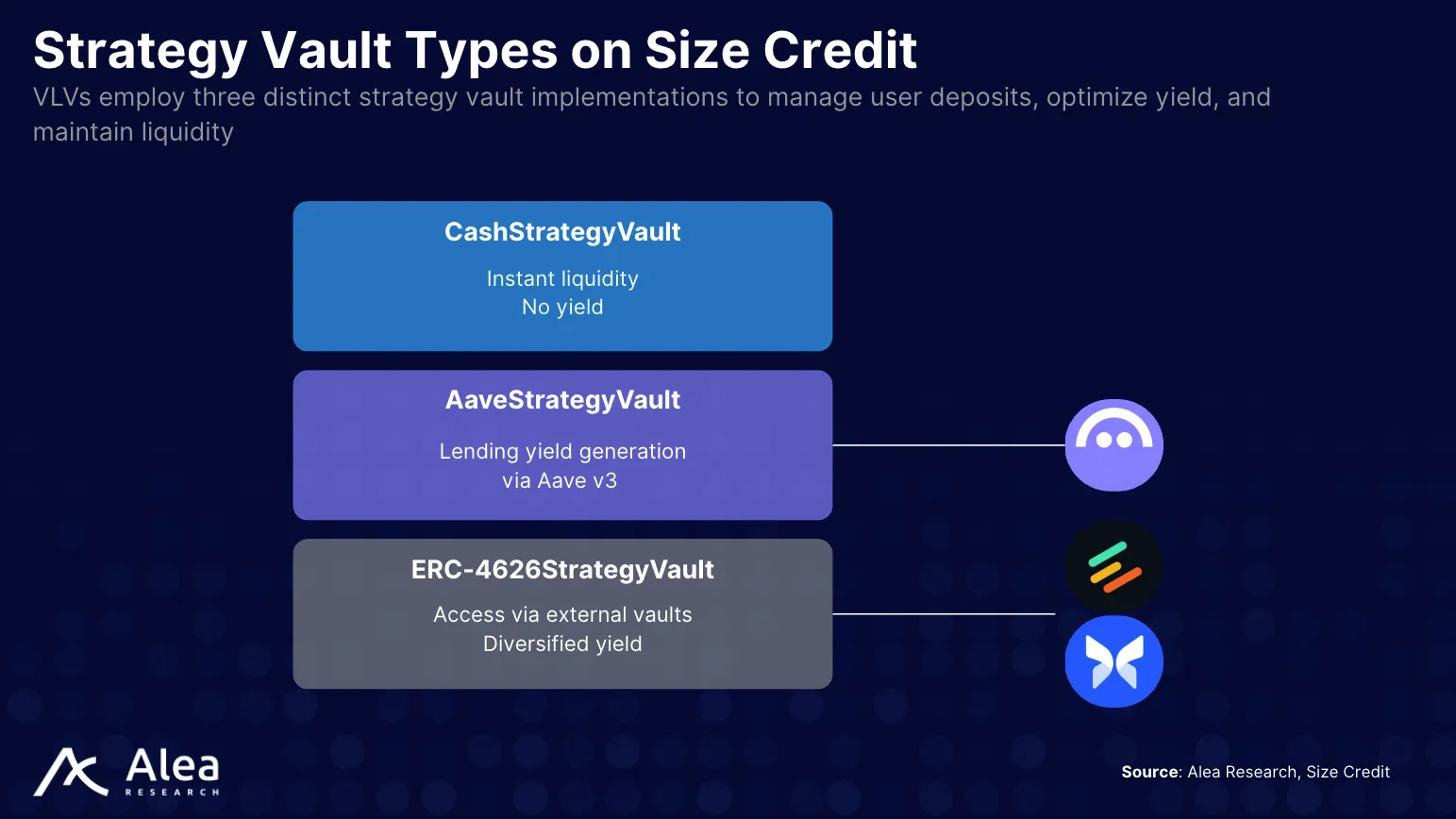
The Earn product specifically relies on these specialized vaults. While Earn handles quoting and term management, VLVs handle carry and readiness, covering both the quoting and liquidity needs. Deposits flow into the VLVs, accrue variable yield while queued, and are atomically withdrawn when the matcher confirms a fixed-rate fill on Size. If the user’s term isn’t hit, the position simply continues to earn in the VLVs or can be re-quoted by Earn’s settings.
Lending & Borrowing Mechanics
Size is used by two main groups:
- Lenders seeking predictable income. They supply cash to earn fixed interest over a set maturity.
- Borrowers seeking predictable funding. They post collateral ($ETH, yield-bearing stables, LSTs, etc.) and borrow against it at a fixed cost for a chosen term.
Lending is equal to buying credit (purchasing a dated receivable for principal plus interest at maturity). Borrowing is equal to selling credit (issuing that receivable while posting collateral).
Lenders can exit early by selling their outstanding claim to another party at a discount that reflects current market rates. This transfer does not affect the borrower, who still owes the same maturity value, but the new lender now steps into the original lender’s place.
Borrowers can also offset debt with credit. If they hold a receivable that matures before their own debt comes due, they can assign it against what they owe. For example, a borrower who owes $1,000 in three months but owns a receivable of $1,050 due in two months can post that receivable, settle their debt, and withdraw collateral.
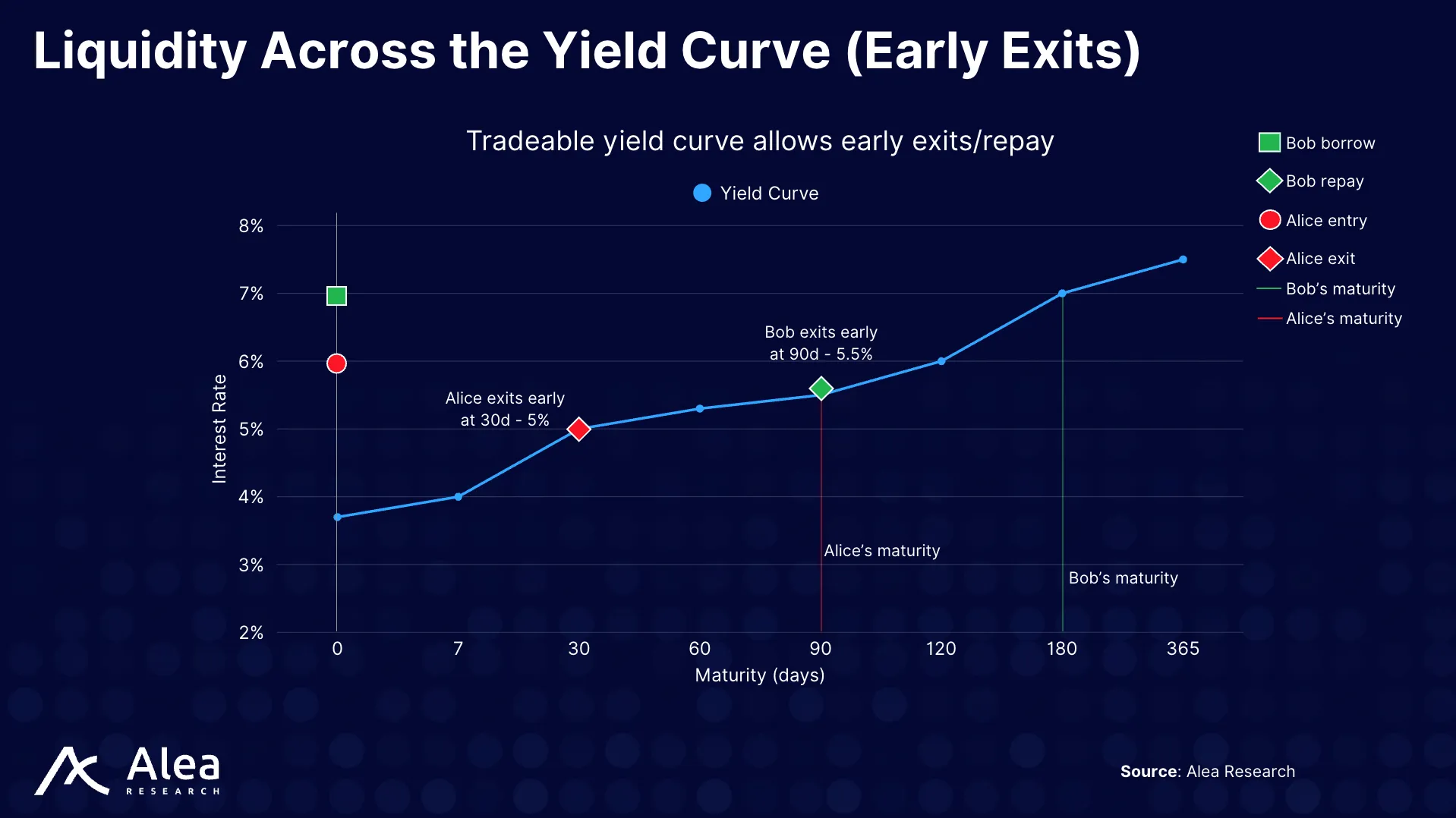
Here is a specific example with numbers for both sides regarding early exits.
- Alice buys a 90-day, 6% APR claim for $1,000; the maturity value is $1,014.79. After 30 days, 60 remain, and the market is 5%. Alice sells the claim at its discounted value, about $1,006.52, locking a 652% gain in a month (~7.9% annualized).
- On the other side, Bob borrows $10,000 for 180 days at 7%; maturity due is $10,345.21. After 90 days, the curve sits at 5%. Buying back the receivable and transferring it to the book costs roughly $10,206.78 (the discounted value of the remaining payoff), closing early, and freeing his collateral.
Use Cases & Strategies
Size can support strategies that depend on predictable funding and tradable claims. Borrowers can run carry trades by pairing fixed borrowing with fixed-yield tokens (PTs) or locking in long-dated funding against major assets ($ETH, $BTC). These strategies work because Size operates through a TSOB where a single quote can extend across maturities and collateral sets, concentrating liquidity instead of fragmenting it across separate pools.
Fixed terms exchange flexibility for certainty. Once locked in, both the rate and maturity are predetermined, removing the option to adjust mid-course but giving borrowers and lenders full visibility over future cash flows. Lenders earn a term premium for committing capital for longer, which can mean higher realized returns than markets where variable rates can decline. The primary benefit is predictability because cash flows arrive on known dates and at known amounts, giving institutions the ability to plan ahead.
To understand how lending and borrowing work, here are three simple strategies facilitated by Size.
Example #1 – Size + Pendle PT Loop Strategy
The most popular strategy on Size is to loop credit against PTs on Pendle for maximum yield exposure. Users start by borrowing $USDC at a fixed rate from Size and using that capital to buy fixed-yield PTs on Pendle with the same maturity. Instead of stopping after a single time, the purchased PTs are deposited back into Size as collateral, allowing the user to borrow additional $USDC and buy more PTs on Pendle, repeating the loop and compounding their position.
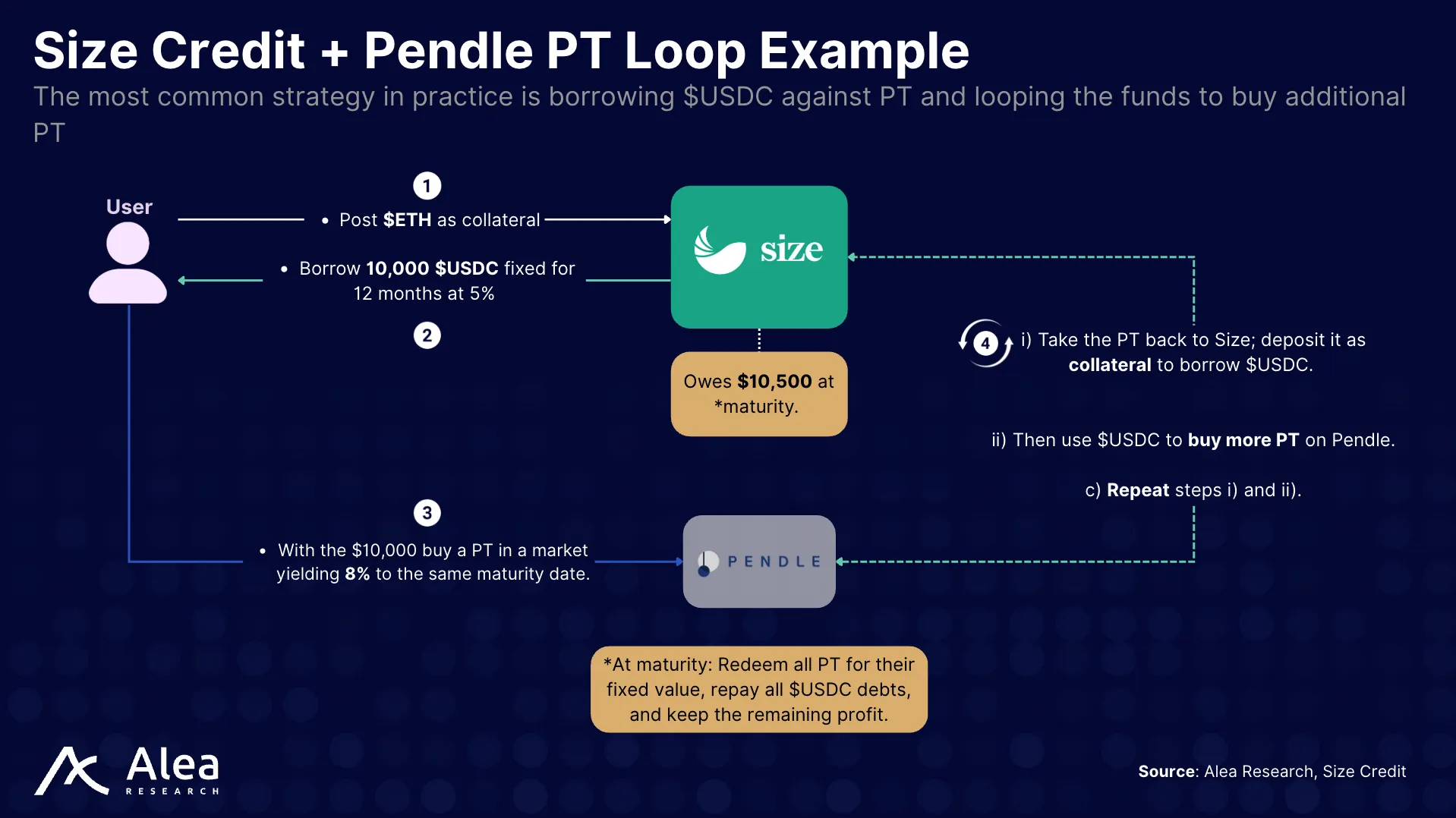
At maturity, all PTs are redeemed at their fixed principal value. The proceeds are used to repay all outstanding $USDC debts—including those incurred from repeated loops and any remaining amount represents net profit from the leveraged yield spread. If rates move or an early exit is needed, users may unwind by selling Pts or repaying loans at a discount value based on time left.
Key risks include PT pricing/liquidity, collateral or loan health on Size, and possible tightening of the yield spread. It’s necessary to regularly monitor position health and collateralization throughout the loop.
The objective is to maximize positive yield carry by recursively compounding exposure, so long as PT yield continues to beat the $USDC borrowing cost.
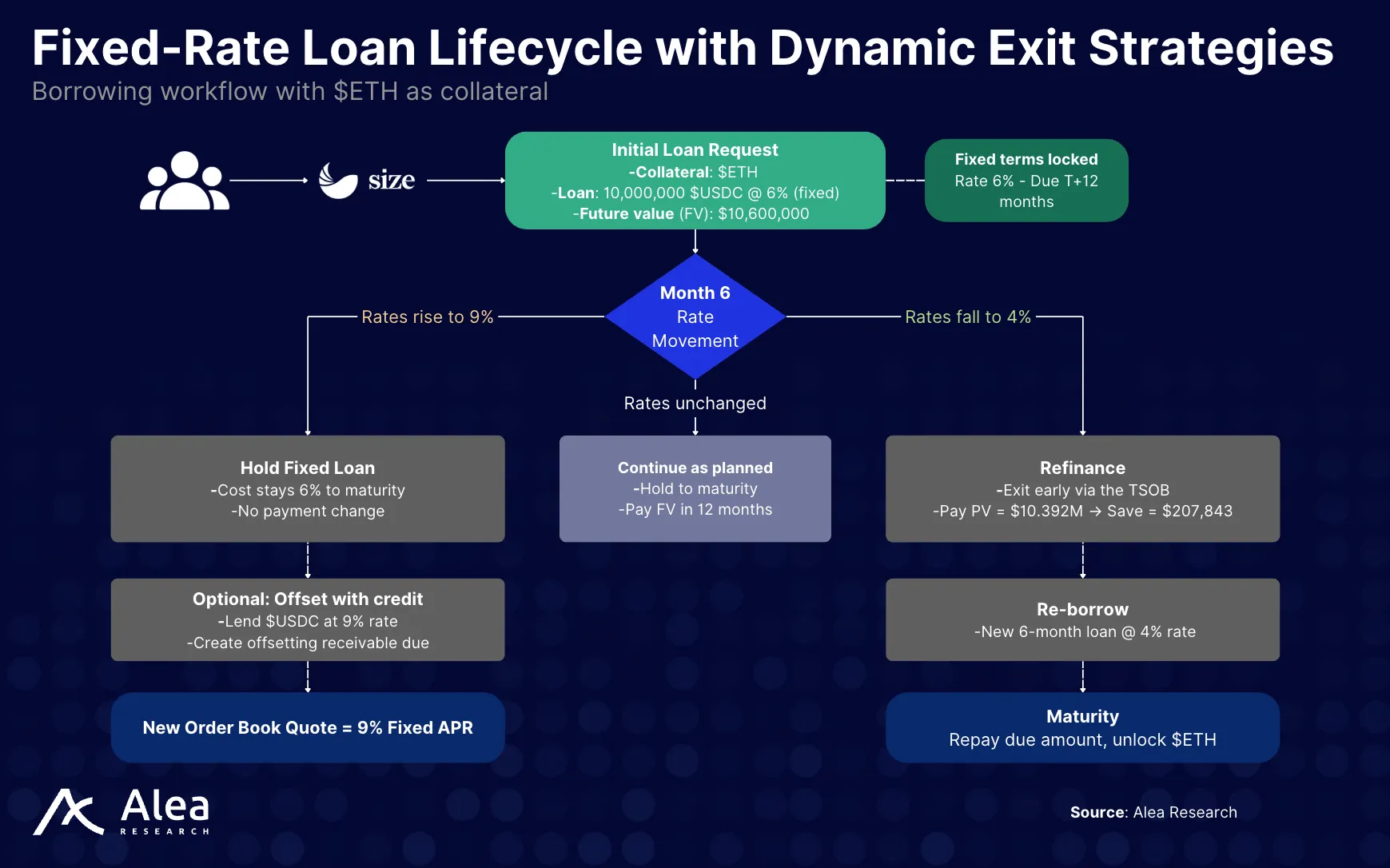
Example #2 – Long-dated Fixed Borrow
Size lets you borrow against majors (e.g., $ETH, $cbBTC) at a fixed rate for a chosen calendar date. It matches your order across the TSOB, locks the APR, and keeps it fixed. If rates drop, you can exit early by paying the present value (PV) of what’s left; if rates rise, your cost stays put.
Main idea: Bring bond-style dated credit to DeFi so desks can plan funding like a treasury desk. Pick a date, fix the rate, and keep optionality.
The example shows how a trading desk can lock in a 12-month $USDC loan against $ETH at 6% fixed, giving them certainty on funding costs.
Conclusion
Size’s thesis is to make time tradable. By running a term-structure order book, it moves price discovery from “what the pool pays today” to “what the market pays for a given maturity.” Liquidity concentrates where it’s needed the most, by tenor and across Collateral Sets. Earn and the VLVs keep capital productive and instantly recallable. This setup delivers a live yield curve, transferable fixed cash-flow claims for early exits, and clearer economics for all participants.
In today’s crypto market, Size sits between variable-rate money markets and ad-hoc OTC credit. It doesn’t try to replace floating liquidity; it adds a term venue that institutions can plan around. Market makers get a surface to quote and hedge. Treasuries get a way to ladder maturities and align cash in with cash out. Structured products, PTs, and rate trades plug into a clearer curve. Every type of user can choose the strategy that best fits them.
With much of the focus around institutions, Size makes a solid case for attracting institutional capital. It offers predictable cash flows, better asset-liability matching, and clearer rate risk. Lenders can lock a tenor to earn term premium and still exit by selling the claim. Borrowers can fix their bill for a year, then roll or buy back if conditions change. The result is steadier funding, cleaner risk management, and a venue designed for balance sheets, not just yield chasers.
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
| Size Credit | A DeFi fixed-rate lending marketplace enabling borrowing and lending at any maturity with early-exit options. |
| Fixed-Rate Loan | A loan with the interest rate and maturity locked at origination. Predictable cash flows for lenders, predictable costs for borrowers. |
| Variable-Rate Loan | A loan with interest that fluctuates based on market utilization, common in protocols like Aave and Compound. |
| Term Structure Order Book (TSOB) | Size’s core engine. A two-sided order book where offers are expressed as yield curves (maturity × rate), enabling continuous pricing across maturities. |
| Term Structure Offer | A lender- or borrower-submitted curve mapping maturities to rates (e.g., 1 month – 3%, 6 months – 5%). Takers pay interpolated rates between points. |
| Buying Credit (Lending) | Lending USDC in exchange for future repayment at a fixed rate. Also called “buying credit.” |
| Selling Credit (Borrowing) | Borrowing USDC by pledging collateral and agreeing to repay at maturity. Also called “selling credit.” |
| Collateralization Ratio | Collateral value divided by debt value. Determines loan health and liquidation risk. |
| Liquidation | Triggered when the collateralization ratio falls below the threshold or when a loan is overdue. Collateral is sold or transferred to lenders. |
| Collateral Set | A predefined basket of collateral assets that a lender is willing to accept when lending via the Earn product. |
| Rate Provider | An entity or contract that sets and updates competitive rates for lending against a Collateral Set. |
| Earn Product | (Coming soon) A lender-facing feature. Deposits earn variable yield until matched with fixed-rate borrowers, then earn a duration premium. |
| Very Liquid Vaults | ERC-4626 vault that manages deposits across strategies (cash, Aave, external vaults). Designed to maximize yield while keeping capital instantly withdrawable. |
| Offset | An adjustment (positive or negative) that a lender applies to the Rate Provider’s reference rate to fine-tune competitiveness. |
| Haircut | The reduction, or trimming, of an asset’s value. |
| Maximum Tenor / Minimum APR | Lender-defined parameters: set the longest acceptable maturity or the lowest acceptable rate when lending. |
| Early Exit | Mechanism allowing lenders or borrowers to transfer their positions before maturity by paying or receiving discounted cash flow value. |
| Offsetting Debt with Credit | Using receivables (credit owed from lending) as collateral to reduce or cover outstanding borrow positions. |
References
- Size Credit Docs
- Technical Docs
- Size Credit Blog
- Size Credit App
- Earn Product
- Very Liquid Vaults
- Size Credit GitHub
- Santiment. Aave v3 USDC Interest Rate
- BIS. OTC Derivatives Statistics
- Interpolation
- Yield Curve
- Pricing Across the Yield Curve
- Term Premium (Duration Premium)
- Duration Management
- Cash Flow Forecasting (Predictability)
- Haircut
Disclosures
Alea Research is engaged in a commercial relationship with Size Credit and receives compensation for research services. This report has been commissioned as part of this engagement.
Members of the Alea Research team, including analysts directly involved in this analysis, may hold positions in the tokens discussed.
This content is provided solely for informational and educational purposes. It does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice.

