Overview
Gains Network is a decentralized leverage trading platform. Liquidity providers deposit funds into the protocol and earn revenue from trading fees executed by traders.
The Gains Network ecosystem is powered by the GNS ERC20 utility token as well as ERC721 NFTs, both of which are designed to be actively used within the platform and to allow users of the protocol to capture revenue and gain voting rights over the protocol.
gTrade
gTrade is the leveraged trading platform offered by Gains Network. It is a decentralized perpetual futures exchange where users keep full custody over their own funds and can trade crypto with up to 150x leverage, stocks with up to 100x leverage, forex with up to 1000x leverage, and indices with up to 35x leverage.
- There is no order book or liquidity for each pair
- There is a single gDAI vault for all listed trading pairs
- Leverage is synthetic (not borrowed)
- The leverage allowed is backed by the DAI vault and the GNS token
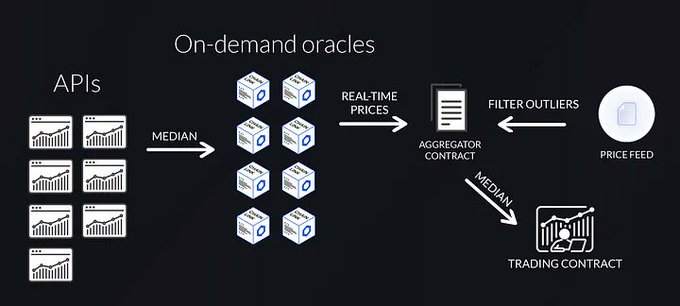
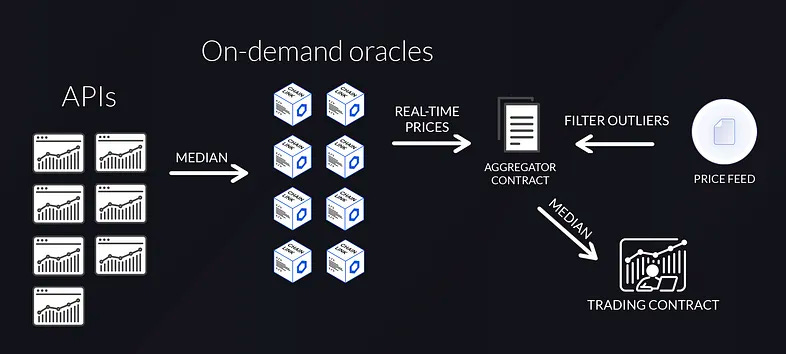
- Spot prices are in real time (fetched from a custom Chainlink decentralized oracle network)
Regardless of the trading pair, all trades are opened with DAI collateral. This is a flexible design that allows Gains Network to offer multiple trading pairs and levels of leverage (since there is no need to maintain liquidity for each pair or every time a new asset is listed).
By building a highly liquid DAI vault, every trading pair that is listed immediately benefits from available liquidity and larger position sizes.
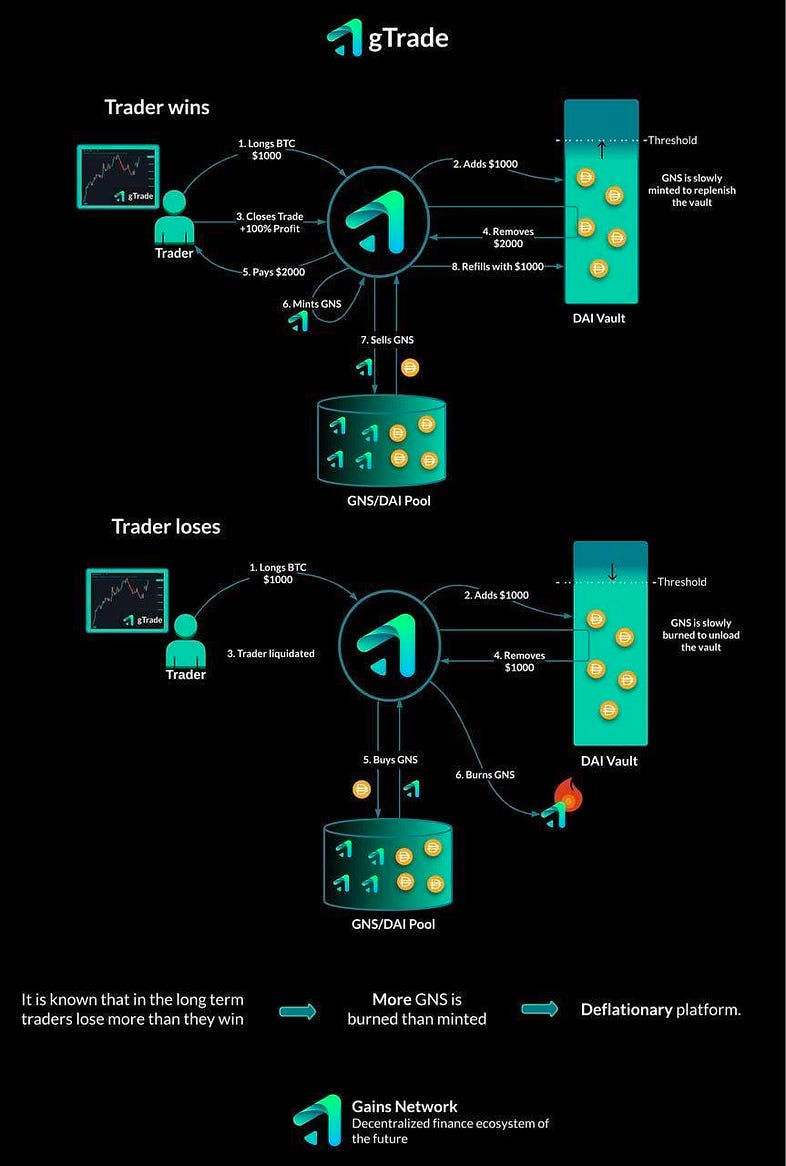
The PnL of traders is calculated in gTrade’s smart contracts and settled against the DAI vault.
- If the traders’ PnL is positive, DAI is taken out of the vault to pay traders
- If the traders’ PnL is negative, DAI is deposited into the vault from the traders’ losses
In order to filter out outlier prices on specific exchanges (whether this is a result of manipulation or lack of liquidity), gTrade relies on a decentralized oracle network that takes price data from multiple exchanges and selects the median price.
This protects traders from liquidations that are caused by price outliers, also known as scam wicks.
Why the Project was Created
The vision of Gains Network is to become the fairest and trader-centric platform. This long-term vision implies that:
- gTrade becomes the most adopted decentralized leveraged trading platform
- Gains Network becomes a DAO governed by the GNS tokens on an alternative governance system (e..g veGNS)
- The protocol is able to keep building products that bring revenue that can be distributed in a GNS staking pool
- Product development scales horizontally so that any team can create governance proposals and receive funding for building more products that drive extra revenue for GNS holders
Roadmap
Gains Network has since updated that they no longer have a roadmap as they noticed that making promises usually does not end well with the rapidly changing environment of crypto. Updates and features will be announced as they come along.
Some of the features in their previously announced roadmap:
- Custom Market Type
- Cross-Pairs, e.g. AAPL/BTC. (ETA was Q3 2022).
- Custom Indices, e.g. 25% BTC, 50% ETH, 25% LINK (ETA was Q4 2022).
- Smart contract v6.4 (ETA was early October 2022) and v7 (ETA was late December 2022), currently on V6.3 on both Polygon and Arbitrum.
- v6.4 will add features such as partial take profits/stop losses and allow increasing/decreasing the collateral of a trade.
- v6.4 introduced lookbacks, allowing gTrade to look back at recent price data and guarantee order executions.
- v7 will minimize RPC calls needed to track trades, have full documentation of the code, and major refactor & optimization of the contracts.
- Zk Rollup Deployment (ETA was Q4 2022)
- In touch with Polygon regarding their Zk solutions.
- Social Features (ETA was Q4 2022)
- To allow traders to share/discuss ideas.
- Transition to Governance (ETA Q1 2023)
- Exploring the Metaverse (ETA Q1 2023)
- Gains Network strongly believes in the Metaverse thesis and wants to explore every possibility for gTrade.
Gains Network aims to have as many white labels and integrations as possible since every new addition is a net positive for them and for the project integrating Gains due to the incentive to earn trading fees.
DeFi Subsector
Gains Network uses a synthetic architecture that makes the platform more capital-efficient than other competitors in the decentralized leverage trading space. This allows for the execution of trades with low fees and a wide range of leverage and pairs: up to 150x on crypto, 1000x on forex, 100x on stocks, and 35x on indices. Its market breadth is one of the key differentiators when compared to other decentralized trading platforms.
Gains Network can be classified as a real-yield project. Whether you provide liquidity to the DAI vault, stake GNS, or provide liquidity to the GNS/DAI pool, you are rewarded in DAI. Besides, it is also possible to get rewarded in GNS by holding a GNS NFT and running a liquidation bot or participating in the referral program.
Forex markets have gained significant traction over time, reaching volume levels at par with crypto.
Due to the way Gains works, gTrade is not actually a DEX. Instead, it is a synthetic decentralized leveraged trading platform that obtains capital efficiency by using DAI as the counterparty liquidity for all trades that are opened in the platform. This makes gTrade more efficient in terms of liquidity than orderbook models that need to incentivize specific trading pairs to facilitate price discovery.
Oracle vs. Orderbook
Gains Network made the decision to build an Oracle-based trading platform because this design provides more control over the price impact of individual traders and offers a unified source of liquidity (gDAI).
gTrade relies on a hybrid architecture that combines the widely used Chainlink Price Feeds with their own custom-built Chainlink DON (Decentralized Oracle Network) in order to provide real time aggregate prices from a series of exchanges. The reason for building their own DON is that Chainlink price feeds on Polygon are not updated in real-time. Thanks to this design, gTrade’s on-demand DON allows users to trigger new oracle price updates on-chain and execute trading orders.
If gTrade receives a price that differs by more than 1.5% from the Chainlink price, a circuit breaker is triggered.
All trades on gTrade are executed against real spot prices. Whenever an order needs to be executed, the trading contract requests the current spot price from an aggregator contract that, at the same time, will request the current asset price from 8 on-demand Chainlink nodes. Each of these nodes takes the median price from 7 exchange APIs and sends the result to the aggregator contract. Next, for every median price that is received from the nodes, the aggregator contract double-checks with the corresponding Chainlink Price Feed to filter for outliers.
Contrary to market makers in decentralized order books, where they need to get in and out of positions, liquidity providers need to protect the protocol from bad debt. Because of that, there are a series of risk management practices in place (dynamic spread, rollover fees). Contrary to market makers in an order book, there is no need to micro-manage liquidity, which makes the trading execution overall more efficient. Besides, trades are executed in real-time using the median spot prices coming from gTrades’ oracle network, which means that there is no specific delay apart from the time for the transaction to be mined.
Comparison With Top Perpetual Decentralized Exchanges
Chains
Gains Network is deployed on Polygon and Arbitrum.
Polygon
- Lower gas costs
- Supports lower position sizes
- Requires 2 block confirmations (4 seconds)
- Occasional reorgs
- Setup guide: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/setting-up-to-trade/polygon-network-setup
A reorg, or block reorganization, is when a blockchain produces multiple blocks at the same time, which results in a temporary duplicate chain. Although this can happen to an attack to the blockchain, it is often the case that block reorgs occur during short periods of time due to network latency.
Block reorgs increase the chance of delayed transactions and lead to a worse user experience
Arbitrum
- Slightly higher gas costs
- Faster transactions
- No block confirmation required
- Higher minimum position size is required
- Setup guide: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/setting-up-to-trade/arbitrum-network-setup
Base is the latest addition to the Gains Network. Like Arbitrum, Base offers a seamless and fast trading experience but requires larger position sizes and comes with slightly higher gas fees compared to Polygon. With the growing popularity of $USDC on Base, traders looking to use Base can follow the Base setup guide for instructions on how to get started.
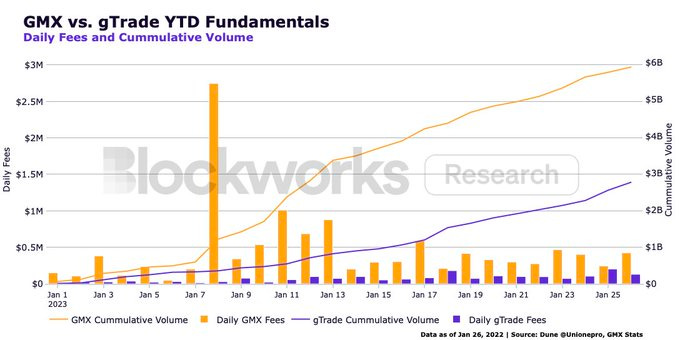
Since launching on Arbitrum in December 2022, Gains Network has gathered significant volume across its forex and crypto pairs and nearly flipped GMX in terms of fee revenue on January 25, 2023 (although GMX has over $500M of liquidity vs. Gains’ $35M).
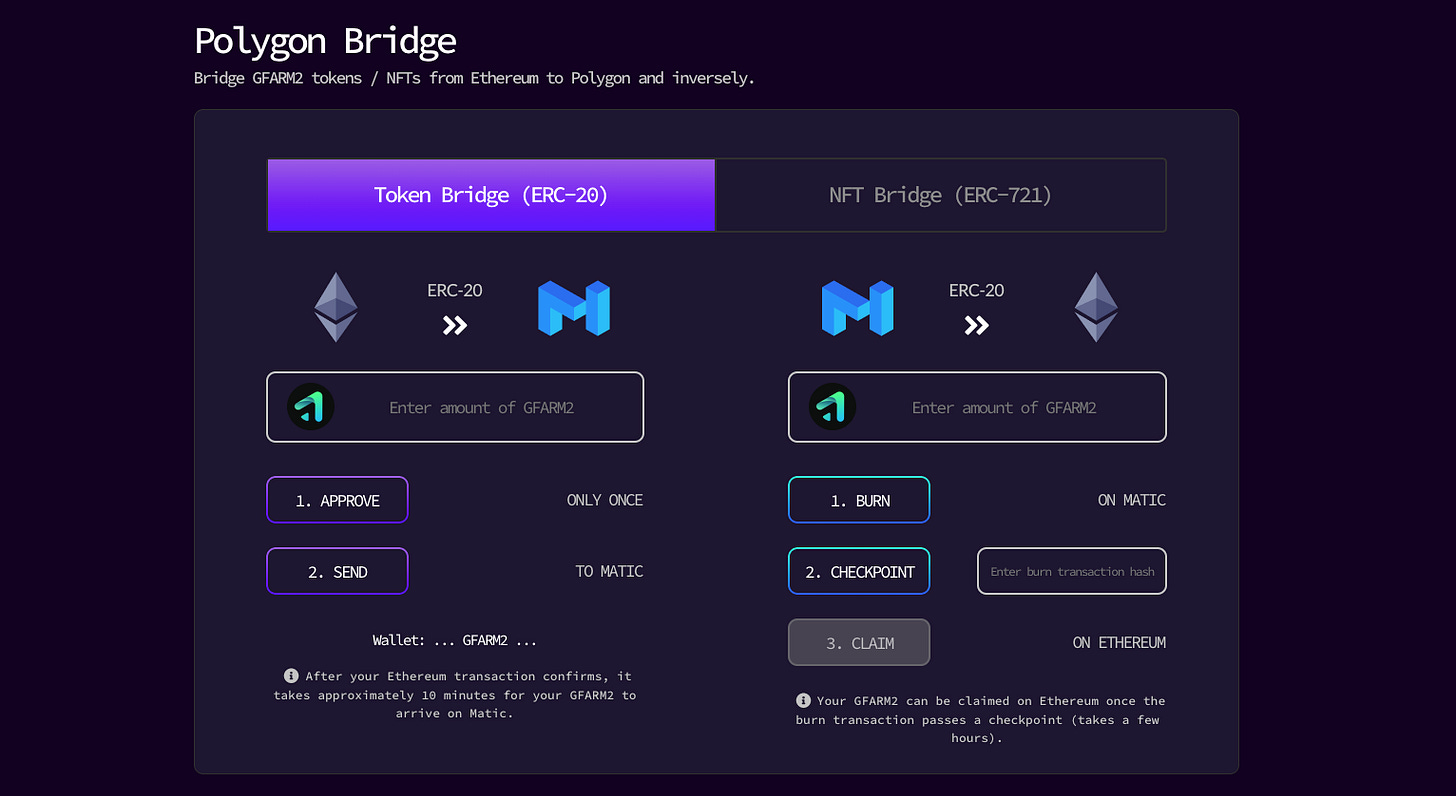
To improve the user experience, Gains built its own bridging interface. This will allow traders to move GNS and GNS NFTs from Polygon to Arbitrum and vice versa
Gains has also integrated with LayerZero, an omnichain interoperability protocol for cross-chain messaging technology.
For Users
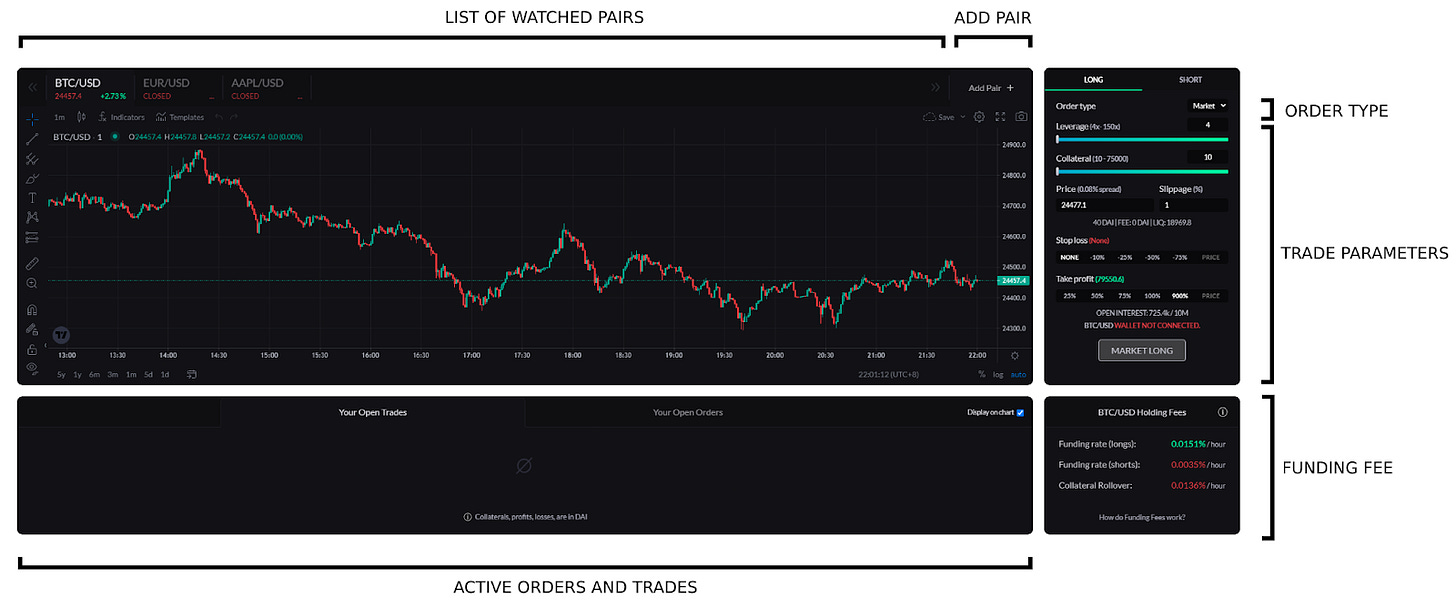
- Trade type (long or short)
- Market orders execute immediately at the market price + spread (to prevent high-frequency trading bots).
- Limit orders execute at the price set by the trader.
- Stop limits are used by traders who want to go long if the price reaches a higher price (e.g. long a breakout), and to go short if the price reaches a lower price (e.g. short a breakdown)
- Collateral is the amount of capital that the trader is willing to put at risk if the position is liquidated.
- The amount of collateral multiplied by the desired leverage must be above the minimum position size.
- Leverage is the multiple of increased exposure on a trade.
- Max slippage is used to cancel market orders automatically when the price moves too fast before the actual trade is opened (e.g. if the trader wants to go long and the price increases by 1%, the market order will be canceled automatically.
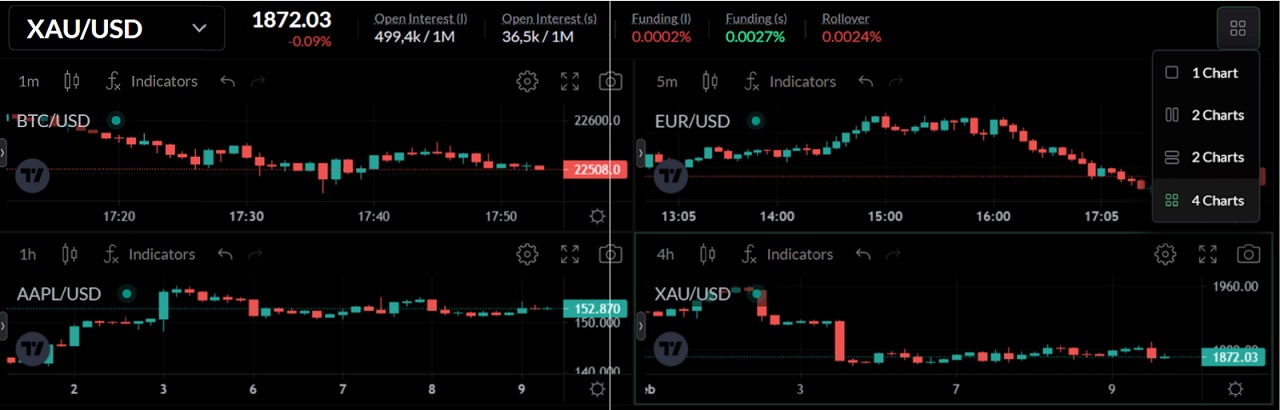
- Multicharts allow users to view up to 4 charts per window on the platform.
- Stop Loss & Take Profit (optional).
- Positions are liquidated when they reach a PnL that is lower than -90%
- Positions can make a maximum profit of 900% PnL (they will be closed when they realize that profit)
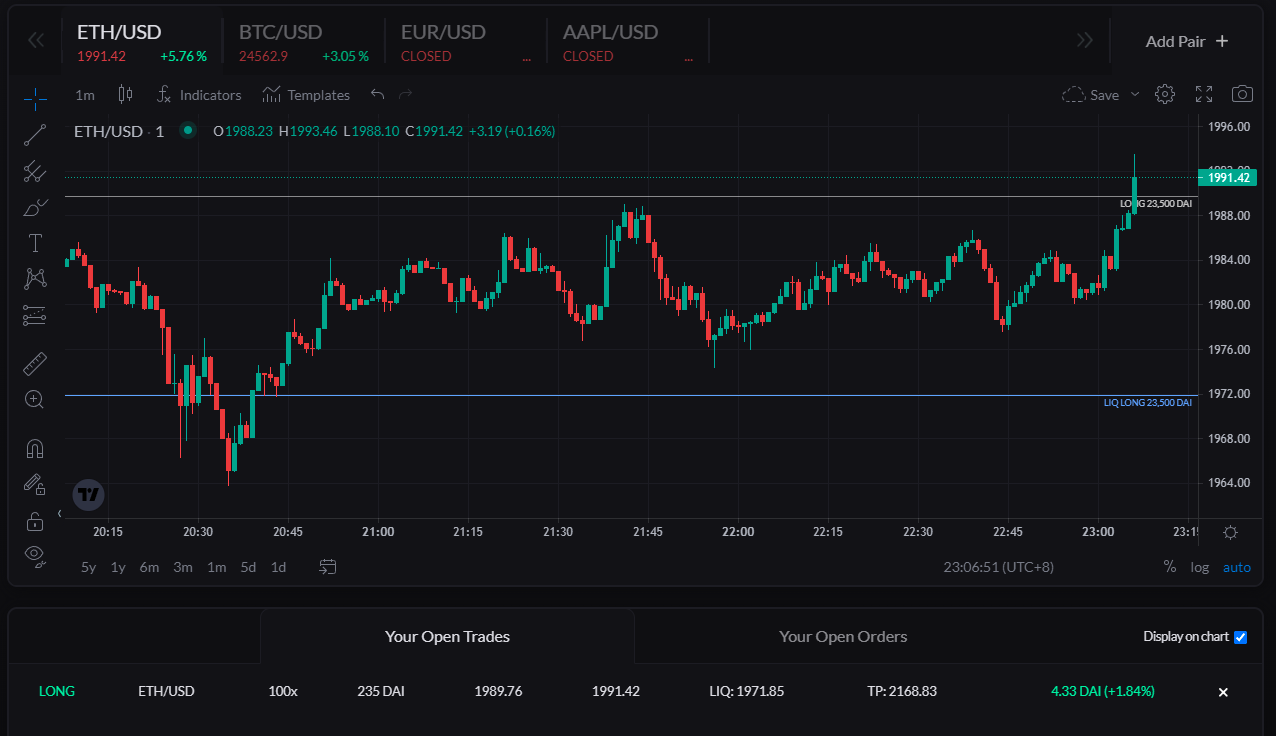
When a trade is opened, the user interface shows all details of the position: liquidation price, stop loss, take profit…
While a trade is opened, the trader can manually adjust the stop loss and take profit levels
Users
Users can earn rewards by:
- Staking LP tokens on the protocol pools to earn rewards paid in GNS
- Staking DAI in Gains’ Single Stake Vault to earn rewards paid in DAI from trading fees
- Staking GNS in Gains’ Single Stake Vault to earn rewards paid in DAI from trading fees
gTrade
gTrade is the leveraged trading platform offered by Gains Network. It is a decentralized perpetual futures exchange where users keep full custody over their own funds and can trade crypto with up to 150x leverage, stocks with up to 100x leverage, forex with up to 1000x leverage, and indices with up to 35x leverage.
- There is no order book or liquidity for each pair
- There is a single gDAI vault for all listed trading pairs
- Leverage is synthetic (not borrowed)
- The leverage allowed is backed by the DAI vault and the GNS token
- Spot prices are in real time (fetched from a custom Chainlink decentralized oracle network)
Regardless of the trading pair, all trades are opened with DAI collateral. This is a flexible design that allows Gains Network to offer multiple trading pairs and levels of leverage (since there is no need to maintain liquidity for each pair or every time a new asset is listed).
By building a highly liquid DAI vault, every trading pair that is listed immediately benefits from available liquidity and larger position sizes.
The PnL of traders is calculated in gTrade’s smart contracts and settled against the DAI vault.
- If the traders’ PnL is positive, DAI is taken out of the vault to pay traders.
- If the traders’ PnL is negative, DAI is deposited into the vault from the traders’ losses.
In order to filter out outlier prices on specific exchanges (whether this is a result of manipulation or lack of liquidity), gTrade relies on a decentralized oracle network that takes price data from multiple exchanges and selects the median price.
This protects traders from liquidations that are caused by price outliers, also known as scam wicks
Spread
When opening a trade, there is a spread (the exact percentage value is visible on the platform) that is used to prevent high-frequency bots from exploiting very small price movements.
The launch of v6.4.2 update introduced the Price Impact Expiration (PIE) mechanism, which involves changes to the platform’s price impact calculations and aims to reduce average spreads offered on altcoins.
gTrade’s price impact calculations were directly influenced by the sum of existing OI (open interest: collateral x leverage) when a new trade is initiated and the OI of the new trade itself. Although effective, it often resulted in less favorable spreads for altcoins when large trades stay open for long periods of time.
The v6.4.2 update introduces an advanced approach. After 4–6 hours, the existing OI used in the price impact calculation expires and resets to 0. This reset mitigates the previous negative effect of long-term trades, ensuring that the price impact reflects more current and relevant trading activities. By tightening altcoin spreads on average, v6.4.2 allows wider access to a range of strategies, helping gTrade’s volume become increasingly scalable. This is particularly beneficial for strategies that are sensitive to even minimal spread variations.
GNS Staking
GNS staking allows GNS holders to stake their GNS tokens to earn rewards paid in DAI from trading fees.
Currently, 56.25% of the fees from market orders and 51.75% of the fees from limit orders are allocated to $GNS staking. More information can be found here. On average, 70% of trades on gTrade are market orders, which means that 54.6% of fees from all orders on average will go to GNS staking.
Holders of GNS NFTs can stake up to 3 NFTs to boost their share of staking rewards:
| Type / Name | Single Side Staking Boost |
| Bronze | 2% |
| Silver | 3% |
| Gold | 5% |
| Platinum | 8% |
| Diamond | 13% |
gToken Vaults
gToken vaults leverage the ERC-4626 tokenized vault standard and represent a staker’s ownership of the vault with an ERC20 token.
ERC-4626 is a tokenized vault standard represented by smart contracts that receive deposits and use those funds to generate yield rewards for the original deposit
gDAI
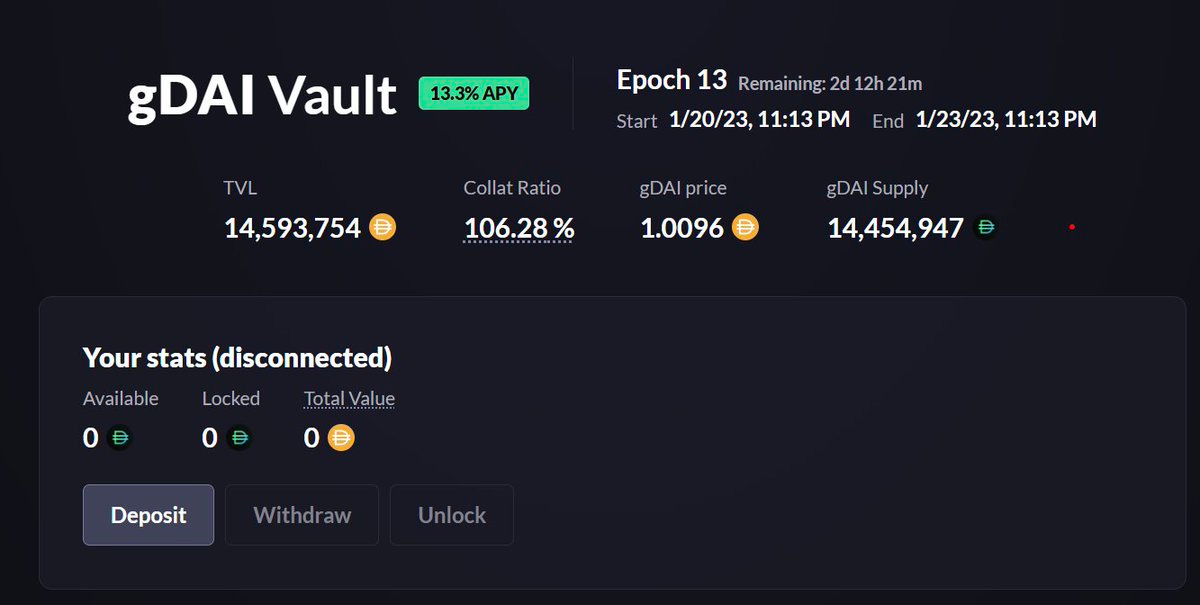
The DAI vault is the backbone of gTrade and serves as liquidity for all synthetic trades that take place on the platform. Rather than using separate liquidity pools for each trading pair, gTrade relies on a single vault model that serves as the counterparty for traders across more than 70 assets.
- When traders win (positive PnL), their winnings are received from the vault.
- When traders lose (negative PnL), their losses are sent to the vault.
gDAI is the first use case of a gToken vault. However, the smart contract code allows for the creation of collateral-agnostic vaults such as gBTC, gETH, gUSDC, gMATIC…
For the gDAI vault, gDAI shares represent the underlying DAI asset
The collateralization of the vault depends on the traders’ PnL. This means that, as long as fees earned are greater than PnL payouts, stakers earn a positive return.
gDAI is the ultimate counterparty to all synthetic trades executed on the protocol.
Gains follows a pool-based counterparty AMM model. When the overall PnL of the vault is negative, the vault starts to create a buffer with those funds in order to protect staker’s funds from future abnormalities in the protocol’s PnL.
The fact that stakers earn revenue from PnL has been proven for two years. There are also risk management measures in place that have the goal of making sure that this will continue being the case
When the vault is overcollateralized by more than 130%, excess DAI is used to market buy and burn GNS token supply in a slow and steady manner
- gDAI is minted when DAI is deposited
- gDAI is burnt when DAI is withdrawn
On average, traders lose more than they win, and hence it becomes less likely for the vaults to reach a state of under-collateralization.
Nonetheless, there is a need to have a risk management framework in place. This framework is built upon dynamic slippage trades, funding rates, and capped open interest.
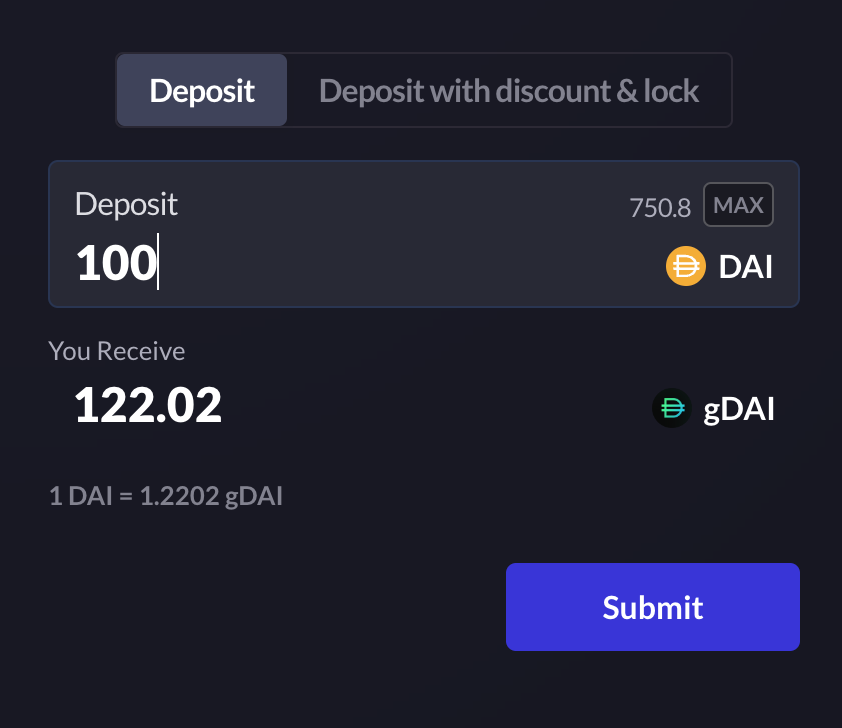
- Users can stake DAI into the gDAI vault in order to supply liquidity for trades to be executed on the platform. In return, liquidity providers earn a percentage of the trading fees.
- Users can withdraw their liquidity from gToken vaults at any time but only at a rate of 25% of their total deposit per day (it will take 4 days to withdraw the full deposit).
This system is an iteration and a significant improvement over the previous design. In the previous vault implementation, stakers were exposed to the following flaws:
- There was an uneven risk for stakers. When the vault suffered losses, few people could exit before others, which left the vault undercollateralized
- When the vault went undercollateralized, there were no incentives to encourage users to refill the vault
- When the vault reached over 130% over-collateralization, GNS was used to be bought and burnt. However, market participants usually ended up frontrunning those transactions
- There was no composability to represent the ownership of shares in the vault – once deposited into the vault, DAI could not be used across DeFi
By having vaults that follow the ERC4626 standard, the protocol solves the problem of making profit-sharing compatible with the composability of the ownership of vault shares.
gDAI can be viewed as a yield-bearing stablecoin that earns revenue from fees and traders’ PnL.
The process of GNS minting and burning has become more efficient over time to prevent frontrunning. Additionally, there is an incentive for stakers to lock liquidity in the vault and help it to remain collateralized in situations where, in the past, stakers took advantage of the withdrawal functionality. This is made more efficient by having an epoch-based withdrawal system as well.
To better approximate the real collateralization ratio and minimize risks for the protocol (and stakers), the vault follows an epoch system to capture the aggregate PnL of traders by taking a snapshot at a specific time.
Calculating the Price of gDAI
gDAI uses an exchange rate model where the exchange rate of the asset for the underlying DAI is set algorithmically. This will be the result of the interaction of two variables: the amount of fees accumulated per unit of gDAI (fixed), and the open and closed PnL per gDAI (variable).
Some of the motives for this design are:
- Avoid increasing the price of gDAI as a result of over-collateralization
- When the vault reaches a collateralization ratio above 100%, the excess of DAI can be used to create a protection layer for stakers
- It becomes less probable for the gDAI price to ever decrease in the future (since the accumulated fees per gDAI always increases)
Due to the exchange rate, the price of gDAI is determined by the PnL of open traders along with the DAI rewards that are accumulated from trading fees. This implementation means that the losses are shared equally between all stakers – not just the last ones to withdraw.
As the vault becomes more overcollateralized, the risk of each gDAI holder decreases evenly
gDAI = 1 + accruedRewardsPerToken – Max(0, accruedPnlPerToken)
- The accruedRewardsPerToken refers to the DAI rewards accumulated per unit of gDAI
- The accruedPnlPerToken is a snapshot of the accruedPnlPerToken at the start of the epoch. As a result, the price of gDAI is updated at the start of every new epoch (apart from the DAI rewards, which are updated on a rolling basis).
The primary goal of this formula is to avoid increasing the price of gDAI as a result of over-collateralization (above 100%). This is achieved by using excess DAI as an extra layer of protection for stakers. Because of this, the price increase of gDAI comes from fees.
Epoch-Based Vault Withdrawals
Withdrawal requests can only be executed in the first 2 days of each epoch, and there is a timelock (delay) between the withdrawal request and the actual withdrawal. The duration of this delay also varies based on how overcollateralized the vault is.
- If the vault is at least 120% collateralized, the timelock duration will be 1 epoch (72 hours)
- If the value is collateralized between 110% and 120%, the timelock will last 2 epochs (6 days)
- If the vault’s collateralization is below 100%, the timelock will take 3 epochs (9 days)
Open Trades PnL Feed
Each epoch lasts 72 hours and there are 4 PnL measurements that are performed every epoch, all of which are powered by the same Chainlink decentralized oracle network. These measurements start 48 hours after the beginning of a new epoch and take place every 6 hours. This way, the protocol can double-check measurements of open trades PnL for the next epoch.
When the median values for the 4 measurements are received, the protocol takes the average of the 4 measurements to determine the PnL (there is a floor of 0 and only positive PnL is taken into account). Next, the delta with the average open PnL of the previous average is taken in order to update the accruedPnLPerToken variable.
The delta in open positive PnL cannot take the accruedPnLPerToken above 1 and is artificially capped (otherwise it would represent a 0% collateralization) to protect against oracle manipulation attacks.
There are two states the epoch system can be in:
- Withdraw window: the period before open PnL values are being received and stakers may make withdraw-related actions (both requests and withdraws).
- Open PnL window: the period before the epoch closes where the protocol requests open PnL snapshots from oracles. This is the stage where the protocol makes multiple requests to an oracle network and takes the median value. This is the PnL value that is then used in the next epoch.
gDAI Composability
Since the protocol issues an ERC20 token when deposits are made into gToken vaults, users benefit from additional token utility and composability across the DeFi landscape.
This is because gDAI can be:
- Transferred between wallets without the need to unstake
- Accepted as collateral in other DeFi protocols
- Serve as an overcollateralized stablecoin backed by gTrade liquidity
- Used to provide liquidity to an AMM pool
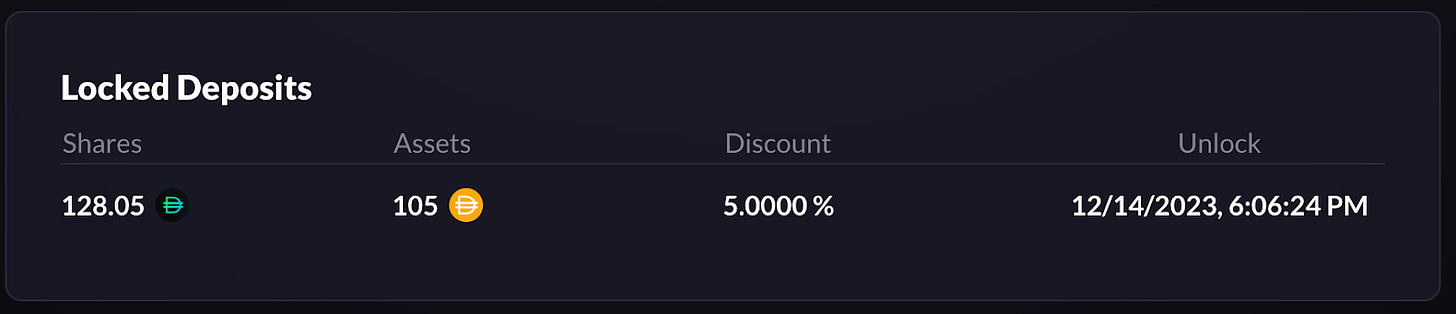
gNFT – DAI Locking Incentives Alignment
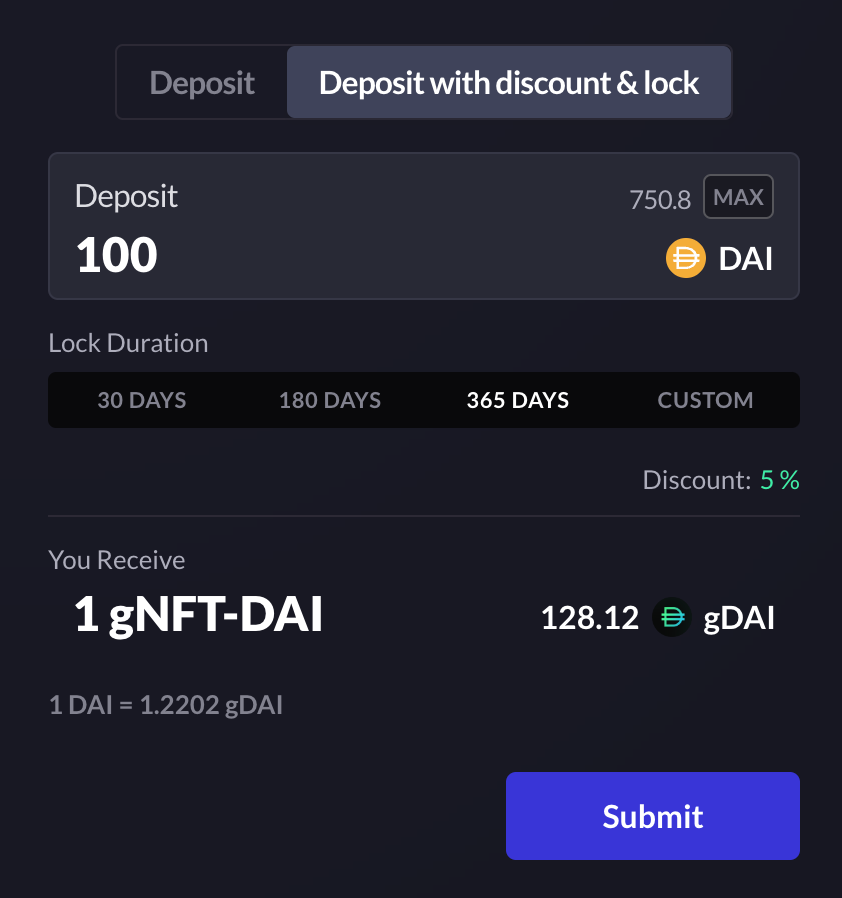
Users can deposit DAI into the vault in exchange for a gNFT that represents rights to a locked gDAI position. The discount percentage is based on the current collateralization ratio of the vault and the duration that the staker is willing to lock gDAI for.
Through this mechanism, users have the option to receive a “discount” on gDAI when staking DAI in the vault and locking the deposit for a certain period of time. The discount is based on two factors:
- Time-based incentive
- Collateralization-based incentive
gNFT is an ERC-721 token that represents ownership of locked gDAI shares and that accumulates fees like all other shares.
Locked gDAI is purchased at a discount, based on the amount of time a lender is willing to lock up their funds, and can be unlocked following the lock duration
gNFT holders are able to claim gDAI anytime after the unlock date. This will burn NFT and transfer gDAI to the owner’s wallet.
The lockup periods range from 2 weeks to 1 year, and the discount is proportional to the collateral level. There is a maximum 5% discount, such that when the vault becomes undercollateralized (< 100%), the maximum allowed discount is 5%. From a 100% to a 150% collateralization ratio, the discount linearly decreases from 5% to 0%.
For example, a user who deposits into the vault when the vault is 120% collateralized and locks for 12 months would get a discount calculated as:
Discount = (150% – 120%) / (150% – 100%) * 5% * 12 months / 12 months = 3% discount
When the vault is <100% collateralized, DAI depositors receive both the highest discount on minting locked gDAI, along with a reduced gDAI price (as it is intrinsically tied to the vault’s health)
Withdraw Locks
For security purposes, DAI cannot be withdrawn by stakers immediately from the vault. Instead, the users must go through a withdrawal request system.
Depending on the collateralization ratio of the vault, a staker may withdraw either 1, 2, or 3 epochs after making a request
The higher the collateralization ratio, the shorter the lock period
If a staker misses their withdrawal window, they must make a new request.
GNS Minting and Burning
The protocol uses a self-adjusting mechanism to manage the vault’s collateralization ratio while also protecting the GNS price from potential selling pressure and creating deflationary pressure on the token’s supply. This way, when the vault is overcollateralized, some portion of the vault profits are used to buy and burn GNS and send DAI to an OTC pool using the 1-hour TWAP price. The amounts depend on the vault’s collateralization ratio as well.
The more collateralized the vault is, the more GNS tokens will be burnt
- While the vault is over-collateralized, a percentage of all trading losses go into a pool that can be used by anyone to sell GNS OTC (over the counter). The vault will then buy and burn GNS and send the equivalent DAI amount OTC using the 1-hour TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price).
- The percentage loss is adjusted based on the collateralization ratio. When it is close to 100% collateralization, it will be lower in order to increase the speed at which the vault becomes overcollateralized. Similarly, as the collateralization ratio increases, the vault will send more to the OTC pool in order to keep the collateralization at a desired range and maximize the burning mechanism.
- When the vault is undercollateralized, it will be refilled by minting and selling GNS OTC (there is a cap at 0.05% of the total GNS supply every 24 hours). By minting GNS, the protocol is able to refill the vault safely while also protecting the GNS token from excessive market sell pressure. In other words, the vault becomes a secondary market for GNS.
Vault Staking
- Users can stake DAI and receive gDAI at any time during an epoch
- Users have the option to receive a discount on their gDAI when staking DAI in the vault by locking their deposit for a certain period of time. This discount will be determined by a time-based incentive and collateralization-based incentive
- Lock up gDA tokens from 2 weeks to 1 year
- Mint gDAI anytime the collateralization ratio is below 150%. In this case, the discount will be proportional to the collateralization level. At a collateralization ratio below 100% the discount will be 5% and the discount will decrease linearly from 5% to 0% as the collateralization ratio moves from 100% to 150%.
Locked gDAI positions are represented as ERC-721 NFTs that can be exchanged, sold, or used as collateral in external protocols.
Even if the position is tokenized as an NFT, it will continue earning trading fees during the lock period
There is a timelock (delay) between the user’s withdrawal request and the actual execution of the withdrawal. The duration will vary based on the vault’s collateralization ratio:
- If the vault is at least 120% collateralized, the timelock duration will be 1 epoch (72 hours)
- If the value is collateralized between 110% and 120%, the timelock will last 2 epochs (6 days)
- If the vault’s collateralization is below 100%, the timelock will take 3 epochs (9 days)
The timelock is a measure implemented for risk management purposes in order to ensure that the vault remains in a healthy state regardless of market conditions
The vault structure encourages liquidity providers to deposit funds into the vault at all collateralization levels – even when the vault is undercollateralized. For example, when the vault’s collateralization is below 100%, DAI depositors receive both the highest discount on minting locked gDAI and a reduced gDAI price.
This dynamic creates an arbitrage opportunity for LPs that expect the vault to return to a healthy collateralization ratio, which allows them to make a profit on their deposit as the price of gDAI goes back above the price of DAI. For example, a user that stakes at a 90% collateralization will have the opportunity to increase the value of its deposit by 11% as soon as the vault gets back to a 100% collateralization.
In order to prevent the gDAI supply from going out of control while the vault is under 100% collateralization (since 1 DAI gets you more than 1 gDAI), the protocol defines a maximum daily supply increase of 2% while undercollateralized.
Example
A user deposits DAI into the vault when the collateralization is 115% and decides to lock gDAI for 6 months.
The discount will be (150% – 115%) / (150% – 100%) collateralization * 5% total discount * 6 months / 12 months = 1.75% discount
For Investors
The following strategies are available for investors:
- GNS staking – Single-sided staking of GNS token.
- gDAI Vault – Yield earning on stablecoin.
- Liquidity Provision – Pairing GNS with other tokens for yield.
GNS Staking
The GNS token can be staked single-sided on the Gains Network UI itself for DAI rewards, on both the Polygon and Arbitrum network, with varying APY.
This way, users are able to keep their GNS tokens and still receive yield, without having to pair it up with other tokens which may bring about extra volatility or a dilution in their GNS tokens holding.
The benefits that the users receive are explored in-depth in the GNS Staking section above.
gDAI Vault
Investors who plan on earning yield on their stablecoins can deposit DAI into the gDAI vaults on either Polygon or Arbitrum.
The yields are accumulated in the gDAI token, meaning investors can withdraw 1 gDAI for a higher ratio of DAI over time.
The benefits that the users receive are explored in-depth in the gToken Vaults section above.
Liquidity Provision
While Gains Network has stopped providing staking rewards to liquidity providers on its site, investors can still provide liquidity for the GNS pairs on other protocols in order to receive swap fees.
Sites include:
- GammaSwap – Actively managed Uniswap v3 pairs.
- Both Polygon and Arbitrum network.
- Uniswap – Decentralised crypto trading protocol.
- Both Polygon and Arbitrum network.
- Trader Joe – One-stop decentralized trading.
- Arbitrum network.
- KyberSwap – DeFi exchange & aggregator.
- Both Polygon and Arbitrum network.
Markets & Asset Classes
Cryptocurrencies
- Trading pairs (40 +): https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/pair-list
- Leverage ranges from 2x to 150x
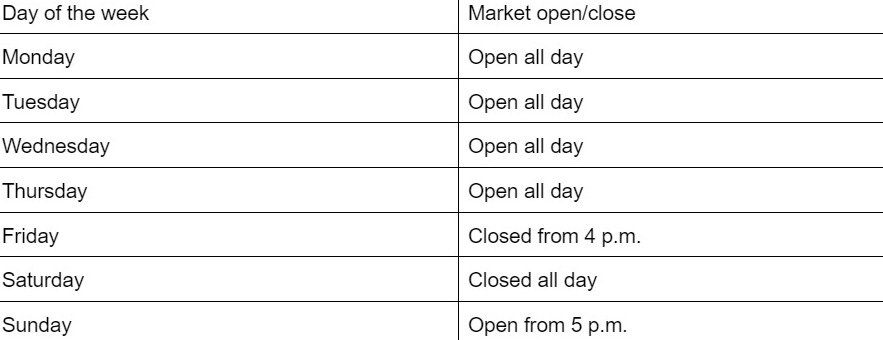
- 24/7 markets
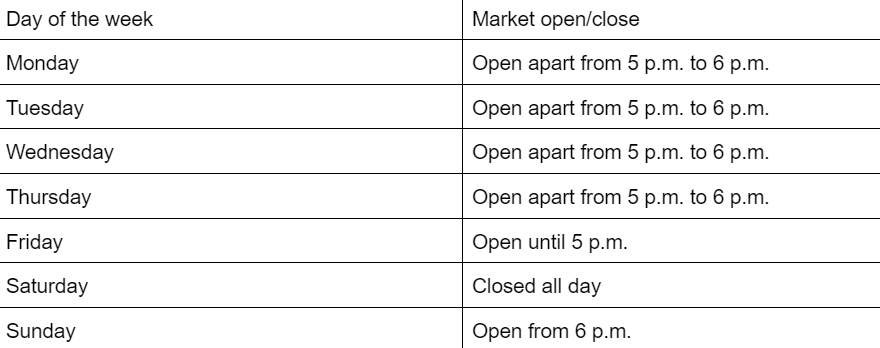
Forex
- 20 trading pairs: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/pair-list
- Leverage ranges from 10x to 100x
- Times referenced in EST:
- Markets are closed on the following holidays:
- December 25th-27th
- January 1st-2nd
Forex markets can experience price gaps (due to the markets opening at different prices than the price at which they were closed).
Stop losses and take profit levels are not guaranteed and traders should monitor their open positions while the market is closed (this could result in a bigger win than originally planned or in a liquidation depending on how big the price gap is).
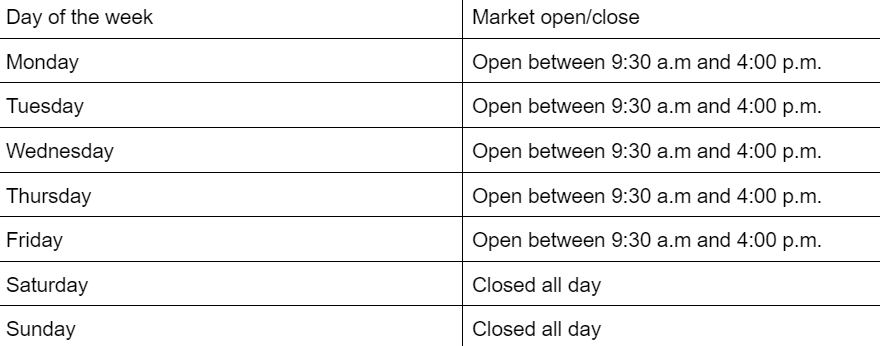
Stocks
- Trading pairs (20+): https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/pair-list
- Leverage ranges from 3x to 100x
- Times referenced in EST:
Closed all-day
- Markets are closed on the following holidays:
- January 2nd
- January 16th
- February 20th
- April 7th
- May 29th
- June 19th
- July 4th
- September 4th
- November 23rd
- November 24th (from 1:00 p.m.)
- December 25th
Stock markets can experience price gaps (due to the markets opening at different prices than the price at which they were closed).
Stop losses and take profit levels are not guaranteed and traders should monitor their open positions while the market is closed (this could result in a bigger win than originally planned or in a liquidation depending on how big the price gap is).
- Limitations:
- It is not possible to open trades the day before earnings and dividends (trades that are opened are not affected by this
- Stock splits are handled by creating a new trading pair (since gTrade cannot edit a trader’s position). When this happens, the trader will not lose any open positions and the price change on the pair opened before the split will continue at the same percentage.
Indices (ETFs)
- 4 trading pairs: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/pair-list
- Leverage ranges from 2x to 35x
- Same market times as stocks
When trading indices, users can experience price gaps (due to the markets opening at different prices than the price at which they were closed).
Stop losses and take profit levels are not guaranteed and traders should monitor their open positions while the market is closed (this could result in a bigger win than originally planned or in a liquidation depending on how big the price gap is).
Commodities
- 2 trading pairs: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/gtrade-leveraged-trading/pair-list
- Leverage ranges from
- 2x to 250x for XAU/USD (Gold)
- 2x to 150x from XAG/USD (Silver)
- Times referenced in EST:
When trading commodities, users can experience price gaps (due to the markets opening at different prices than the price at which they were closed).
Stop losses and take profit levels are not guaranteed and traders should monitor their open positions while the market is closed (this could result in a bigger win than originally planned or in a liquidation depending on how big the price gap is).
Lifecycle of a Trade
1. Opening Fee
Opening fees are calculated by taking the total size of the position (collateral * leverage).
For example, the opening fees for a position that uses 250 DAI and 10x leverage would be calculated to the total amount of 2,500 DAI.
With the opening fee set at 0.08%, the total opening fee would be equal to 2,500 * (0.08 / 100) = 2 DAI.
This results in a collateral size of 248 DAI and a total position size of 2,480 DAI.
2. Fixed Spread
When opening a trade in gTrade, the protocol applies a fixed spread to the price returned by the Chainlink oracle.
The protocol’s fixed spread can be reduced by holding a Gains Network NFT
For example, when the Chainlink oracle reports a price of 3,003.19 and the fixed spread is 0.04%, then the open price would be 3,004.39 (before the consideration of the dynamic spread).
If the user had a Diamond NFT (which lowers the spread by as much as 35%), the opening price would have been 3,003.97
The fixed spread is different for each pair – smaller pairs with lower liquidity have a higher spread
The parameters for the fixed spread are displayed on the front end and can be confirmed in the Pairs Storage contract by searching for the relevant pair index
3. Dynamic Spread
The dynamic spread was formerly known as “price impact”
The dynamic spread is added on top of the fixed spread.
The dynamic spread is calculated based on the trading pair and its fixed spread, the size of the positions, and the direction of the trade (long/short).
Dynamic spread (%) = (Open Interest {long/short} + New trade position size / 2) / 1% depth (above / below
- Cryptocurrencies dynamic spread uses 2x the 1% depth in each direction (longs use 1% depth above, and shorts use 1% depth below) from Binance data, except for the BTC/USD and ETH/USD pairs, which use the fixed spread.
Since gTrade uses the median spot prices of 7 exchanges, using the 1% depth of Binance would be overly conservative. Because of that, gTrade applies a multiplier of 2x on top of that. This multiplier can be updated in the future.
- Forex pairs have a dynamic spread on top of the fixed spread during:
- Major news: 1% depth is set to 250,000 on relevant pairs – for instance during a CPI release
- Low liquidity sessions: 1% depth is set to 10m on all pairs for 2 hours after the New York market close
- Market closing: 1% depth is set to 250,000 on all pairs 30 minutes before the market closes
- Stocks have a dynamic spread applied on top of the fixed spread during:
- Major news: 1% depth is set to 250,000 on all pairs – for instance during a CPI release
- Market closing: 1% depth is set to 250,000 on all pairs 30 minutes before the market closes
For example, with a position of $2,480 after fees, if the “1% depth above price” parameter for the ETH/USD pair is 8m and there is 100,000 DAI of open interest in longs:
Dynamic spread = (100,000 + 2,480 / 2) / 8,000,000 = 0.0126%
The dynamic spread of 0,0126% is then applied to the opening price including the fixed spread. In the case of crypto, since there is no fixed spread, the final opening price is calculated as:
Final opening price = 2,480 + (2,480 * 0.0126 / 100) = $2480.31248
4. Rollover and Borrowing Fees
Rollover and borrowing fees are applied to trades while they are open.
Borrowing fees
With the update of gTrade v6.3.2, the funding fees system has been replaced by borrowing fees. This shift creates a more efficient approach to managing the profit risk of open trades.
Under this new system, borrowing fees treat open trades of the dominant side as vault borrowers. This enables the following benefits:
- Greater scalability of max OI per pair without increasing vault TVL.
- Better risk management.
- Allows traders to open larger positions without increasing fee APRs.
The new borrowing fee structure also offers several advantages compared to the previous funding fee model:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Borrowing fees are now 100% efficient as they directly contribute to the vault’s negative PnL, improving the protocol’s overall efficiency.
- Improved Over-Collateralization: The new borrowing fee structure supports the over-collateralization of the vault, providing increased safety for liquidity providers’ capital.
- Exposure Regulation: The borrowing fee structure effectively regulates net exposure by providing a negative incentive, encouraging traders to avoid or close expensive positions.
- Reduced Rollover Fees: While the borrowing fee doesn’t replace the existing rollover fee, it is significantly lower, making lower leverages more cost-effective.
- Enhanced Risk Management: The borrowing fees now take into account individual trading pairs and correlated asset groups, allowing for better management of the platform’s overall risk exposure.
- Increased Revenue Generation: The revised fee structure aligns with maximizing revenue generation by scaling open interests and volume on the platform.
- Improved Scaling: With improved price exposure risk management, the maximum allowed open interests on all pairs can be significantly increased without requiring additional vault TVL.
How it Works
The borrowing fees are applied to the dominant side of the market, which typically has the majority of the open interest. For instance, if there is $10 million of long open interest and $5 million of short open interest on a trading pair, the borrowing fee will be charged to the long positions, while the short positions won’t incur any borrowing fees. There are three main concepts to this structure, being:
- Borrowing APR
- Pair borrowing
- Group borrowing
Borrowing APR
The borrowing APR represents the borrowing fee charged for a specific trading pair or group of correlated pairs at 100% vault utilization (net OI = vault TVL).
It is calculated using the following methodology: “Borrowing APR = volFactor / Max vault exposure % * marketFactor”, where:
- volFactor: volatility coefficient (more volatility = more expensive).
- volFactor = (dailyVolatility * 365) ^ 1.25 / 150
- dailyVolatility = (3 * Avg_Daily_ATR%_1_Days + 2 * Avg_Daily_ATR%_7_Days + Avg_Daily_ATR%_30_Days ) / 6
- Max vault exposure %: This parameter is set depending on how much maximum vault exposure is targeted ideally.
- marketFactor: The coefficient allows for adjusting costs for groups of pairs (between 0 and 1).
Under volFactor -> dailyVolatility, the daily ATR % is a technical indicator measuring an asset’s daily volatility in percentage. For groups, the average value for all pairs is used instead. The weighted average of recent and older volatility allows us to consider short-term and longer-term volatility.
The max vault exposure % is set at 20% based on historical trading data collected until now.
The marketFactor is 1 on all pairs (no effect on the APR) and for groups, it will be proportional to the correlation of all pairs it contains (low correlation 0 = closer to 0, higher correlation = closer to 1). This leads to a lower cost on the group level which allows for more activity on popular pairs of the group without increasing the fees on all its other pairs too fast.
Pair Borrowing
Pair borrowing refers to the fee charged for holding a position in a specific trading pair. The fee is calculated taking into account the net OI and the borrowing APR for that pair, as well as the TVL in the associated vault. By considering these factors, the pair borrowing fee is determined for traders holding positions in the pair.
The APR charged at any point in time is calculated using the formula: “Borrowing APR * Net OI / Vault TVL”
Group Borrowing
In the new structure, trading pairs that exhibit significant correlation are organized into groups, and a collective borrowing fee is applied to the entire group.
The APR for the group borrowing fee is calculated using a similar formula as the pair borrowing fee. It takes into account the total net OI of all pairs within the group, the group borrowing APR, and the TVL in the associated vault. By considering these factors, the group borrowing fee APR is determined and applied to all pairs within the correlated group.
The formula is the same as pair borrowing.
Final Borrowing Fee Calculation
The final borrowing fee paid by the user at any point in time is determined by the maximum of the pair borrowing fee and the group borrowing fee.
For example, if the pair APR is 4% and the group APR is 4.8%, the user will pay 4.8%.
This method ensures that the platform’s overall risk is managed effectively, considering the exposure of individual and correlated trading pairs.
Rollover fees
The rollover fee is charged every block and is only applied to the collateral.
The goal of implementing rollover fees is to allow traders to use lower leverage levels while maintaining solid risk management for the protocol.
Rollover fee = (Current block – Trade open block) * rollover fee per block % * trade collateral
For instance, a trader with $1,000 collateral that closes a position that was opened for 10,000 blocks, if the rollover fee per block is 0.00001%, would pay a rollover fee of 10,000 * 0.00001 / 100 * 1,000 = 1 DAI
Similarly, a rollover fee of 0.0082% per hour means that, if you had a trade with a 10x long, you would pay 0.00082% on your position size.
In the example above, the trader is paying 0.00082% on rollover fees applied to its position size but, at the same time, is earning 0.0481% on the position size from funding fees. The trader would be earning a net positive of 0.04782% per hour.
The rollover fee per block of a given trading pairs depends on the volatility of the pair, which is measured using the ATR (Average True Range) indicator.
With the update of gTrade v6.3.2, rollover fees are expected to become 3x lower, making lower leverages cheaper.
Closing fee
Closing fees are applied on the initial position size (without PnL).
For example, for a user going 10x long on ETH with 248 DAI collateral, the closing fee will be calculated as:
Closing fee = 2,480 * (0.08 / 100) = 1.984 DAI closing fee
Using a 0.08% closing fee for cryptocurrency pairs
If the trade results in a positive PnL of $24.8, the closing fee is subtracted and this results in a 22.816 DAI PnL.
On top of that, the funding and rollover fees are applied. For instance, if the trade earned 1.2 DAI from funding and paid 0.5 DAI of rollover fees, this would result in a final PnL of 22.816 + 1.2 – 0.5 = 23.516 DAI.
After closing the trade, the user receives the original 248 DAI collateral + 23.516 DAI = 271.516 DAI
Liquidations
The liquidation prices of opened trades can get closer or further away over time as you pay or earn from funding and rollover fees.
Liquidation price distance = Open price * (Collateral * 0.9 – rollover fees – funding fees) / collateral / leverage
- If long, the liquidation price is calculated by subtracting the liquidation price distance to the open price
- If short, the liquidation price is calculated by adding the liquidation price distance to the open price
For example, a user with a long on BTC/USDT using a 100x leverage and 50 DAI collateral at a BTC price of $20,000 would have a liquidation price calculated as:
Liquidation price = 20,000 – 20,000 * (50 * 0.9 – 0.5 – (-1)) / 50 / 100 = 19,818
One-Click Trading (1CT) Experience
1CT removed the need to interact with a wallet when submitting transactions, reducing the time required to trade. This is done through the use of two new mechanisms:
- 1CT Wallet
- Trade Delegation
1CT Wallet
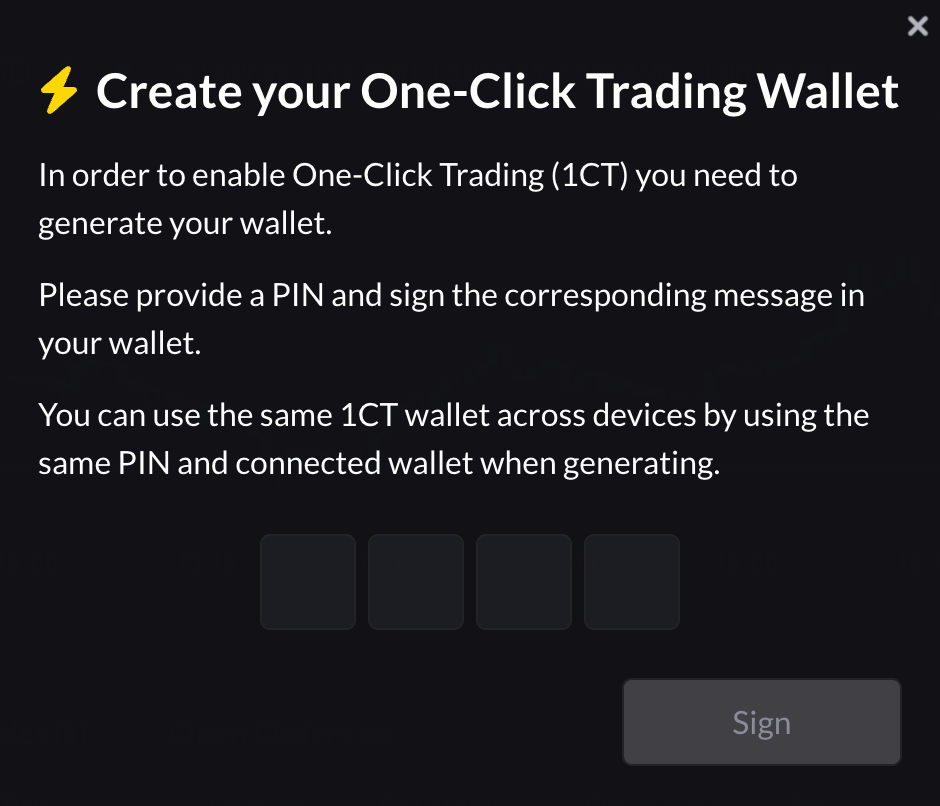
gTrade uses a derived externally owned account (EOA) wallet for submitting trading transactions. The process sequence goes:
- Trader provides a 4-digit PIN. Pin should be remembered for future recovery.
- Traders sign a prefixed message of the PIN using their wallet. The wallet used to sign the message should be remembered for future recovery.
- gTrade website generates an Secp256k1 key pair using the signed message as a seed.
- gTrade website encrypts and stores the key material on the local device.
The 1CT wallet is a delegation wallet. Once a 1CT wallet is created, traders must grant it permission to trade on their behalf by approving it as a delegate.
Trade Delegation
- gTrade smart contracts support a delegation feature, allowing EOAs to submit transactions on behalf of other EOAs.
- To delegate to another EOA, a trader must approve the address as a delegate through the trading contract.
- A delegation wallet only needs gas funds for submitting transactions as collateral and PnL are tied to the trader address.
Onboarding and Managing for 1CT
- Create PIN
- Sign Message
- Approve 1CT Wallet
- Fund 1CT Wallet
- Enable Feature
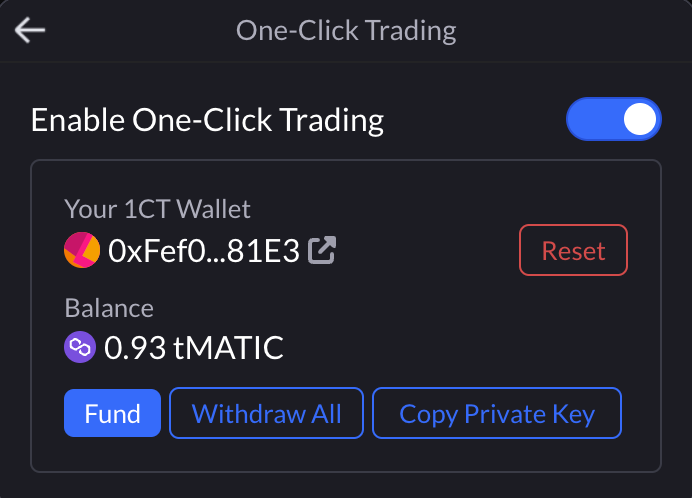
Once a trader has been onboarded, they may manage the feature under the accounts dropdown:
- Enable/disable 1CT feature
- Fund 1CT wallet
- Withdraw all funds from 1CT wallet
- Export private key
- Reset/wipe all 1CT data
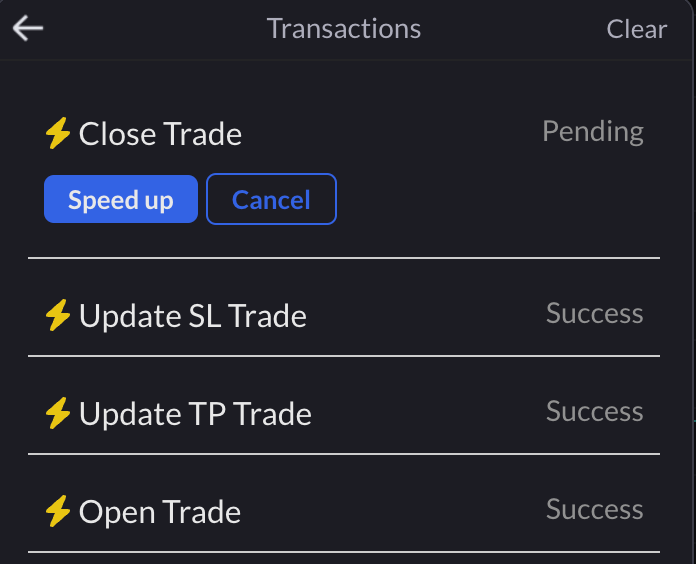
Once a trader is onboarded and the feature is enabled, there is nothing different other than not having to confirm transactions in a wallet. Since 1CT wallet is managed by the site, transaction management is taken in-house. This provides a place to track transactions and interact if they are stuck by speeding up or cancelling it.
Running an NFT bot
NFT bots monitor asset prices and execute Limit, Stop Limit, Take Profit, Stop Loss, and Liquidation orders.
Instructions for running the NFT bot:
The instructions for running an NFT bot are listed in github and may not be easy for most users to run.
The process consists of:
- Creating a specific address/wallet to prevent address conflict.
- Sending the NFT to your new wallet using the block explorer.
- Running the bot locally off your laptop/workstation via github repo and editing variables.
- An “nft-chat” discord channel is available for related discussions.
Costs
Running the NFT bot requires spending MATIC and LINK tokens in order to execute transactions and pay the oracles for price provision.
Reward
The reward for the order is 5% of the collateral for a liquidation, paid in GNS. For all other types, the reward is 0.02% of the position size (with leverage) for crypto and 0.002% for forex.
With the update to gTrade v6.3.1, the reward system has been changed. While the above rewards are still in effect, the rewards distribution has been adjusted to the following:
- Being the first NFT bot to trigger a transaction (in the same block) is no longer an advantage.
- This means that all participants will pay the same amount of LINK required to execute the transaction. The first to trigger technically pays the full cost, but the other triggers in the same block refund them a portion of the LINK so that in the end everyone pays the same.
- If there are not enough same block triggers to refund the first to trigger, the $LINK refund will come from the $GNS reward itself to always guarantee a fixed $LINK cost.
- All rewards — except LINK transaction participation costs, which are refunded in GNS — will go into the next round’s reward pool.
- Since NFT bot runners don’t know the size of the orders to trigger in the next round, they are incentivized to trigger all orders equally to maximize their share of the rewards of the next pool. On the contrary, the GNS rewards corresponding to the LINK refunds are distributed immediately.
- One trigger per bot / NFT per order in the same block.
- To protect against spamming same-block triggers using the same bot address / NFT, we now prevent users from triggering the same order multiple times within the same block and taking up extra same-block space.
Business Model
Gains Network’s business model is based on providing a decentralized trading platform for users to trade digital assets, while also incentivizing liquidity provision and supporting a deflationary token economy through the use of the GNS token and unique NFTs. The platform charges fees on trades, which are used to buyback and burn GNS tokens, thereby reducing the total supply of tokens and increasing their value over time, and also providing yields to stakers and vault users.
Additionally, the NFTs offer exclusive benefits to holders, which can drive demand and value for these assets as well. GNS also receives additional utility from being used as the governance token of the DAO.
The long-term goal of Gains Network is to have enough POL (Protocol Owned Liquidity) so that rewards from trading fees can go to holders that stake GNS tokens in a single-sided staking pool.
Referrals
The referral system is the primary organic marketing campaign. Gains uses a whitelisted referrals system where only accounts that produce organic volume in the exchange will be considered. The core team reserves to itself the right to remove any whitelisted referral if bad behavior is detected.
The amount of rewards depends on the opening volume that has been referred to and are paid in GNS. The rewards for every new referral link start at the low range and increase as the total opening volume referred reaches $10M. After the first $10M, rewards are capped at the higher end of the range forever. Rewards increase from 0 to $10M in volume as follows:
- Stocks tier 1 – 0.025% to 0.033%
- Stocks tier 2 – 0.044% to 0.059%
- Stocks tier 3 – 0.074% to 0.099%
- Crypto – 0.015% to 0.02%
- Forex – 0.0015% to 0.002%
Traders do not pay fewer fees by using a referral link
- Since there is no way to distinguish between new and existing users, the protocol revenue would be significantly decreased, since traders could just refer to themselves and pay fewer fees.
The referrals program is implemented through a two-tier system where:
- Users who help onboard new users through referrals earn 10% of the referral rewards.
- Users who introduce the protocol to an influencer earn 10% of whatever they generate with referral fees.
gTrade Ambassador Requirements
There are two ways to become a gTrade Ambassador, either by applying for it or being recommended through a gTrade Ally. Allies are those who have direct connections with someone who is aligned with gTrade’s vision and meets their Ambassador requirements.
To be eligible for becoming a gTrade Ambassodor, the following inclusion guidelines are listed:
- Value alignment: 100% non-shill content, no harassment or hate speech.
- At least 50% of Ambassador’s content is related either to DeFi OR Trading.
- Have an active Twitter account with consistent engagement;
- Minimum follower count of 1k
- Minimum engagement of ≧ 5 likes on average
- Activity level of ≧ 3 tweets per week
- Have an active youtube account with consistent engagement;
- Minimum subscriber count of 1k
- Minimum engagement of ≧ 250 views on average
- Activity level of ≧ 2 videos per month
Users can sign up to become a gTrade Ambassador here or become an Ally for referring an Ambassador here.
Revenue Streams
GNS holders receive platform fees through single-side staking vaults and the burning of GNS using platform revenue.
NFT holders benefit from boosted rewards as well as NFT bots executing limit orders and liquidation.
By staking GNS, users are able to earn DAI from the trading fees generated by the protocol as well. This creates a strong incentive for the community to increase the trading volume on the platform.
-
- 40% of the fees from market orders are allocated to GNS stakers
- 15% of the fees from limit orders are allocated to GNS stakers
- Referral rewards earn between 0.015% and 0.02% of the opening volume referred and are claimable at any time in GNS:
- 0.015% if there is no trading volume coming from referrals
- 0.02% if the trading volume exceeds $10M
- Linear increase between 0.015% and 0.02% based on the volume that is referred (e.g. 0.0175% for $5M in volume)
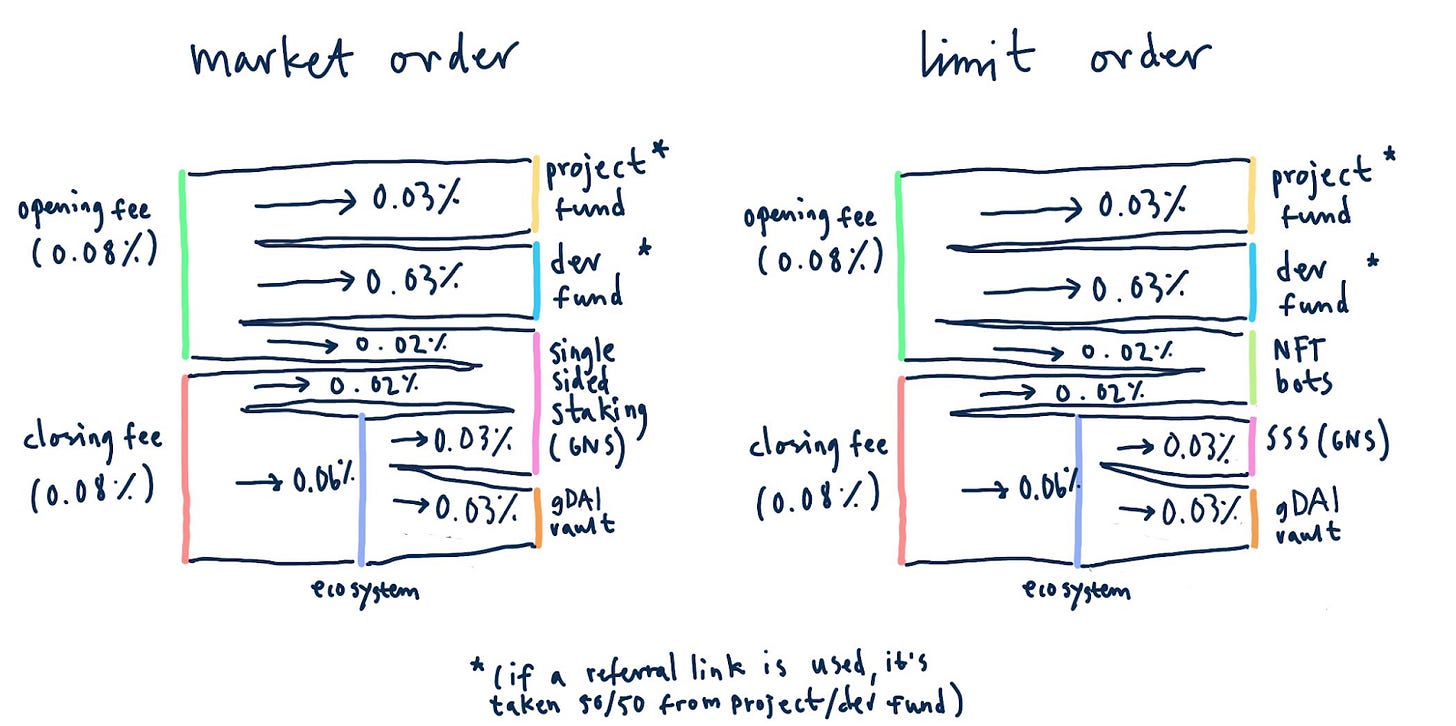
Fee Breakdown
gTrade charges funding fees on the notional position size (collateral * leverage) and rollover fees on the collateral. The exact value for each pair will be displayed on the site
This fee structure manages the risk of the DAI vault based on the exposure and volatility of a given pair.
Fees are distributed to the team, the project fund, liquidity providers, GNS stakers, affiliates, and GNS NFT holders. Across all pairs, fees are distributed 50/50 between governance and team fees, and the ecosystem fee.
- Market/limit order fees go to GNS staking if the order is a market order and to NFT bots if it is a limit order
- Referrer rewards are taken from the governance and team fees
The governance fund is used to pay developers, pay for oracles, architecture, competitions, marketing…
While trades are open, they pay the rollover fee and pay/earn the funding fee
With the introduction of DAI vaults, GNS-DAI LPs become less relevant in the overall protocol architecture, since GNS minting by the DAI vault has been disabled.
Distribution of closing fees:
- 40% to GNS staking
- 40% DAI vault
- 20% GNS-DAI Lps
There used to be a 0.5% collateral fee that was removed in August 2022
Cryptocurrencies Fees
The spreads on BTC/USD and ETH/USD are fixed at 0.04%, and dynamic depending on the Dynamic Spread on all other pairs. (A detailed explanation on Fixed and Dynamic Spreads are at the end of this section.)
The fees for cryptocurrencies are:
- Opening a trade: 0.08%
- 0.06% -> Governance & Team
- 0.015-0.02% -> Referrer
- 0.02% -> Market/Limit
- Updating a stop loss (guaranteed execution):
- 0.015% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade: 0.08%
- 0.06% -> Ecosystem
- 0.02% -> Market/Limit
Forex (Major)
Spreads on all major forex pairs are fixed at 0.01%.
- Opening a trade: 0.012%
- 0.009% -> Governance & Team
- 0.00225-0.003% -> Referrer
- 0.003% -> Market/Limit
- Closing a trade: 0.012%
- 0.009% -> Ecosystem
- 0.003% -> Market/Limit
Forex (Minor)
Spreads on all minor pairs are fixed at 0.01%.
- Opening a trade: 0.016%
- 0.012% -> Governance & Team
- 0.003-0.004% -> Referrer
- 0.004% -> Market/Limit
- 0.012% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade: 0.016%
- 0.012% -> Ecosystem
- 0.004% -> Market/Limit
Forex (Exotic)
Spreads on all exotic forex pairs are set per pair depending on their volatility.
- Opening a trade: 0.02%
- 0.015% -> Governance & Team
- 0.00375-0.005% -> Referrer
- 0.005% -> Market/Limit
- 0.015% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade: 0.02%
- 0.015% -> Ecosystem
- 0.005% -> Market/Limit
Stocks (Tier 1)
Tier 1 stocks are the least volatile ones, where we allow up to 50x (eg. $GOOGL). Spreads on all tier 1 stocks are fixed at 0.02%.
- Opening a trade (0.08%)
- 0.06% -> Governance & Team
- 0.015%-0.02% -> Referrer
- 0.02% -> Market/Limit
- 0.06% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade (0.8%)
- 0.06% -> Ecosystem
- 0.02% -> Market/Limit
Stocks (Tier 2)
Tier 2 stocks are slightly more volatile stocks, and up to 40x is allowed (eg. $FB). Spreads on all tier 2 stocks are fixed at 0.04%.
- Opening a trade (0.12%)
- 0.9% -> Governance & Team
- 0.0225-0.03% -> Referrer
- 0.03% -> Market/Limit
- 0.9% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade (0.12%)
- 0.09% -> Ecosystem
- 0.03% -> Market/Limit
Stocks (Tier 3)
Tier 3 stocks are the most volatile stocks, and up to 20x is allowed (eg. $GME). Spreads on all tier 3 stocks are fixed at 0.06%.
- Opening a trade (0.16%)
- 0.12% -> Governance & Team
- 0.03-0.04% -> Referrer
- 0.04% -> Market/Limit
- 0.12% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade (0.16%)
- 0.12% -> Ecosystem
- 0.04% -> Market/Limit
Indices (ETFs)
Spreads on all indices ETFs are fixed at 0.02%.
- Opening a trade (0.05%)
- 0.0375% -> Governance & Team
- 0.009375-0.0125% -> Referrer
- 0.0125% -> Market/Limit
- 0.0375% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade (0.05%)
- 0.0375% -> Ecosystem
- 0.0125% -> Market/Limit
Commodities (Tier 1)
This category currently only includes XAU/USD (Gold). Spreads on all tier 1 commodities are fixed at 0.01%.
- Opening a trade (0.05%)
- 0.0375% -> Governance & Team
- 0.009375-0.0125% -> Referrer
- 0.0125% -> Market/Limit
- 0.0375% -> Governance & Team
- Closing a trade (0.05%)
- 0.0375% -> Ecosystem
- 0.0125% -> Market/Limit
Commodities (Tier 2)
This category currently only includes XAG/USD (Silver). Spreads on all tier 2 commodities are fixed at 0.04%.
- Closing a trade: 0.08%
- 0.06% -> Ecosystem
- 0.02% -> Market/Limit
- Opening a trade: 0.08%
- 0.06% -> Governance & Team
- 0.015-0.02% -> Referrer
- 0.02% -> Market/Limit
- 0.06% -> Governance & Team
Tokens
GNS
GNS is the utility and governance token of the platform. The reason for the GNS token is to be used in a mint and burn mechanism to fund the DAI vault used for rewarding traders. This way, when a trader wins, GNS is minted and sold on the secondary market to refill the DAI vault when its collateralization ratio is below 100%. Similarly, when a trader loses and the vault is beyond the 110% collateralization threshold, the protocol will slowly buy GNS and burn it to reduce the supply of the token.
The goal of the token is to make the trading experience more capital efficient by:
- Minting rewards for GNS/DAI LPs, NFT bots, and affiliates.
- This allows DAI to remain within the vault and adds stability by supporting the vault’s over-collateralization.
- Burning GNS when the DAI vault is sufficiently overcollateralized.
- This allows the protocol to offset the extra inflation from the GNS allocation to GNS/LP and NFT bot rewards.
- Being a backstop to traders winning on gTrade.
- The reason for that is that GNS can be minted to collateralize the gDAI vault (as long as it does not exceed a maximum inflation rate of 18.25% per year)
Initially, the GNS token was the GFARM2 token. GFARM2 was deployed on Ethereum in January 2021 and was distributed between an ETH pool and GFARM2/ETH LP pool where the development fund and the government each received a 5% share. The GFARM2 token was bridged to Polygon to be used as collateral. In October 2021, the community agreed to migrate to the rebranded token name GNS with a 1:1000 split. Subsequently, the collateral asset was changed to DAI
- Supply cap: 100,000,000 GNS
- Initial supply: 38,500,000 GNS
- Dynamic total supply due to the burning mechanism
- GNS supply and market cap: https://dune.com/queries/1309098/2240934
$GNS Staking
$GNS staking allows $GNS holders to stake their $GNS tokens to earn rewards from trading fees, paid in $GNS that has been bought back using the underlying collateral (that the trade was opened with).
The rewards are accrued from the platform revenue on each chain, i.e., if you stake $GNS on Arbitrum you will get rewards from the trades on Arbitrum and vice versa for Polygon.
Currently, 56.25% of the fees from market orders and 51.75% of the fees from limit orders are allocated to $GNS staking. More information can be found here.
On average, 70% of trades on gTrade are market orders, which means that 54.6% of fees from all orders on average will go to GNS staking.
Holders of GNS NFTs can stake up to 3 NFTs to boost their share of staking rewards:
| Type / Name | Single Side Staking Boost |
| Bronze | 2% |
| Silver | 3% |
| Gold | 5% |
| Platinum | 8% |
| Diamond | 13% |
GNS NFTs
Under gTrade update 6.4.1, GNS NFTs are to be retired.
The NFTs would be redeemable once burned at the following rates:
- Bronze: 800 $GNS
- Silver: 1,200 $GNS
- Gold: 1,800 $GNS
- Platinum: 3,700 $GNS
- Diamond: 12,000 $GNS
There would be 2 options for NFT holders to redeem the $GNS, with no deadline:
- Receive the $GNS immediately against a 25% penalty (penalty directed to the gov fund to be used strategically and/or burned, as decided by the community)
- Receive linearly vested $GNS over 6 months, beginning from the date of redemption (staked throughout the vesting period)
Governance
The governance forum and snapshot website were introduced on August 28, 2023.
Governance in Gains goes through two processes, the forum on discord and a on-chain snapshot vote. The snapshot vote is only available for $GNS holders.
Forum (Discord)
The new Governance category on the Discord server is theplatform for engaging in meaningful discussions and collaborative decision-making. Here’s a breakdown of how it operates:
- Proposal-Discussion Channel: This channel serves as the hub for submitting and deliberating on two distinct types of posts:
- Grant Proposals: A dedicated template to guide users through the submission process for grant proposals. Once submitted, the community and the team can offer insights, feedback, and suggestions for enhancement. While the team leads the evaluation and refinement, they actively encourage community participation.
- GIP (Gains Improvement Proposals): This channel is for more substantial feedback that has the potential to influence smart contract adjustments or changes to the protocol/token. Please note that GIPs are not restricted by templates, but should focus on impactful proposals rather than minor tweaks or user experience refinements.
- Informal-Discussion Channel: Engage in open conversations related to governance in this channel. Share your ideas for grants and GIPs, or seek clarifications on governance processes and principles.
Please note that any other type of posts will get deleted and the user will be banned. Ideas and feedback that pertain to minor changes or tweaks belong in the ideas-feedback channel. If in doubt, please post in the latter.
Snapshot (On-chain Proposals)
Once a proposal gains consensus and refinement within the Forum on Discord, it can transition to the Snapshot platform for broader community consideration. Here’s an overview of how Snapshot works in this regard:
- Submission Process:
Admins will curate and refine proposals before presenting them on the Snapshot-submissions channel. This channel serves as a notification center for all server members, providing visibility into the upcoming proposals. - Voting with $GNS Tokens:
Each member’s voice matters. Utilize your $GNS tokens on Arbitrum/Polygon to cast your vote on Snapshot proposals. Remember that this is a proto-governance phase, meaning there’s no direct on-chain enforcement. This means that only admin-approved proposals will be the ones moving forward.
Your participation and input are crucial as Gains evolve their governance framework. One $GNS token equals one vote, so make your voice heard and contribute to shaping the collective future.
Risks
Prior to the updates that were made in December 2022, gToken vaults had problems in terms of:
- Risk management. The risk was not distributed evenly across the vault structure. If there was a run on the bank (the vault goes uncollateralized), those who withdrew last would be left handling the majority of the losses.
- Efficiency. When the vault collateralization reached 130% and the protocol began buying and burning GNS, it was often frontrun when the buys were substantial. This means that an individual could accumulate in anticipation of the protocol’s market buy and then sell it to gTrade for an arbitrage profit.
- Incentives alignment. There are no incentives for stakers to take on the risk of supplying extra liquidity in times when the vault goes undercollateralized.
- Composability. Liquidity contributions are not tokenized, meaning that when stakers deposit DAI they do not get a “receipt” token that they can use elsewhere to access extra liquidity.
The smart contracts are audited, and there are a number of risk protections in place, such as a maximum allowed collateral per trade of 75,000 DAI, a 900% max win, and strict open interest limits.
Security
The gDAI vault contract is upgradeable in order to minimize the impact on traders and stakers if any vulnerability was found. In order to protect stakers from upgrades that could be deemed harmful, all upgrades go through a 14-day timelock contract. This timelock duration will always be longer than the amount of time given to users to withdraw their assets.
When it comes to mutable state variables, the timelock duration will vary from 3 to 14 days.
The following roles are in place:
- GTokenAdmin: no timelock – used for urgent actions that do not impact user funds
- GTokenManager: 3-day timelock – used for non-urgent actions that do not impact user funds
- GTokenOwner: 14-day timelock – used for non-urgent actions that could impact user funds
Bridge
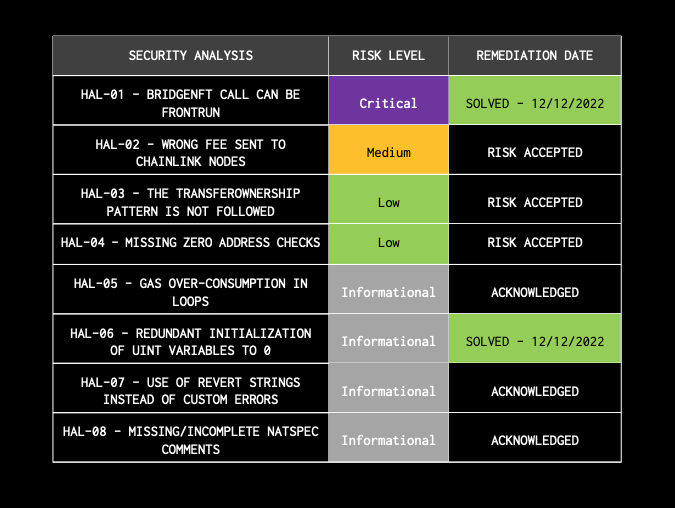
Gains’ bridge is rate-limited to prevent any exploit to the messaging protocol from significantly impacting the supply of either the GNS token or the GNS NFTs. This solution was suggested by Halborn’s security audit.
Audits
All recommendations and security fixes were mitigated and resolved by the team with the exception of some issues where the team accepted the risk, such as:
- Wrong fee sent to Chainlink nodes. It is recommended by Chainlink to set a fixed LINK fee based on the blockchain and type of oracle used (usually 0.1 LINK). However, the Gains Network team calculates this fee based on the contract’s balance, which means that the fee is variable instead of fixed
- Gains Network accepted the risk and stated that “we will send enough to the contract so that divided by 1,000 it represents the amount we want, and then we will refill it every few months. This pattern allows everyone to send LINK to the contract in a decentralized manner.”
- The “transferOwnership” pattern is not followed. The ownership of the gToken contract may be lost if the nominated account is an uncontrolled account (losing access to all functions with the “onlyOwner” modifier
- Transfer to the zero or null address is not checked.
Gains Network also announced a Bug Bounty listing on Immunefi in March 2022 with rewards of up to $100,000
- Smart contract rewards
- Critical – up to $100,000
- High – $50,000
- Medium – $25,000
- Low – $10,000
- Websites and application rewards
- Critical – $50,000
- High – $25,000
- Medium – $12,500
- Low – $5,000
Economic Attack Vectors
Previous to the release of gTrade v6.1, there was the possibility of exposing the protocol to oracle manipulation attacks. This release mitigated the consequences of such scenarios by adding a dynamic spread to the reported oracle price.
The goal of this measure goes beyond preventing manipulation risk and also allows the platform to add trading pairs with lower liquidity. Gains assigns a specific dynamic spread to each trading pair and ensures that the price impact will depend on the direction of the trade (long or short). This way, each pair will have two parameters, the 1% depth above (for longs), and the 1% depth below (for shorts).
Team
The team consists of 13 members who are anonymous. Seb, the founder, is active on Discord, along with a few team members.
- Seb (Founder, Full-stack dev, Strategy)
- Nathan (Full-stack dev, Management)
- Crumbs (Full-stack dev)
- Dreamersnat (Frontend dev)
- Konrad (Frontend dev)
- Drew (Backend dev)
- Uri (Full-stack dev, Research)
- Sam (Biz Dev, Partnerships & Connections)
- Lunaman (Biz dev)
- Ross & Kenji (Social media)
- Jim (Designer)
- Alex (Research)
- Vesnushki (Moderator)
Seb, the founder, worked alone on the project for the first year of development. As the project grew with further development and marketing, he began growing the team to achieve its long-term vision as efficiently and rapidly as possible.
Project Investors
There was no VC funding. The GFARM2 (Gain’s initial token) tokens were fairly distributed in an ETH pool and a GFARM2/ETH LP pool on Ethereum.
Additional Information
Partnerships
Gains Network has integrated and partnered with other protocols and projects to enhance its DEX performance and experience for users.
Accessibility
- DeBank – Web3 portfolio tracker.
- gTrade’s portfolio tracking.
DEX Improvement
- Giddy DeFi – Self-custody recoverable crypto wallet.
- Aims to onboard a new wave of crypto users by integrating GNS staking directly into its wallet front end.
- Trader Joe – Decentralized trading.
- GNS/ETH pool bringing GNS Liquidity to Arbitrum.
- Gamma Strategies – Active liquidity management and market-making strategies
- Improved liquidity on GNS/DAI pools.
- SperaxUSD – Liquid staked stablecoin (USDs) and DEX liquidity manager (Demeter)
- gDAI/USDs pool improves gDAI composability and liquidity.
- Purchase gDAI using any asset listed on Demeter.
- Beefy Finance – Multi-chain Yield Optimizer.
- Auto-compounding vaults for GNS.
- InsurAce Protocol – Multi-chain decentralized cover.
- Insurance coverage for smart contracts vulnerabilities.
- KyberSwap – Multi-chain exchange and aggregator.
- Trade gDAI and improve liquidity for gDAI pools.
- 0VIX Protocol – First veTokenomics lending market with dynamic interest rates.
- Boosted yield + $gDAI vault returns via strategies.
- Voyager – Cross-chain swap.
- Buy/Swap $GNS across 10 different blockchains.
- Chainlink – Oracle and mass data services
- First hybrid architecture that combines the widely used Chainlink Price Feeds with their own custom-built Chainlink decentralized oracle network (DON) to provide real-time, aggregated prices for their leveraged trading products.
- ImmuneFi – Bug bounty platform for blockchain.
- Bug bounties from $10k to $100k depending on threat levels.
- Silo Finance – Risk-isolating money markets on Ethereum & Arbitrum.
- Lend, borrow, or collateralize GNS holdings.
- QiDAO
- An open-source and non-custodial stable protocol for extracting value out of priced assets.
- Bitkeep Wallet
- Web3 Wallet.
- Quickswap
- Next-gen DEX.
- DefiLlama
- Open and transparent DeFi analytics.
- MUX Protocol
- One-stop access for leveraged trading.
- Perpy Finance
- Web3 Social Trading Protocol on Decentralized Perpetual Exchange.
- Silo Finance
- Risk-isolating money markets on Ethereum & Arbitrum
- Pendle Finance
- Pendle is a permissionless DeFi yield-trading protocol, currently built on the Ethereum blockchain, where users can execute various yield management strategies.
- Ramses Exchange
- Native liquidity layer & decentralized exchange on Arbitrum.
- Fluidity Money
- Fluidity is super powering cryptocurrencies – rewarding you yield when you use them.
- Crypto.com Exchange
- A cryptocurrency exchange.
FAQ
- Why can’t I immediately withdraw my funds?
- For the security of the vault, and to prevent stakers from front-running PnL changes. An epoch-based withdrawal system has been implemented to provide a level playing field for all stakers
- What determines when I can withdraw my funds?
- The collateralization ratio of the vault, was determined using the snapshotted total PnL from the beginning of the current epoch.
- Depending on the ratio, you can withdraw your funds in 1 (ratio > 120%), 2 (> 110%), or 3 epochs.
- Why do we need to wait up to 3 epochs to withdraw?
- Because it increases guarantees of liquidity availability for traders and removes risks related to anticipating new epoch open PnL updates.
- Can I withdraw my funds anytime after my withdrawal?
- NO! This is important. You may only withdraw your funds during your designated withdrawal epoch. If you miss the window, you need to make a new request.
- Why use epochs?
- Epochs are necessary because we can’t have the open trades PnL feed in real-time due to practical reasons (API calls, gas costs).
- Can I unlock my gDAI anytime after my unlock date?
- Yes, you may unlock gDAI for any gNFT you own anytime after the unlock date.
- I can’t open a trade with 10 DAI – Is there a minimum position size?
- The minimum total position size is 1500 DAI, which is calculated by your collateral multiplied by your leverage. This means if you would like to use a position size of 10 DAI, you should use a leverage of 150x (10*150=1500). You can use lower leverage by using higher collateral, for instance, you should use 300 DAI collateral for 5x leverage (300*5=1500).
- Forex / Stocks says “Closed”. Why?
- Unlike crypto markets forex and stock markets are not open 24/7. Please refer to Forex Trading and Stock Trading.
- The price hit my TP/SL/LIQ but did not execute. Why?
- As there is a slight delay from when an NFT bot executes an order to the response from the DON the price may have very briefly crossed into an executable range but returned to a non-executable range by the response time (if it stayed less than 10 seconds in the zone and the chain was congested for example). In the coming 6.3 update, there will be a lookback to ensure no executions are missed.
- Can I go into debt?
- No, you cannot go into debt. You can only lose the collateral you stake. Naturally, if your position has reached a position where it must be liquidated (-90%) your loss will be all of your collateral. Otherwise, your gain or loss will be what is returned to you. Do not put up more collateral than you could afford to lose. Stop Losses and Take Profits can be used to help ensure you close your position where you like.
Community Links
- Website: https://gainsnetwork.io/
- Docs: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/GainsNetwork_io
- Telegram: https://t.me/GainsNetwork
- Discord: https://discord.com/invite/gains-network
- Referrals: https://gains.trade/referrals
- Medium: https://gainsnetwork-io.medium.com/
- Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/GainsNetwork
- Contract addresses: https://gains-network.gitbook.io/docs-home/what-is-gains-network/contract-addresses