Overview
Particle Network is a Layer 1 (L1) blockchain designed to unify all chains through Universal Accounts, addressing the fragmentation of users and liquidity across different blockchain networks.
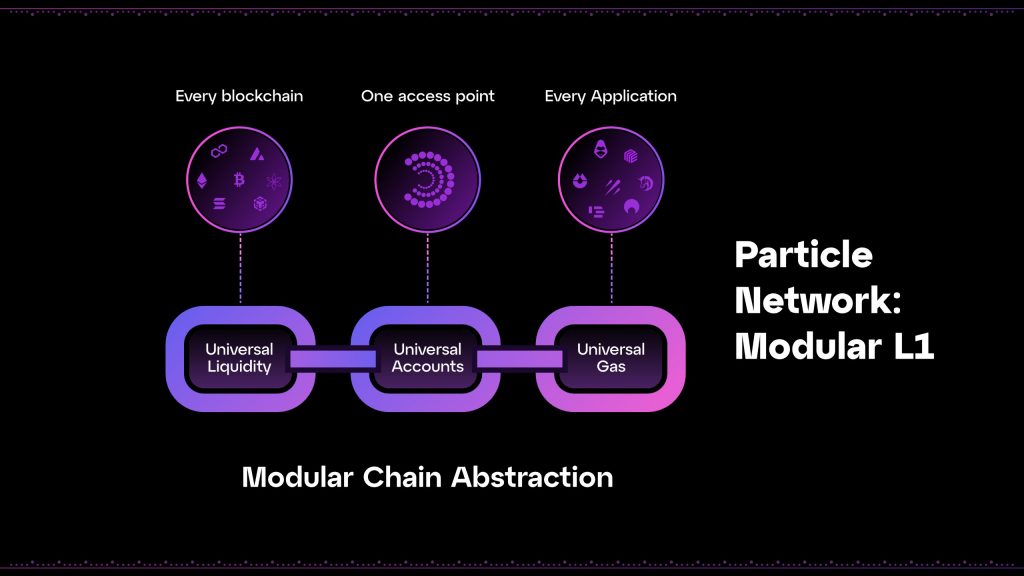
Particle Network’s technology platform is built on a L1 architecture, utilizing the Cosmos SDK for intrinsic modularity. This architecture allows it to retain sovereignty while outsourcing critical functions such as validation and data availability to specialized ecosystem actors. The network enables features such as Universal Accounts, Universal Liquidity, and Universal Gas, which simplify the user experience across blockchain ecosystems.
Why the Project was Created
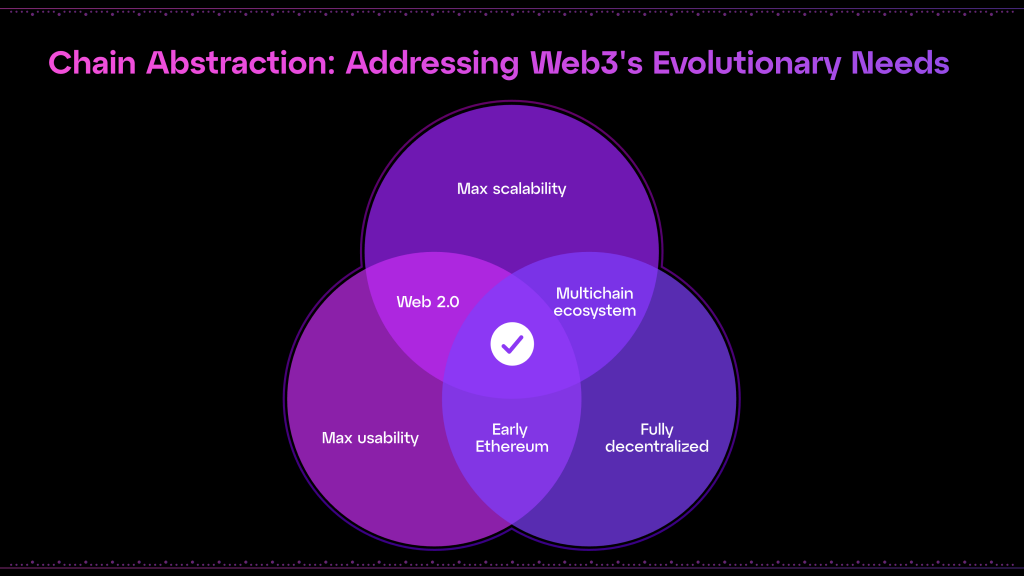
The creation of Particle Network aims to address one of the most significant challenges in the current Web3 ecosystem: fragmentation. This fragmentation manifests as a dispersion of users and liquidity across various isolated blockchain networks, each operating with its own standards, tokens, and protocols. This not only complicates user interactions but also suppresses the industry’s growth by creating inefficiencies that drain value and hamper the scalability of a potentially multi-trillion-dollar market.
Fragmentation in Web3 results in several core inefficiencies. First, there are technological inefficiencies caused by incompatible blockchain networks which necessitate redundant development efforts and create barriers to seamless user experience. Second, there are incentive inefficiencies where a rapid proliferation of new chains leads to significant funds being allocated to bootstrap these ecosystems; funds that often do not yield proportional returns in terms of user adoption or ecosystem vitality. Lastly, the ecosystem inefficiencies emerge from a lack of creativity and innovation, with developers repeatedly creating similar foundational products like AMM DEXs or lending markets across multiple platforms rather than innovating new solutions that could attract users.
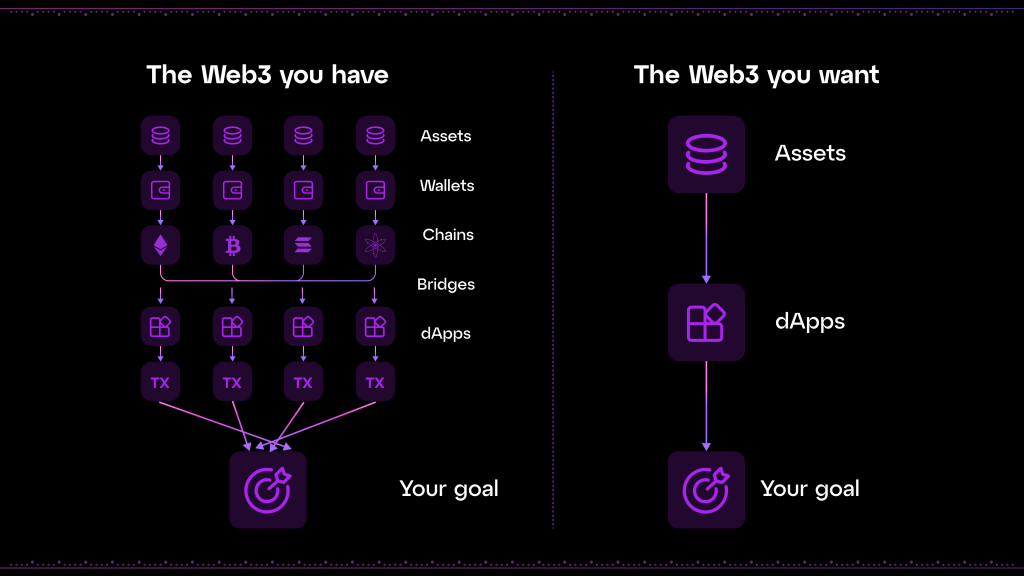
Particle Network’s approach to solving these problems is through chain abstraction. Chain abstraction simplifies the user experience by allowing them to interact with multiple blockchain products and assets without worrying about the complexities of multi-chain interactions. It integrates critical functionalities such as Universal Accounts, liquidity, and gas management across chains. This not only promises to enhance the user experience by eliminating the need for multiple wallets and managing different types of gas tokens but also aims to unify liquidity. On the one hand, users can perform transactions across chains using a single wallet and potentially a single type of token for transaction fees, thus reducing the cognitive and operational overhead. On the other hand, builders can deploy their applications where they fit best, leveraging the strengths of each chain and not having to worry about users or liquidity not being able to reach them.
By implementing chain abstraction, Particle Network addresses Web3’s inefficiencies in several ways. For developers, it reduces the need to replicate efforts across multiple chains, allowing them to focus on creating unique and innovative products rather than re-building the same solutions for different platforms. For users, it streamlines interactions within the Web3 space, making blockchain technology more accessible and less daunting to a broader audience. This could lead to increased adoption as the barrier to entry lowers and the user experience improves.
The Vision of Particle Network
Particle Network’s journey began with a clear focus on simplifying interactions within the Web3 ecosystem. Initially launched as a Wallet Abstraction tool for developers, the platform leveraged Multi-Party Computation (MPC) with Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) and social logins to enable the creation of non-custodial, decentralized application (dApp)-embedded wallets. As the concept of account abstraction (AA) emerged and became integral to Web3, Particle Network identified an opportunity to evolve its services to match the advancing landscape, thus introducing the Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS). This adaptation was aimed at providing developers with a seamless, flexible, and programmable environment, facilitating an enhanced user experience through upgraded account structures.
The success of these initial offerings, evidenced by over 900 integrations and more than 17 million activated wallets, underscored a prevalent issue in the Web3 space, the fragmentation of users and liquidity across multiple blockchain networks. Recognizing this as the largest user experience challenge within Web3, Particle Network launched its L1 blockchain solution to pioneer the next level of integration and simplicity through chain abstraction.
Chain abstraction is essentially about simplifying and unifying the Web3 experience. Traditional blockchain interactions require users to manage multiple wallets and assets across different chains, navigate the complexities of bridging and contend with various gas tokens for transactions. Particle Network’s chain abstraction aims to dissolve these barriers by allowing users to interact with any dApp or asset across any blockchain without the usual hassle.
Particle Network’s modular L1 plays a critical role in enabling such fluid Web3 interactions through three core services:
- Wallet Abstraction: By eliminating the need for multiple wallets and separate balances across various chains, Particle Network creates a singular interaction point—the Universal Account. This account serves as a hub for users’ activities across the multi-chain ecosystem, consolidating their experience into one streamlined interface.
- Liquidity Abstraction: This feature unifies liquidity across all networks, enabling seamless asset transactions through atomic swaps and automated processes. It allows users like Alice to easily move and utilize their assets anywhere in the Web3 ecosystem without the typical barriers or delays.
- Gas Abstraction: Particle Network allows users to pay for transactions with any token, sourced from any blockchain, thereby removing the need to acquire and manage multiple chain-specific gas tokens. This significantly reduces the complexity and cost of operating across different blockchain networks.
In summary, Particle Network’s vision is centered on making Web3 accessible, intuitive, and unified for all users. By addressing the key challenges of fragmentation and complexity, Particle Network aims to accelerate the growth and adoption of Web3 technologies, making them as straightforward and user-friendly as possible.
History and Background
Established in 2022, Particle Network initially launched as a Wallet Abstraction service provider. This service enabled users to create smart contract wallets linked to Web2 social accounts, usable within dApp-embedded interfaces. Since its inception, Particle Network has seen significant adoption, with over 17 million wallet activations, 10 million UserOperations, and integration into more than 900 decentralized applications (dApps). Today, Particle encompasses a larger vision beyond being a wallet provider, operating as a Layer 1 that will power chain abstraction through core technological features such as Universal Accounts, Universal Liquidity, and Universal Gas.
Particle Network Technology
Modular L1
Particle Network’s modular L1 powers chain abstraction by enabling users to maintain a single address and balance across every chain and to pay for transaction fees in any token. This is possible through the exclusive role of the L1 to coordinate the Universal Accounts. Additionally, this L1 solution leverages key modular nodes to secure the network and manage its decentralized operations, including transaction validation and data availability.
This modular L1 enables three core functionalities: Universal Accounts, Universal Liquidity, and Universal Gas.
Universal Accounts
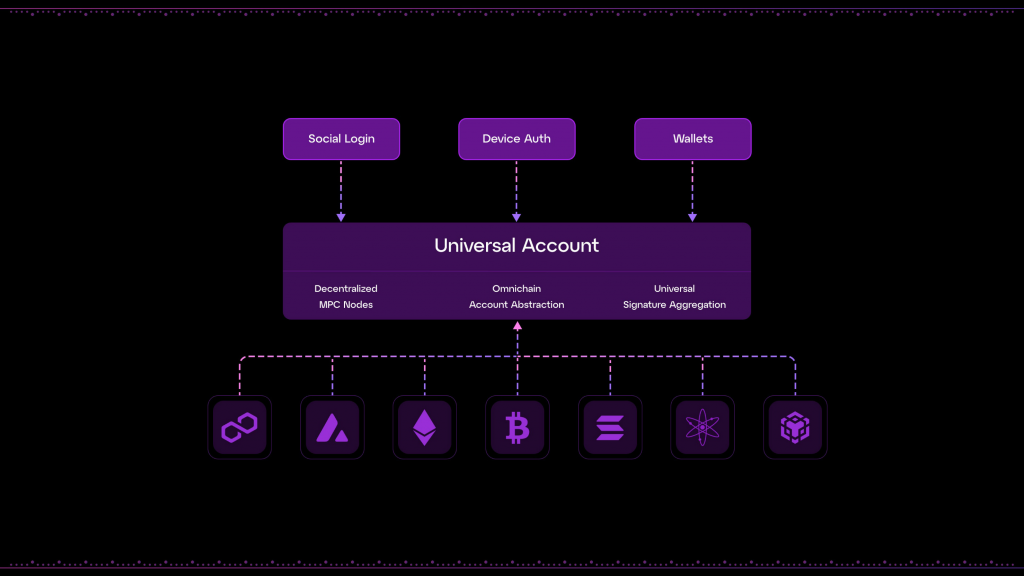
Particle Network introduces Universal Accounts as a main component of its chain abstraction strategy, revolutionizing how users interact across the diverse landscape of the Web3 ecosystem. These accounts provide a single, consolidated interface for users, merging numerous blockchain interactions into one seamless experience.
Users of Universal Accounts benefit from having one address and one balance that can be used across all supported blockchains, whether EVM-based or otherwise. This addresses the common pain point in Web3 where users must manage multiple addresses and balances across different networks.
The use of Universal Accounts simplifies the user experience, making it blockchain-agnostic. This is achieved by leveraging Particle Network’s Universal Liquidity technology, which automatically handles the execution of atomic cross-chain transactions. This technology pools funds from a user’s balance across various chains to fulfill transaction requirements seamlessly.
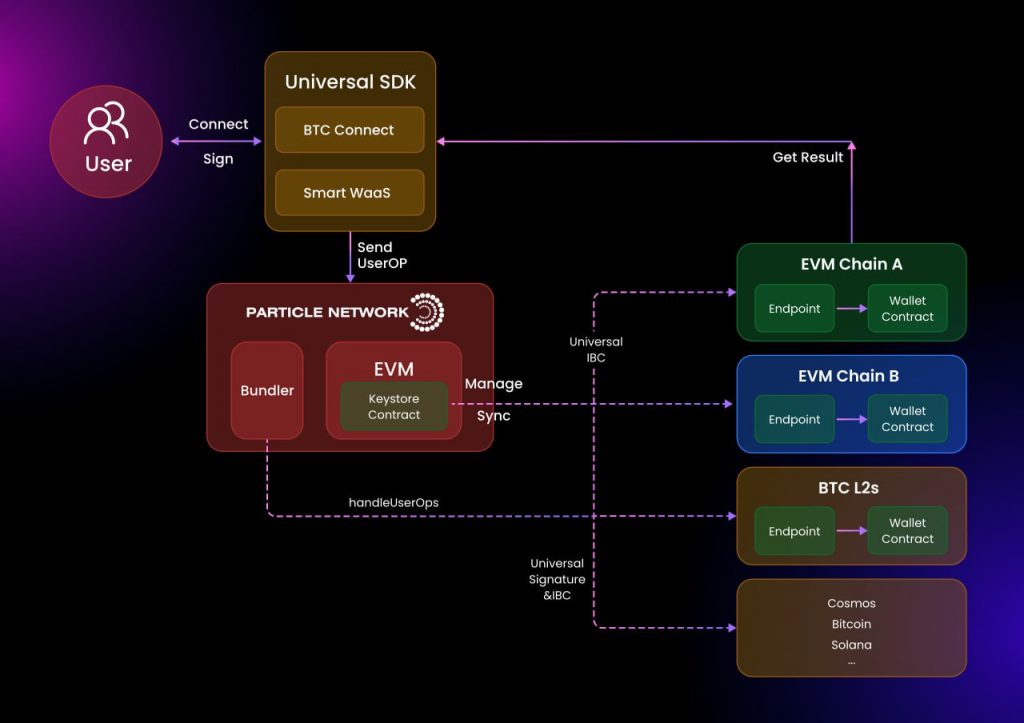
At the heart of Universal Accounts is the Universal Liquidity technology, which facilitates the atomic execution of transactions across chains. Particle Network acts as the settlement layer for these transactions, with its globally distributed network of Modular Nodes managing the accounts and coordinating cross-chain interactions. These nodes play a crucial role in bundling, relaying, and verifying transactions across the network.
Universal Accounts are implemented as ERC-4337 smart account implementations linked to an Externally Owned Address (EOA). This setup allows for flexible integration with various login methods, including social logins through Particle Network’s Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service, or more traditional Web3 wallets. This versatility extends to native Bitcoin wallets through services like BTC Connect, further broadening the accessibility and usability of Universal Accounts.
Here’s an example illustrating the functionality of Universal Accounts:
- Initial Interaction: Alice discovers a Play-to-Earn dApp hosted on Arbitrum, which utilizes Particle Network’s Universal SDK to enable Universal Accounts.
- Seamless Transactions: As Alice interacts with the dApp, her assets, originally native to Polygon, are automatically used for gameplay without her needing to manually bridge them. This process is executed atomically, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted user experience.
- Cross-Chain Functionality: After earning tokens from the game, Alice purchases an NFT for her friend Bob’s birthday. The NFT, located on Optimism, is seamlessly transferred to Bob’s Universal Account without Alice having to manage different chain interactions or tokens.
- Further Interactions: Bob then uses his Universal Account to take out a loan against the NFT on Solana, and subsequently purchases a meme Bitcoin Ordinal, all within a few minutes and without switching accounts or handling different currencies.
Universal Liquidity
The functionality of Universal Liquidity enables seamless and atomic interaction across different blockchain networks, fundamentally supporting the concept of Universal Accounts. This functionality is key to unifying balances and simplifying transactions across the diverse landscape of the Web3 ecosystem.
Universal Liquidity enables the atomic movement of funds across different blockchains as part of relevant cross-chain transactions. This capability is crucial for maintaining a cohesive user experience, similar to interacting within a single-chain environment despite engaging with multiple chains.
In scenarios where transactions are executed on chains where the user does not have funds, Universal Liquidity automatically pulls the required liquidity from the user’s balance on other chains. This process is managed without the user having to manually bridge funds or handle complex token swaps, as these are executed automatically.
Furthermore, transactions can be facilitated using any token that the user holds in his Universal Account, coordinated and settled seamlessly through Particle Network. This level of flexibility significantly reduces the friction typically associated with needing specific tokens for gas and transaction fees on different blockchains.
Universal Liquidity operates through an infrastructure comprising Particle Network’s Modular Nodes and a Decentralized Messaging Network. These elements work in concert to:
- Coordinate and settle cross-chain transactions.
- Automatically execute operations across chains, allowing users to utilize a universal balance that can be accessed and spent on any blockchain.
Integrating Bundler Nodes within this framework is particularly critical. These nodes facilitate the seamless execution of transactions by handling the complex logistics that would typically require manual user intervention, such as bridging assets or swapping tokens to meet network-specific requirements.
The practical implementation of Universal Liquidity is deeply integrated with the use of Universal Accounts. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
- Onboarding and Account Setup: When a user onboards to a dApp that integrates Particle Network’s Universal SDK, their existing wallet (be it MetaMask, Keplr, Particle, or UniSat) is designated as a signer for a Universal Account. This setup process is streamlined to ensure ease of use right from the start.
- Funding and Usage: Users can fund their Universal Account and immediately begin interacting with the dApp. Importantly, this account, once funded, can be utilized across all compatible applications on different chains without the need for additional steps from the user, such as bridging assets between chains.
- Seamless Cross-Chain Interaction: Universal Liquidity ensures that users can engage with multiple dApps across various blockchains as if they were operating on a single chain. This is accomplished by automatically managing and deploying the user’s assets wherever necessary, guided by the user’s activities and transaction requirements.
Through Universal Liquidity, Particle Network improves the functionality of Universal Accounts and simplifies dramatically the user experience by automating the technical complexities of cross-chain interactions.
Universal Gas
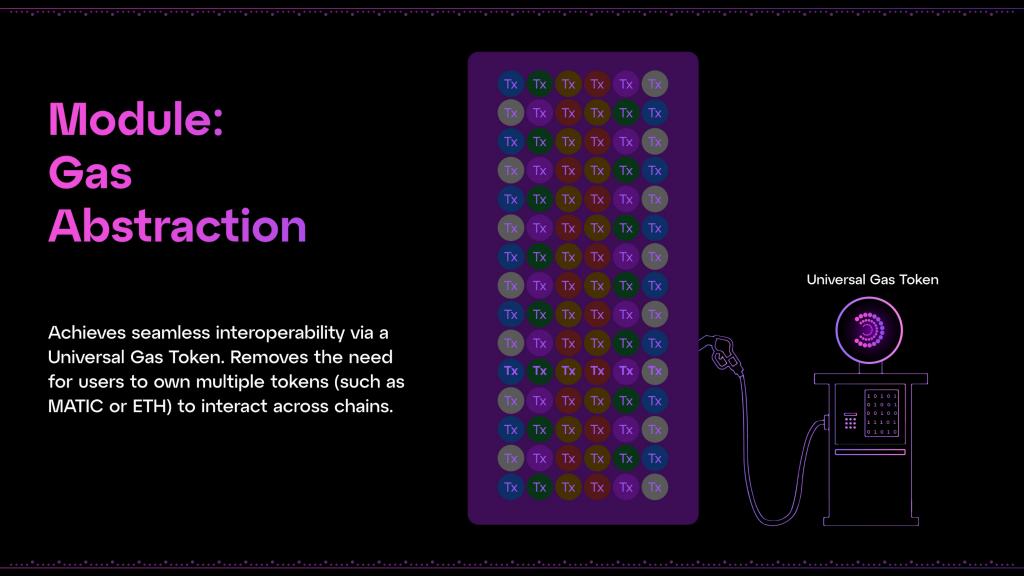
Another important component of Particle Network is the Universal Gas specifically designed to address the complexities associated with gas payments in a fragmented blockchain ecosystem. Universal Gas, also known as gas abstraction, reshapes how transaction fees are handled across different blockchains, enhancing user convenience and flexibility.
Universal Gas fundamentally changes the traditional mechanism where transactions on any blockchain network require fees to be paid in the native token of that network. With Universal Gas, users can pay transaction fees using any token from any chain (paying gas on Base with $USDC from Arbitrum), irrespective of the network on which the transaction is executed. This flexibility is a significant departure from conventional practices, where users must manage and hold various tokens to interact across multiple blockchain platforms.
When a user initiates a transaction through a Universal Account, Particle Network’s dApp-embedded modal, enabled by the Universal SDK, prompts the user to select the token they wish to use for paying gas fees. This selection can include tokens from the same chain on which the transaction is being executed or from external chains. The chosen token is then automatically utilized to cover the transaction fees.
The integration of Universal Gas with Universal Accounts simplifies the transaction process by eliminating the need for users to manually bridge or manage tokens across different chains. This seamless integration allows users to focus on their activities rather than the logistics of token management.
All gas payments are eventually settled on the source and target chains involved in the transaction. A portion of the fee is automatically converted into Particle Network’s native token, $PARTI, to settle the transaction within the Particle Network ecosystem. This automatic conversion further simplifies the user experience by managing the complexities of cross-chain fee payments internally.
Wallet Abstraction
Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service
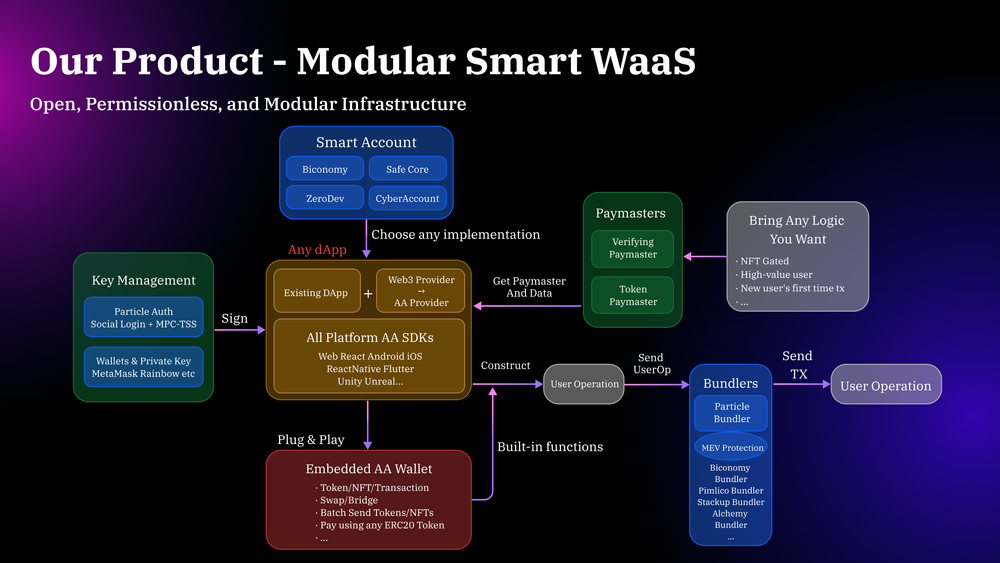
Particle’s main offering and innovation which is also the main entry point to Universal Accounts. The Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS) combines ERC-4337 account abstraction (AA) with innovative wallet solutions to facilitate dApp integration and improve flexibility for developers. This integration provides a robust framework for developers to incorporate advanced Web3 functionalities directly into their applications, optimizing user experience and security.
The Wallet-as-a-Service model simplifies the integration of blockchain functionalities into various platforms by embedding wallets directly into user interfaces. This eliminates the need for separate wallet applications like MetaMask to authorize transactions or sign messages. Instead, users can perform these actions within the platform they are using, simplifying the process and enhancing user engagement.
Additional features of the WaaS include:
- Social Login Integration: Allows users to create or access their wallets via social logins, bridging the gap between Web2 experiences and the Web3 ecosystem. This feature is crucial for onboarding users unfamiliar with blockchain technologies, as it bypasses the complexities of private key management and wallet setups.
- Enhanced Security and Autonomy: Particle Network employs Multi-Party Computation Threshold Signature Schemes (MPC-TSS), which enhance security by dividing the responsibility of signing transactions among multiple parties. This means no single party ever possesses the complete private key, thus distributing risk and enhancing security while ensuring users maintain control over their assets.
AA Stack
Particle Network’s approach to Smart WaaS is distinguished by its native integration of account abstraction, providing a flexible and powerful toolkit for developers. This modular system allows developers to seamlessly integrate WaaS with AA, regardless of the application’s complexity or backend architecture.
- Native AA Integrations: These integrations simplify the use of smart accounts, providing developers with familiar transaction structures, account management, and building processes, all handled seamlessly by Particle’s SDK.
- Cross-Compatibility: Particle’s commitment to modularity and intrinsic cross-compatibility ensures that developers are not restricted to a single provider within the ecosystem. This allows for the selection of different smart account implementations, Bundlers, or Paymasters that best fit the project’s needs.
Also, Particle’s AA SDK can be employed in various configurations to suit different developer needs:
- Account Management and Transaction Sponsorship: Developers can use Particle’s SDK for user operation (UserOp) building and sponsorship, pushing transactions through external Bundlers and Paymasters.
- Flexible Signer Options: The externally owned account (EOA) derived from Particle’s WaaS can act as the Signer in different smart account implementations, offering further customization for developers.
WaaS Components
In addition to the AA stack, some additional components work in synergy to create the WaaS product. Namely, Particle Auth and Particle Wallet.
Particle Auth
At the core of Particle Network’s WaaS is Particle Auth, which handles the onboarding process through social logins. This central component manages authentication across the Particle Network ecosystem, routing all social logins—such as Google, Twitter, email, phone, and GitHub—through its system. Particle Auth integrates seamlessly with existing account systems via custom JWT-based authentication, thereby enabling the creation of on-chain accounts linked to users’ social identities. Available across multiple platforms via robust SDKs, Particle Auth provides developers with essential tools to facilitate user interaction within the Particle Network’s WaaS environment.
Particle Wallet
Particle Wallet extends the functionality of Particle Auth by providing a native, application-embedded wallet interface that supports the accounts generated through social logins or external Web3 wallets via Particle Connect. This wallet interface features a range of standard wallet interactions that are accessible directly within the application or through web and mobile platforms (iOS and Android). Developers can integrate the Particle Wallet into their applications through a customizable on-screen popup, ensuring a smooth and integrated user experience. This component not only supports accounts created via Particle Auth but also facilitates interactions with external blockchain networks through Particle Connect.
Modularity & Security
The modular nature of Particle’s Smart WaaS is particularly beneficial in the nascent field of AA, where developers may prefer different components based on specific project requirements. This flexibility ensures that Particle’s solutions are adaptable and developer-friendly, accommodating a wide range of use cases and customization levels.
Security is a paramount feature of Particle’s Smart WaaS, highlighted by its advanced MPC-TSS setup:
- 2/2 Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS): This approach involves splitting the key into two separate shares, with each share securely stored and incapable of revealing the full key even with both shares. The shares remain independently stored and accessed individually to each generate signature fragments, which collectively authenticate a transaction. The full private key remains distributed forever. This method significantly enhances security by ensuring no single point of failure.
- Master Password and Key Restoration: Users have the option to create a Master Password to encrypt their local key fragment. This encrypted key can be safely stored and used to restore wallets across devices, maintaining security and user control.
In summary, Particle Network’s Modular Smart WaaS provides a comprehensive, secure, and flexible solution for integrating advanced Web3 functionalities into applications.
Particle Bundler
The Bundler is a component designed to streamline the transaction process on Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) networks through enhanced account abstraction. As an open-source ERC-4337 Bundler, it acts as a transaction aggregator that collects individual UserOperations from a specialized mempool (short for memory pool; a staging area where transactions go before being included in a block), bundles them together, and submits them as a single transaction to the network. This process not only simplifies transactions but also optimizes the performance and reliability of smart contract interactions using the ERC-4337 standard.
These are the advantages of Particle’s Bundler:
- Seamless UserOperations: The Particle Bundler enhances the transaction process by managing the persistence of UserOperations, Smart Account Nonce management, and the automatic batch sending of User Operations. These features collectively improve the accessibility and user-friendliness of ERC-4337, making it more approachable to a wider audience.
- Smart Ops: Recognizing the need for stable and reliable operational features, the Particle Bundler includes functionalities such as Bundler Signer configuration, automatic recharging, blocking and recovery, and monitoring alerts. These tools enable easy management and facilitate the automatic expansion of services, simplifying the deployment process on new chains to a single command with minimal configuration. This efficiency allows support for a new chain to be implemented within just five minutes.
- High Performance and Stability: Engineered for high performance, the Particle Bundler can handle demanding workloads efficiently, ensuring that transactions are processed swiftly and effectively. Its robust architecture provides a reliable platform even under challenging conditions, making it a cornerstone for developers and users needing dependable transaction processing capabilities.
Also, the Bundler offers these features:
- Standard and Configurable RPCs: The Bundler supports all standard RPCs and offers customizable options for RPCs and Signers, adapting to various user needs and preferences.
- Multi-Chain Support: It is equipped to work with any chain, enhancing its utility across the diverse landscape of blockchain technologies.
- UserOp Concurrent Handling: This feature allows for the simultaneous processing of multiple UserOperations, enhancing throughput and efficiency.
- Built-in Gas Price Oracle and Multi-Bundler Signers Manager: These features ensure that transactions are executed at optimal gas prices and manage multiple Bundler Signers to maintain efficiency and security.
- Auto-fulfill Bundler Signers’ Balance and Auto-retry for Failed Transactions: These mechanisms ensure continuous operation and reliability, automatically replenishing Signer balances and retrying failed transactions to maintain service continuity.
- MEV-Resistant Transactions: The Bundler is designed to return the correct transaction even when potentially affected by Miner Extractable Value (MEV), providing an additional layer of transaction security.
- Rapid Deployment on New Chains: The Bundler’s design allows for quick and easy deployment to new chains, a critical feature for maintaining agility in the fast-evolving blockchain ecosystem.
The Particle Bundler stands out as a high-performance, infinitely scalable implementation of the ERC-4337 standard, providing a comprehensive solution that addresses the needs of developers and users in the multi-chain Web3 era.
Omnichain Paymaster
Particle Network’s Omnichain Paymaster is an underlying component of the network’s account abstraction ecosystem, designed to simplify and improve the experience of managing gas payments across multiple chains. Integrated with WaaS, the Paymaster facilitates over 500,000 UserOperations across various networks, streamlining the transaction process for end-users.
Paymaster is an important part of the Omnichain AA ecosystem since it provides several appealing benefits:
- Multi-chain Usage: Developers can deposit $USDT into the Paymaster to sponsor UserOperations across all EVM-compatible chains, enabling a broad, versatile approach to handling transaction fees.
- Adaptable Sponsorship Logic Using Webhooks: The Paymaster utilizes webhooks to allow developers precise control over which UserOperations are sponsored. This includes pre-signature and post-signature hooks, which provide critical checks and balances to ensure that only desired transactions are processed.
- Monitoring and Expiration Times: Developers can actively monitor the transactions they sponsor and set expiration times for Paymaster signatures. This feature ensures that unused signatures automatically lapse after a certain period, enhancing security and control over transaction sponsorships.
The use of the Omnichain Paymaster not only reduces the cognitive load on users but also boosts the overall usability and appeal of dApps integrated with Particle Network.
WaaS Key Differentiators
The Modular WaaS is designed to provide a standout experience in areas such as developer and end-user experience, security, and private key management. This section highlights the key differentiators that set Particle Network’s WaaS apart from other solutions in the market.
1. Private Key Management
One of the primary areas where Particle Network excels is in the management of private keys, which is crucial for maintaining user autonomy and security.
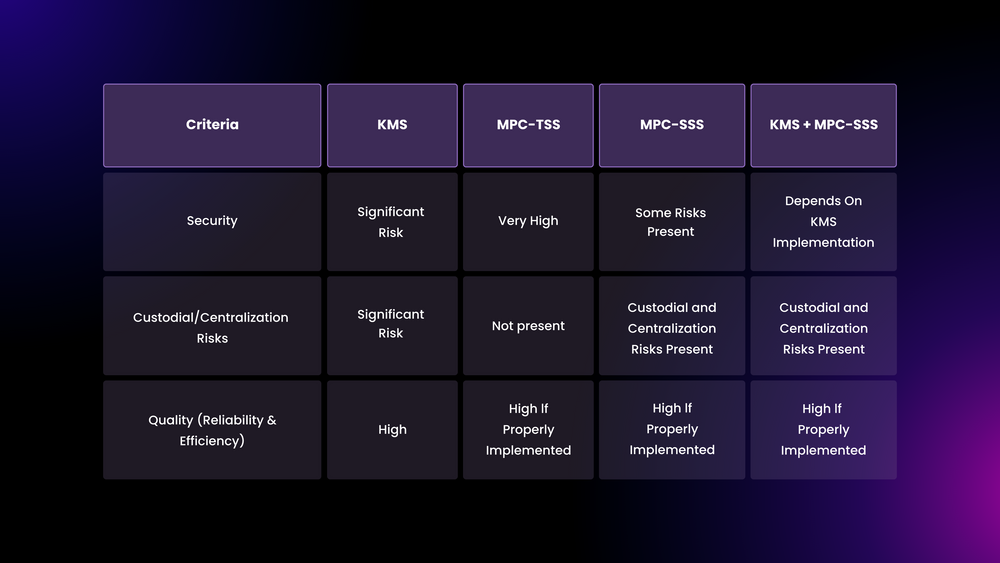
- Multi-Party Computation with Threshold Signature Scheme (MPC-TSS): This advanced method allows multiple parties to collaboratively compute functions or sign transactions without any single party having access to the complete secret. Particle Network specifically focuses on and utilizes MPC-TSS, ensuring that:
- Security and Non-Custodianship: No single entity controls the entire key, maintaining user control and security. Transactions can be signed collaboratively without exposing the full key, making it an ideal non-custodial solution that balances security with efficiency.
- Key Management Service (KMS): KMS solutions store and manage cryptographic keys, typically encrypting private keys as a whole. While they offer straightforward operations, there are significant trade-offs:
- Custodial Risks: If configured as custodial, KMS may allow providers to retain ultimate control over keys, contradicting claims of non-custodianship.
- Centralization Risks: Dependence on a single KMS provider introduces a single point of failure, potentially leading to service discontinuation or compromised security.
- Shamir’s Secret Sharing (SSS): SSS distributes a secret among a group, requiring a quorum to reconstruct the secret for any signature to occur. This method increases security but also presents risks:
- Attack Vectors: Frequent reassembly of the secret for signatures provides multiple opportunities for attackers to compromise the secret, especially at reconstruction points.
- Multi-Party Computation with Shamir’s Secret Sharing (MPC-SSS): This combines SSS with distributed computations, enhancing security by requiring multiple shares to perform actions without revealing the entire secret. However, this method still involves recovering private keys on the client side, exposing users to potential risks associated with SSS.
- KMS + SSS: Combining KMS with SSS offers convenience but at the cost of increased custodial and centralization risks, making it less desirable than standalone SSS or more secure methods like MPC-TSS.
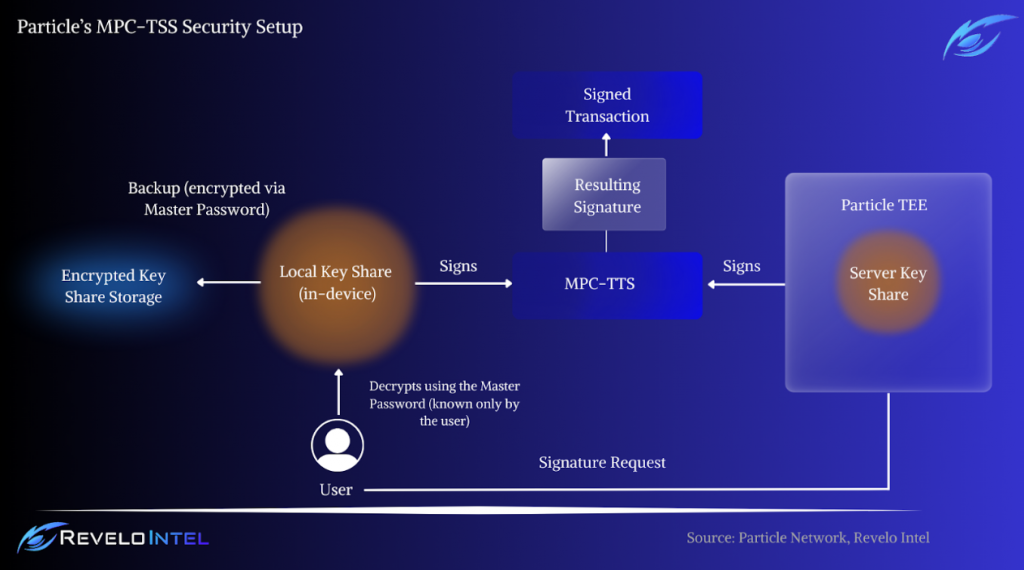
Particle Network employs a 2/2 TSS approach, where the key is split into two independent shares:
- Local User Storage: One share is stored locally by the user.
- Trusted Execution Environment: The other is secured within Particle’s environment, ensuring that cryptographic operations are executed without ever combining the shares.
This method is supported by allowing users to create a Master Password to encrypt their local key fragment, further enhancing security and enabling safe cross-device wallet restoration. Continuous key share refresh mechanisms fortify this setup, preventing attacks and ensuring robust protection of user assets and data.
2. Native Support for Account Abstraction (AA)
Particle Network’s WaaS integrates natively with Account Abstraction, offering a seamless experience that meshes with various use cases:
- Smart Contract Wallets: AA enables the creation of programmable smart contracts that act as non-custodial wallets. These wallets offer advanced automation capabilities, allowing for a more personalized and user-centric approach to asset management.
- Session Keys: This feature simplifies the transaction process by facilitating transactions that do not require signatures, enhancing the user experience by allowing for pre-approved transactions and reducing the cognitive load on users.
- Paymasters: Particle’s integration of Paymasters within its AA framework allows dApps to sponsor transaction fees for users, which is particularly advantageous in solutions hosted on Layer 2s (L2s) where costs are generally lower. This feature enables the acceptance of gas fee payments in any native token, which simplifies transactions for users.
- Bundlers: Bundlers aggregate user actions for more efficient blockchain interactions, leading to potentially reduced transaction fees and faster confirmations. Particle has developed an open-source Bundler that is natively integrated into its AA stack, enhancing cost-efficiency and performance.
- Social Recovery: AA will also support social recovery features in the future, which will allow users to recover their wallets with the assistance of whitelisted accounts, bypassing traditional methods like seed phrases and enhancing both security and user experience.
Looking forward, Particle is developing an Omnichain implementation of AA, aiming to establish a unified framework that bridges AA solutions deployed across different chains.
3. Modularity
The modular design of Particle’s Smart WaaS tools allows developers to customize and scale their applications effectively. Additional features include::
- Authentication: The platform currently offers only social login.
- Cross-Compatibility: Particle Network’s WaaS facilitates easy integration with different blockchain networks, enhancing its utility across the Web3 ecosystem. This feature supports cross-chain and interoperability modules, making it simpler for developers to plug into diverse networks or switch between them without significant overhead.
- Account Abstraction (AA): The importance of AA was highlighted previously, and Particle Network’s modular approach allows for the integration of an Account Abstraction module that can be adopted independently of other platform components. This modularity extends within the AA stack itself, accommodating various functionalities that support a broad range of use cases.
- Product Customization: Developers can utilize custom UI modules to ensure brand consistency across their applications. These modules allow for the integration of specific brand elements such as color schemes and logos, and extend to functional aspects like setting transaction limits, customizing transaction fees, or designing special approval workflows.
- Interoperability with Other Services: The platform’s modularity also includes modules that facilitate integration with third-party services and platforms. This could involve interactions with token swapping and bridging platforms, allowing developers to customize these integrations according to their application’s needs.
4. Feature Richness
The WaaS platform is distinguished by its rich set of features that extend beyond basic wallet services:
- Fiat Ramps: Particle integrates direct fiat onboarding and offboarding solutions, allowing users to seamlessly acquire USDC/USDT without the need to purchase native crypto tokens or rely on centralized exchanges (CEXs). This integration is crucial for providing a streamlined experience, and it is important to note that these services are native within the platform, ensuring users remain within the dApp environment without needing third-party services.
- Cross-Chain Bridging: The WaaS platform supports extensive cross-chain bridging capabilities, facilitated by integrations with leading services like li.fi. This feature is essential for enhancing the platform’s versatility and reducing friction, enabling seamless interactions across different blockchain networks.
- Swaps: Particle supports token swaps directly within the wallet’s UI, utilizing partnerships with prominent services like 1inch to ensure a wide range of swap options. This functionality is integrated natively, providing a smooth and efficient user experience that simplifies asset management and exchange within the ecosystem.
- Additional API Endpoints: The platform offers a diverse range of API endpoints that allow developers to interact more effectively with Web3 technologies. These endpoints support various functions such as contract locking, log retrieval, token management, and interaction with different DeFi platforms and marketplaces, providing significant customization options and flexibility.
- Support for Multiple Chains: Particle Network’s capability to support multiple blockchain networks underscores its adaptability and readiness to meet the demands of an expanding blockchain ecosystem. This multi-chain support ensures that developers can easily transition between different chains, benefiting from a high level of support and seamless integration across the platform.
The integration of these features directly into the wallet and the minimal reliance on external services means that users can enjoy a cohesive and uninterrupted experience. Whether it’s through fiat ramps, cross-chain bridging, or direct swaps, Particle ensures that all functionalities are streamlined and accessible, enhancing the overall utility and ease of use of the platform.
5. Performance
Performance is a feature of Particle’s WaaS. The system is optimized for speed, ensuring that new wallets are generated and ready for use swiftly, and returning users can log in and transact with minimal delay.
The underlying technical infrastructure is designed to handle high loads and complex operations efficiently, ensuring that WaaS remains responsive and reliable even under peak demand.
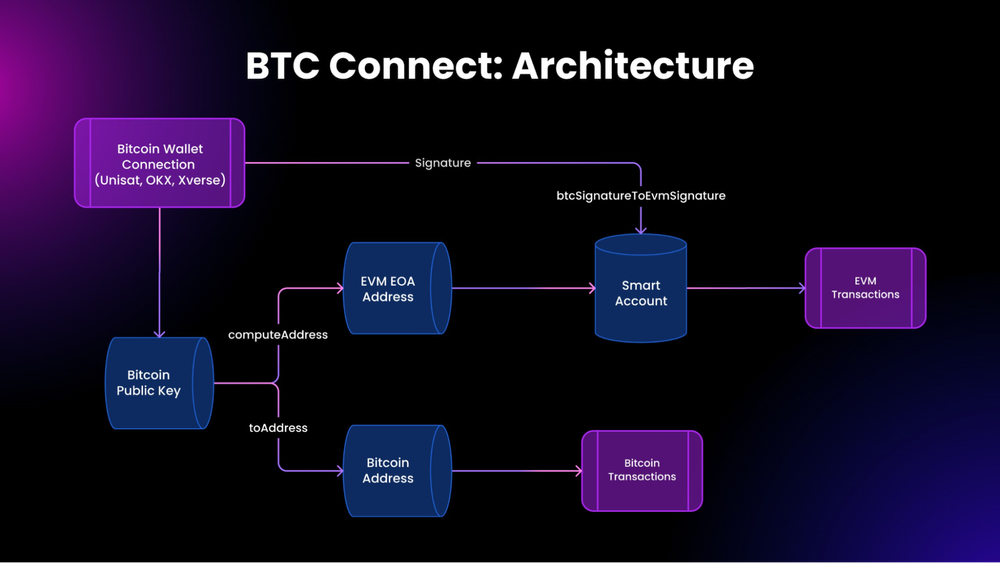
BTC Connect
BTC Connect is the first EVM-compatible ERC-4337 account abstraction (AA) protocol designed specifically for the Bitcoin ecosystem. Supported by leading players in the Bitcoin space, BTC Connect integrates Bitcoin wallets into the broader EVM ecosystem, enhancing both user experience (UX) and functional capabilities.
Bitcoin remains the most valuable blockchain and sets the industry standard for security. Innovations such as Ordinals and BRC-20 “tokens” have spurred a new wave of creativity, particularly around Bitcoin’s Layer-2 expansions which aim to extend Bitcoin’s utility beyond the limitations of its base chain. These include several EVM-compatible Bitcoin L2s like Merlin Chain, BEVM, and bSquared. Despite their potential, the adoption of these L2s by a mainstream audience is hindered by significant friction at the wallet and UI/UX levels when interacting across networks.
ERC-4337 account abstraction is globally recognized as enhancing the EVM ecosystem’s UX, crucial for the mass adoption of Web3 technologies. BTC Connect merges this AA framework with Bitcoin L2 functionalities, allowing users to maintain their usual Bitcoin wallet interactions while engaging with EVM-compatible capabilities, thus bypassing the need for secondary interfaces like MetaMask.
Design Philosophy
BTC Connect simplifies the integration of Bitcoin wallets with EVM-based smart accounts by allowing a Bitcoin wallet to act as the Signer for a smart account on a Bitcoin L2 or EVM network. This approach enables the user’s existing Bitcoin wallet to be the central interaction point, eliminating the need for additional interfaces or complex interactions.
The system incorporates several components:
- Smart Account: Serves as the main interface for executing transactions on EVM networks.
- Paymaster: Manages transaction fees, potentially pre-paid by dApps, facilitating gasless transactions for users.
- Bundler: Groups transactions for efficient processing.
- Bitcoin-Specific Wallet Connection Modal: Facilitates the connection of native Bitcoin wallets (like UniSat, BitGet, or OKX) to the EVM smart accounts.
These elements work together to enable seamless, efficient interactions across Bitcoin and EVM platforms without requiring users to manage multiple keys or install additional software.
Bitcoin AA Advantages
BTC Connect brings several advantages to the Bitcoin ecosystem, enhancing both functionality and user experience:
- Enhanced UX: Simplifies user interactions and transaction structures within the Bitcoin ecosystem, supporting features like popup-less signatures, automated transactions, and batch processing which are currently limited in traditional Bitcoin interactions.
- Improved Security: Allows for the incorporation of advanced security features like multi-signature schemes or complex conditional transaction criteria, thus enhancing the overall safety of transactions.
- Increased Privacy: Offers potential integration with advanced privacy features, improving users’ control over their transaction data and enhancing confidentiality.
BTC Connect not only streamlines the use of Bitcoin in an increasingly complex Web3 environment but also promotes the adoption of Bitcoin L2 ecosystems by simplifying user onboarding and interaction paths.
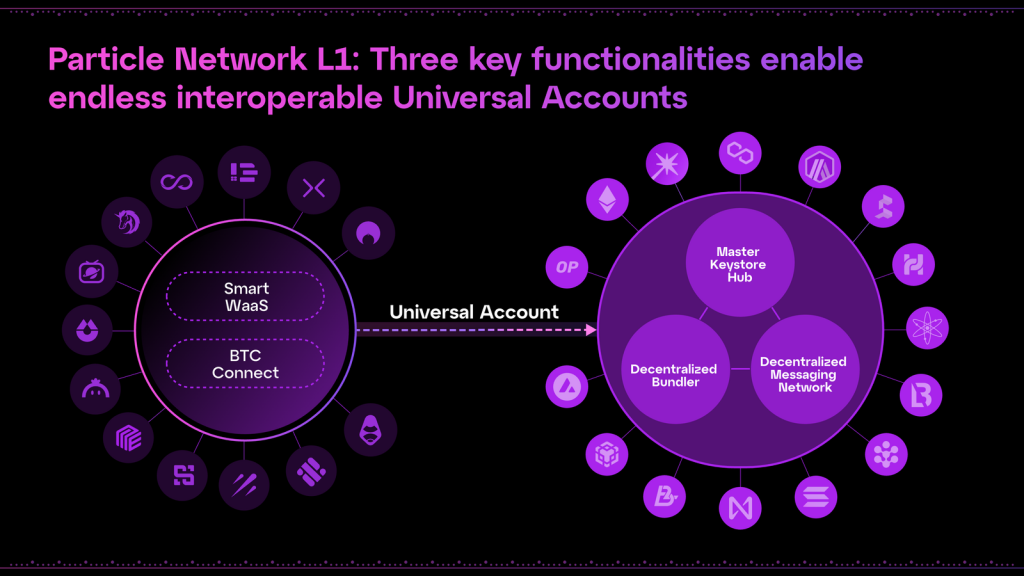
Protocol Architecture
Particle Network approaches its fundamental design distinctively and creatively. The modular L1 divides up its architecture into distinct compartments to decentralize some duties and even outsource some to outside parties. Modular Nodes, a group of nodes powering Particle Network’s fundamental functions, make this a reality.
Key Modules
Particle Network addresses the challenge of Web3’s fragmentation with three strategically designed key modules that ensure seamless interaction and state consistency across multiple blockchain networks. These modules are pivotal in managing user accounts and operations, enhancing the network’s efficiency and scalability.
Master Keystore Hub
- The Master Keystore Hub is the core component within Particle Network’s architecture, serving as the central source of truth for coordinating smart contract deployments and updates across all networks. It automatically synchronizes settings such as modules and signers between each Universal Account instance, ensuring uniformity and state parity across different blockchain networks.
Account settings are centrally stored on Particle Network, facilitating efficient management and deployment of settings across every instance.
Lastly, the Master Keystore Hub utilizes Particle Network’s L1 to send cross-chain messages, deploying new instances or updating existing ones according to the synchronized settings.
Decentralized Messaging Network (DMN)
- The Decentralized Messaging Network is essential for monitoring and settling cross-chain operations by utilizing a messaging protocol powered by Hyperlane; Relayer Nodes on the DMN monitor the execution of UserOperations on external chains. Following the successful execution of operations, the DMN settles the execution status on Particle Network’s L1, ensuring accurate and timely updates of user activities across different chains.
- This network of decentralized Relayer Nodes is tasked with the critical function of monitoring external chain events and settling state events, enhancing the robustness and reliability of cross-chain interactions.
Decentralized Bundler
- Addressing the limitations of current ERC-4337 account abstraction bundlers, which are often centralized and subject to censorship, Particle Network has developed a fully decentralized Bundler network.
- Designed for high-volume, cross-chain UserOperation processing, this network allows for effective handling of operations across multiple chains. Node operators running Bundler nodes initiate and execute UserOperations on external chains, decentralizing the process and reducing potential points of failure or censorship.
- The decentralized nature of this Bundler network ensures greater security and independence from central control, promoting a more resilient and censorship-resistant framework for transaction processing.
Together, these key modules form the backbone of Particle Network’s strategy to combat Web3 fragmentation, offering a comprehensive solution that improves user experience, ensures consistency, and promotes operational efficiency across diverse blockchain environments.
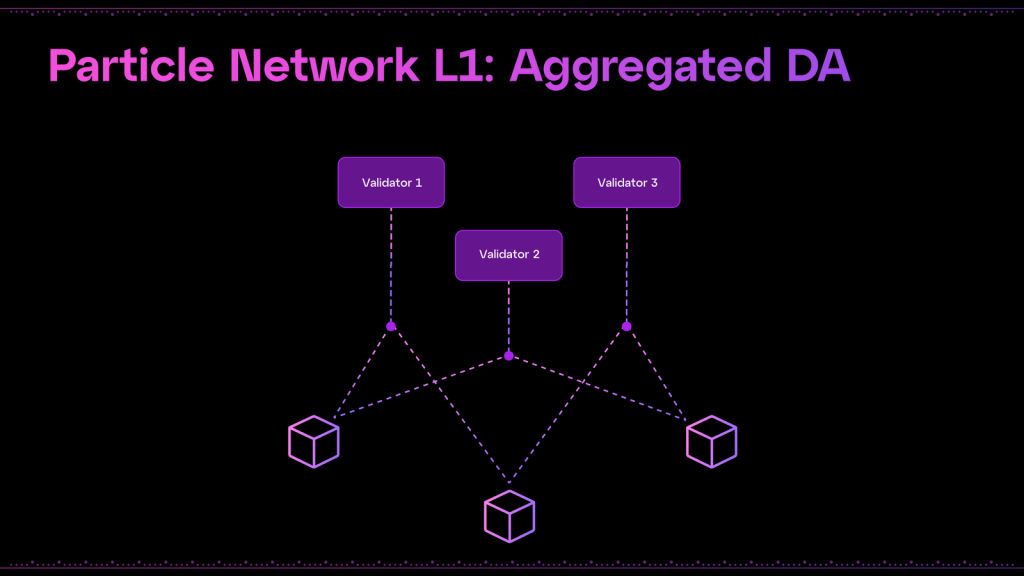
Aggregated Data Availability (AggDA)
Similarly to other modular blockchains, Particle Network outsources the Data Availability (DA) component to external providers. This approach is vital for coordinating cross-chain transactions and maintaining consistent state across every Universal Account.
Particle Network enhances security and operational stability by integrating services from multiple DA providers, thereby avoiding reliance on a single provider and enhancing the network’s resilience. The primary providers included in Particle’s ecosystem are Celestia, known for its scalability and decentralized data storage solutions; Avail, which focuses on robust and efficient data availability layers for decentralized apps; and NEAR DA, offering high-performance data availability solutions tailored for extensive cross-chain operations.
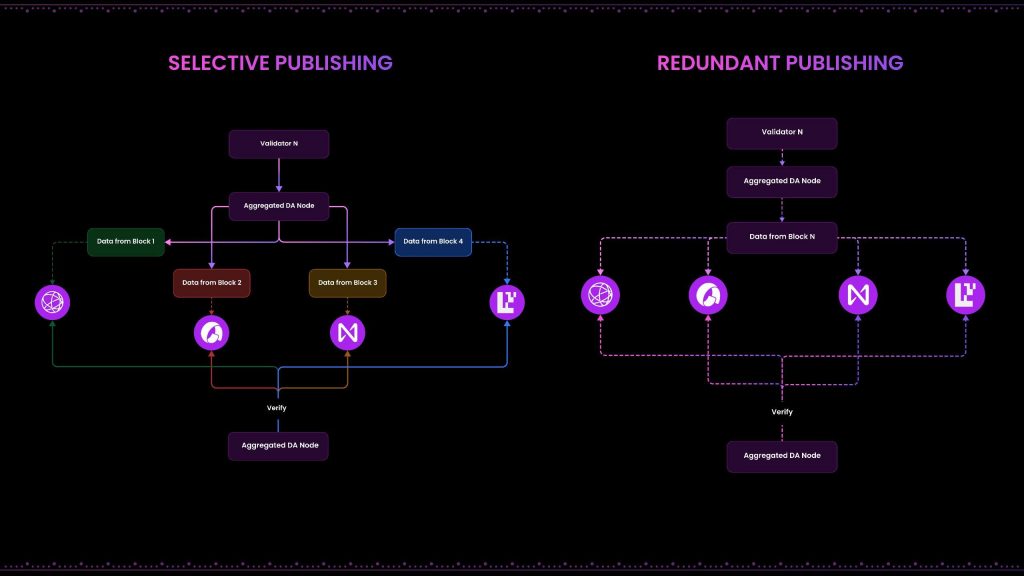
To manage data across these diverse DA layers, Particle Network utilizes strategies like random deterministic redundancy or selective conditional publishing. This approach involves posting and verifying data between different DA layers through dedicated Aggregated DA nodes. These nodes ensure that the aggregated data from various providers is accurately and reliably maintained within the network.
The use of AggDA brings several significant advantages to Particle Network:
- Enhanced Security and Stability: Leveraging multiple DA providers ensures that the network’s data handling is not only secure but also highly stable, minimizing risks associated with data unavailability or corruption.
- Increased Redundancy and Efficiency: Redundant publishing guarantees that critical data is always accessible, even if one or more DA layers fail. Meanwhile, selective publishing optimizes resource use by processing and storing only necessary data, enhancing overall network efficiency.
- Decentralization: The strategy supports greater decentralization by distributing data across various independent platforms, aligning with Particle Network’s commitment to a decentralized blockchain architecture.
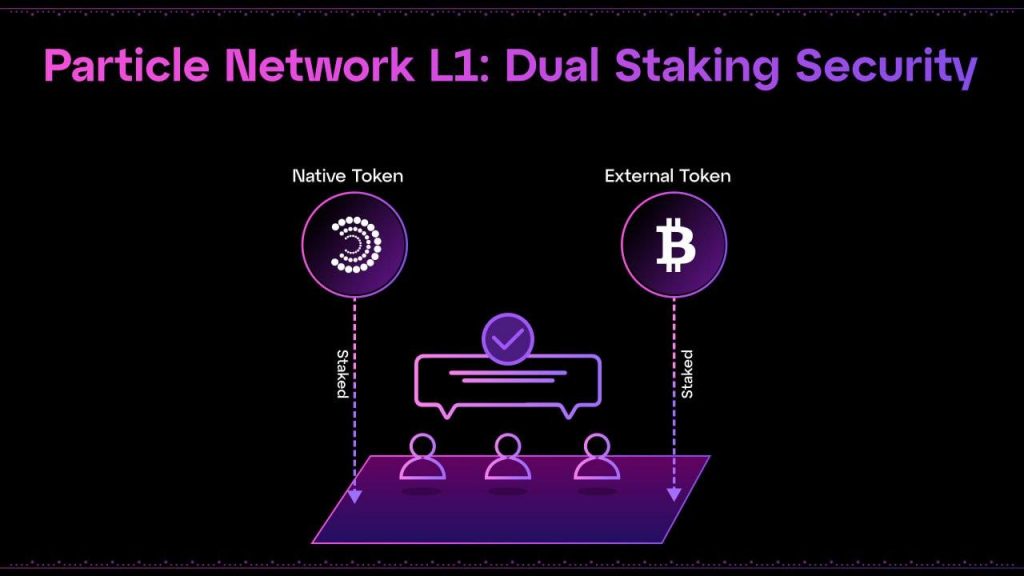
Dual Staking
Particle Network employs a dual staking approach to consensus, which aligns with its broader strategy of enhancing cryptoeconomic security and accessibility within its blockchain infrastructure. This innovative model addresses the inherent risks associated with bootstrapping a new Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network, particularly the volatility that can affect a network’s stability due to its reliance on a native token.
The dual staking model in Particle Network leverages the economic security of both $BTC through the Babylon protocol and its native token, $PARTI. This approach involves two distinct pools of validators:
- $PARTI Validators: One group of validators is secured by staking Particle Network’s native token, $PARTI.
- $BTC Validators: The other group is secured by staking $BTC, utilizing the stability and widespread recognition of Bitcoin to bolster network security.
Both groups of validators must independently agree on the validity of transactions and blocks, ensuring robust security and distributed consensus. This requirement for dual agreement from both $PARTI and $BTC staked validators introduces a layer of redundancy and security uncommon in traditional single-token PoS models.
By not solely relying on its native token, which can be subject to high volatility, especially in its early stages, Particle Network ensures greater stability in its consensus mechanism.
The dual staking model decreases the pressure and security dependence on the $PARTI token alone. This is particularly beneficial during the initial phases of the network’s operation, where the native token might not yet have established significant market trust or stability.
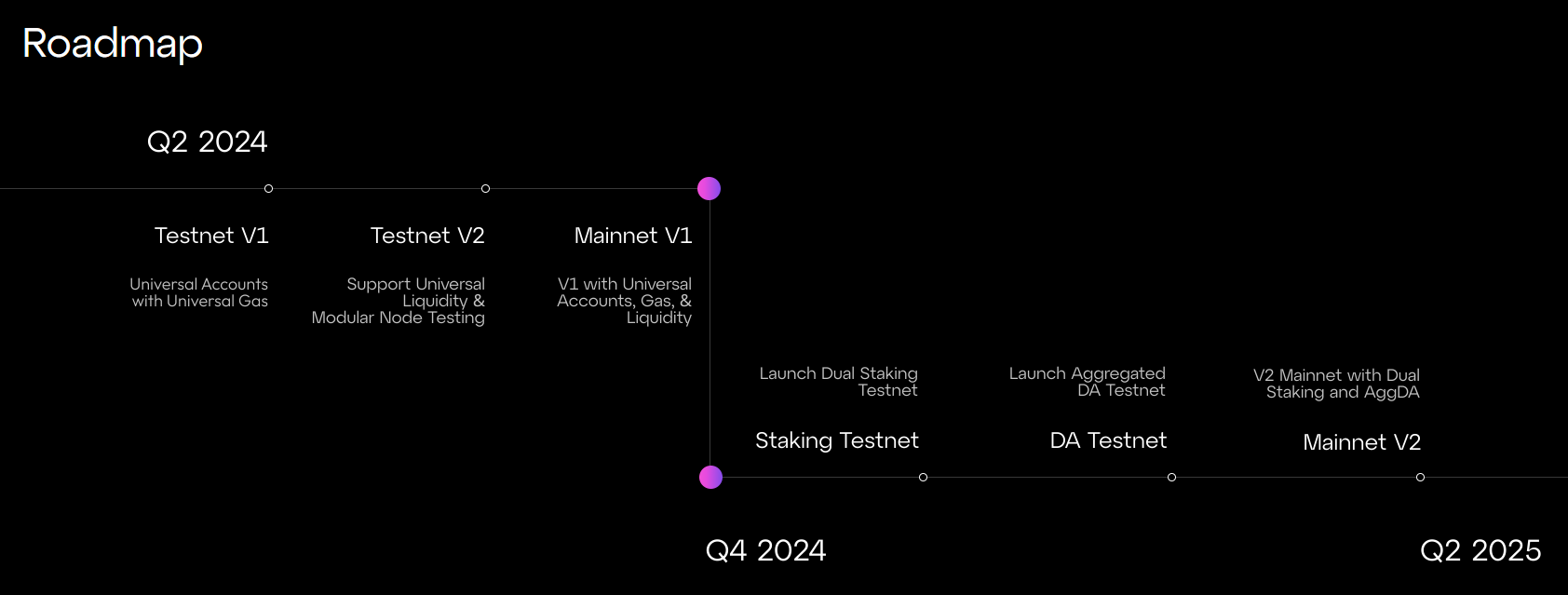
Roadmap
Sector Outlook
The crypto space is experiencing a shift towards a chain abstracted future where users don’t have to navigate through a vast number of chains, bridging through numerous bridges and using different wallets. The vision is to have a single wallet where users can interact with it without having to think about what chain or gas token they are using or having to interact with multiple smart contracts to reach their end goal.
Advocates of this wave claim that the crypto onboarding for new users must be an easier process and not as underwhelming as it is right now. To achieve global adoption the current tools need to be revamped to address all users, regardless of their level of competency or experience.
As Web3 continues to expand rapidly, particularly with the proliferation of Layer 2 (L2) solutions and rollups, the demand for a unified user experience across various blockchain platforms is becoming increasingly important. This demand underscores the necessity of chain abstraction, a framework designed to integrate multi-chain asset and account management to address the existing fragmentation within the blockchain ecosystem. The development of chain abstraction solutions presents numerous challenges, ranging from the technical complexities of coordinating accounts across chains to strategic hurdles in transitioning to a unified Web3 paradigm.
Comprehensive Chain Abstraction Approaches
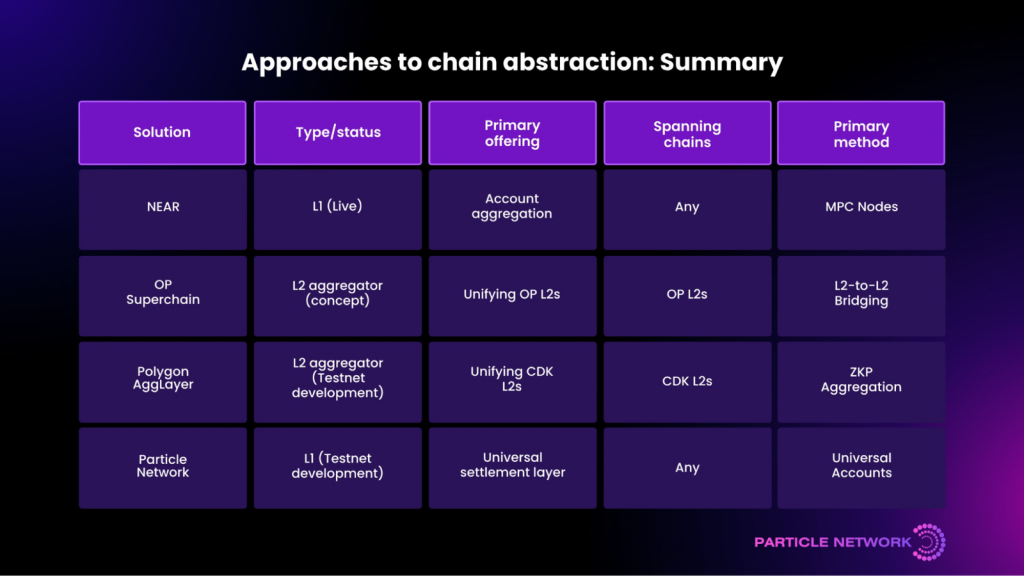
Chain abstraction is a broad goal that seeks to address multiple challenges inherent in the Web3 ecosystem, such as enhancing cross-chain communication and streamlining transactions across different blockchain environments. Various projects are adopting diverse strategies to implement comprehensive chain abstraction solutions. For instance:
- NEAR: Utilizes a Blockchain Operating System that allows users to manage multiple accounts across different chains, facilitating cross-chain transactions via Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and Threshold Signature Schemes (TSS).
- Polygon’s AggLayer: Aims to provide a Unified Bridge for L2s, enhancing asset and liquidity management across newly launched L2 solutions based on Polygon’s Cross-Chain Development Kit (CDK).
- Optimism’s Superchain: Focuses on creating a unified network of blockchains that share security, communication, and bridging features, enhancing the ecosystem’s scalability and interconnectivity.
Each solution, such as those from NEAR, Polygon, and Optimism, is tailored to the specific technological and strategic contexts of their respective ecosystems. For example, Polygon concentrates on ZK-proof aggregation to address liquidity issues, while Optimism aims to scale computational capabilities across a network of chains built on the OP Stack. NEAR approaches chain abstraction by leveraging its high-throughput capabilities to facilitate a central coordination layer for cross-chain interactions.
Particle Network’s Unique Position
Particle Network, initially as a SaaS platform evolved into a significant player in the Account Abstraction (AA) space, leverages its technology to synchronize Smart Accounts across various chains. This enables a unified user experience (UX) where users maintain consistent account addresses and balances across different platforms. Particle’s approach not only aims to simplify user interactions but also integrates advanced features like Universal Liquidity and gas abstraction, settling transactions on its Layer 1 (L1) built on the Cosmos SDK.
A critical aspect of chain abstraction involves managing the underlying economic and liquidity challenges. Projects need robust mechanisms to ensure seamless asset transfers and liquidity management across chains to support the unified UX promised by chain abstraction. Solutions like NEAR and Particle Network utilize their native tokens and cross-chain transaction protocols to facilitate these processes, aiming to minimize friction and maximize efficiency.
The ultimate success of these chain abstraction efforts hinges on their impact on both user and developer experiences. Developers benefit from simplified integration and deployment processes across multiple chains, while end-users enjoy a more seamless and integrated Web3 experience. However, the complexity of these solutions and their reliance on the broader adoption and support from the community and other chains could pose significant challenges.
Future Prospects
As the sector evolves, the trajectory of chain abstraction technologies will likely be influenced by ongoing innovations, user adoption rates, and the integration of emerging technologies that could further streamline cross-chain interactions. The continuous refinement of these technologies, coupled with strategic partnerships and community engagement, will be crucial for overcoming the current limitations and fully realizing the potential of a unified blockchain ecosystem.
Therefore, the sector outlook for chain abstraction is optimistic yet cautious, recognizing the significant potential for innovation and improvement in Web3 UX alongside the substantial challenges that lie ahead. As developers and stakeholders continue to navigate these complexities, the evolving landscape of chain abstraction will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of blockchain technology and its adoption.
Potential Adoption
One of the primary factors that could drive the adoption of Particle Network is its solution to the fragmentation of blockchain networks. Currently, users and developers face significant challenges due to the isolated nature of existing blockchains, which require separate interfaces, wallets, gas tokens, and liquidity pools. Particle Network’s Universal Accounts and liquidity system address these issues directly by enabling cross-chain interactions. This capability is likely to appeal to casual users, who seek simplicity and efficiency in their transactions, and to developers, who require more integrated and efficient systems for building dApps that can operate across multiple blockchains and are easier to reach, thus driving growth.
Particle Network’s emphasis on improving user experience through features like Universal Gas payments and wallet abstraction could attract a large user base. By allowing users to transact across chains using a single wallet without managing multiple tokens for gas payments, Particle Network significantly simplifies the user experience, especially for new crypto users. This ease of use is a crucial factor in attracting a broader audience to the crypto space, which is often perceived as overly complex and inaccessible by mainstream users. Additionally, the ability to integrate social logins and provide a more familiar authentication experience can lower the entry barrier, making Particle Network an attractive platform for new and less technically inclined users.
Looking ahead, the potential for Particle Network to become a key player in the blockchain space is connected to its alignment with the trend towards blockchain agnosticism and interoperability. As the blockchain landscape continues to evolve, the ability of platforms like Particle Network to provide cross-chain functionality while maintaining high levels of security and user-friendliness will likely become increasingly required. Also, with the increasing number of new chains being launched, the demand for a solution that connects all of them and their dApps will increase significantly.
In summary, Particle Network’s approach to solving significant blockchain usability and interoperability issues, combined with its scalable architecture and focus on user experience, positions it well for general adoption across both the crypto-savvy and the yet-to-adopt blockchain sectors of the market.
Chains
Particle Network supports more than 60 chains and 900 dApps, a significant coverage of the Web3 ecosystem.
Using the Protocol
Example of Universal Liquidity
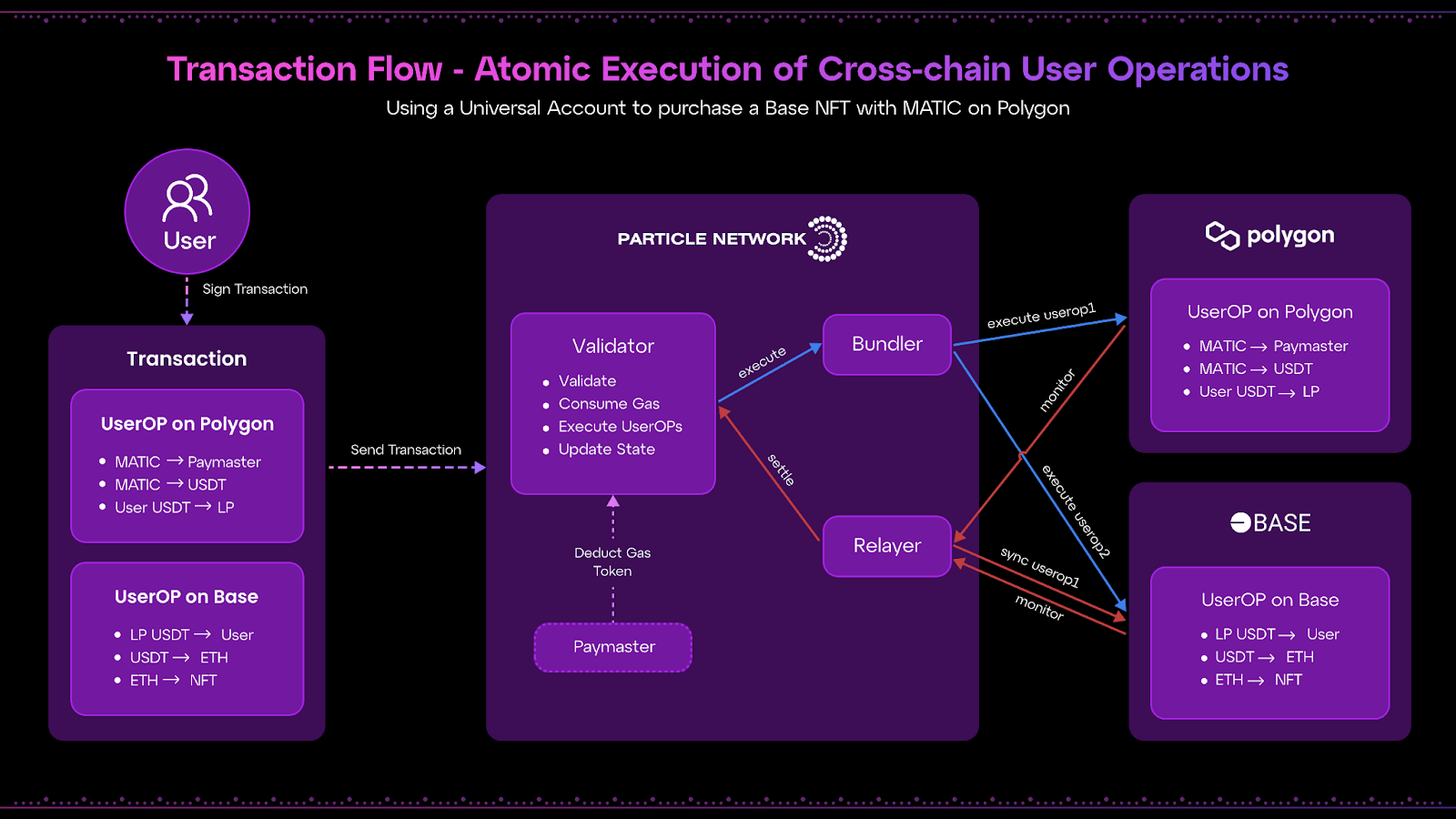
To better understand how Particle Network facilitates Universal Liquidity, let’s explore a practical example that demonstrates the seamless integration of assets across multiple chains. This example involves a user attempting to purchase an NFT priced at $300 in $ETH on Chain D, using their $USDT balance which is distributed across Chains A, B, and C.
Here’s the how-to the process goes:
- Initiating the Transaction: The user decides to purchase the NFT and initiates the transaction by clicking “Buy”. This action triggers a process that involves bundling UserOperations across five different chains—Chains A, B, C, D, and Particle Network. The user completes this through a single signature sent to the Particle L1.
- Token Exchange Across Chains: Once the signature is executed on Particle L1, the $USDT held on Chains A, B, and C is converted into an intermediary token, such as $USDC, through decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operating on each of these chains. This step is crucial as it consolidates the user’s funds into a single type of token across the chains, simplifying the next steps of the transaction.
- Transferring to a Liquidity Provider: The converted $USDC from Chains A, B, and C is then transferred to a Liquidity Provider (LP). This LP acts as a facilitator to aggregate the funds from multiple chains and prepare them for the final purchase on Chain D.
- Releasing Funds on the Target Chain: The LP then releases the aggregated $USDC on Chain D. This step is critical as it positions the funds on the same chain as the NFT, making the final purchase possible.
- Final Conversion and Purchase: On Chain D, the $USDC is exchanged for $ETH, the required currency for the NFT purchase, using a DEX on Chain D. Once the $ETH is available, the user completes the transaction by purchasing the desired NFT.
There’s also the visual of the transaction flow:
Note, that while this example includes the process of swapping $USDT for an intermediary token ($USDC), in some scenarios where the intermediary token is universally accepted across the involved chains, such swaps might not be necessary.
This example illustrates the efficiency of Particle Network’s Universal Liquidity. By enabling the use of a single account and balance across multiple chains, the network simplifies the user’s interaction within the blockchain ecosystem. The process eliminates the need for the user to manually manage multiple wallets or perform several currency exchanges across different platforms. Additionally, it shows how Particle Network can automate the process of fund aggregation and currency conversion, which are essential for conducting seamless transactions across different blockchain networks.
Example of Universal Gas
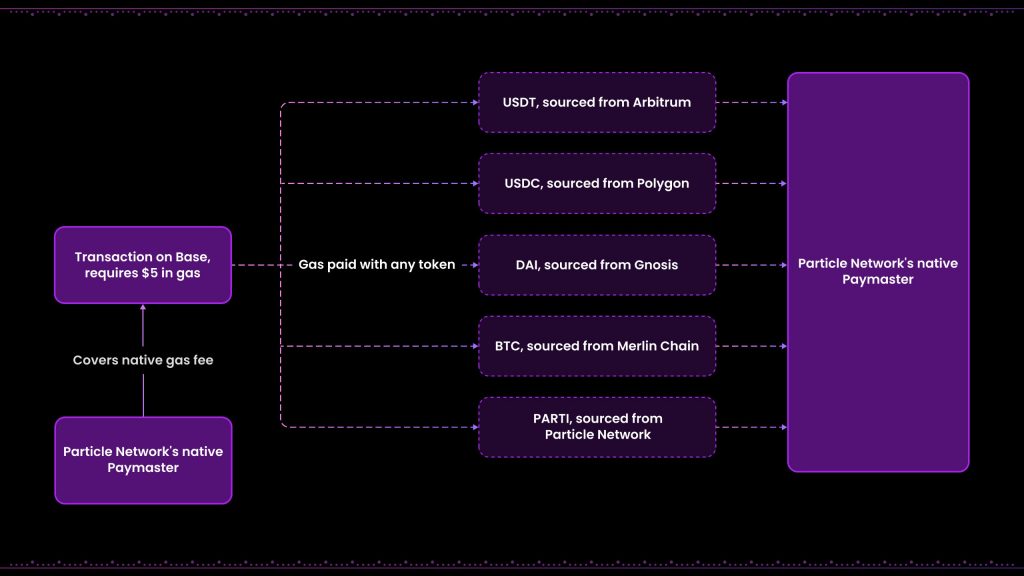
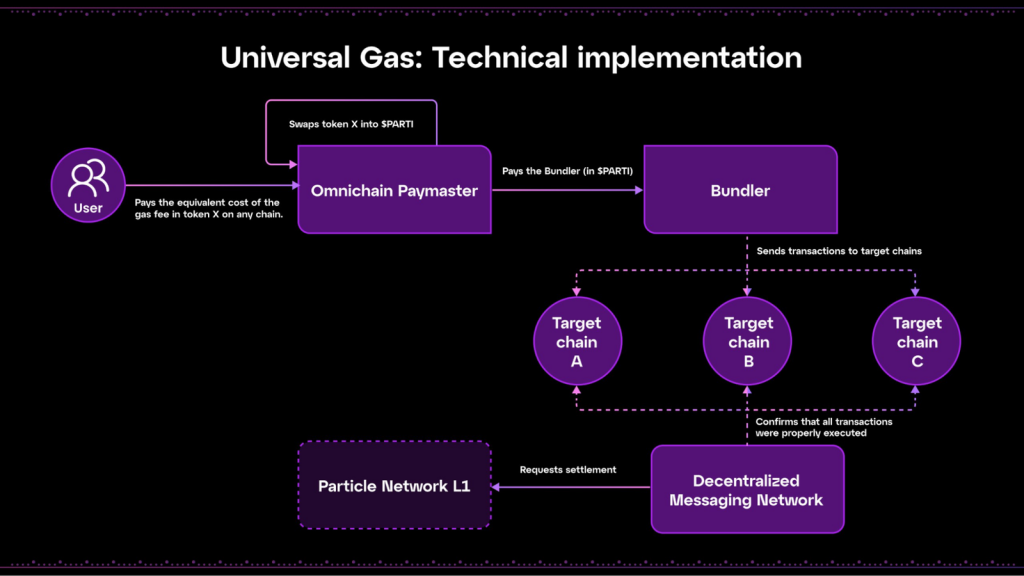
Universal Gas operates through a combination of Particle Network’s Universal Liquidity and an Omnichain Paymaster system. This approach allows users to use any token they own on any chain to pay for transaction fees, with Particle Network’s native token, $PARTI, serving as the central medium for final fee settlement.
- Token Selection and Payment: When a user initiates a transaction, they can choose to pay the transaction fee with any token they prefer, regardless of the blockchain on which the transaction is executed. This user flexibility is a core advantage of Universal Gas, removing the hassle of acquiring specific gas tokens for different chains.
- Role of Omnichain Paymaster: The Omnichain Paymaster is pivotal in the Universal Gas system. It handles the conversion of the user-selected token into $PARTI, the native token of Particle Network. This Paymaster ensures that the value of the transaction fee is maintained regardless of the token used, calculating the equivalent amount of $PARTI needed to cover the transaction costs.
- Transaction Processing by Bundler Nodes: Once the payment is made to the Paymaster, Bundler nodes come into play. These nodes are responsible for packaging and sending the transaction to its designated blockchain for execution. They are compensated for their services in $PARTI, regardless of the original token used by the user.
- Settlement Across Chains: After the transaction is executed on the target chain, the gas payment is finalized through a settlement process that involves converting a portion of the transaction fee back into $PARTI. This ensures that all fees are ultimately settled on the Particle Network, maintaining consistency and stability in the network’s economic model.
- Simplifying User Experience: The entire process is designed to be seamless and transparent to the user, who benefits from not having to manage multiple types of gas tokens or engage in complex bridging activities. This ease of use significantly enhances the user experience, particularly for those who frequently interact across different blockchains.
Below is the technical workflow of Universal Gas.
Universal Gas exemplifies Particle Network’s commitment to reducing complexity in the blockchain space. By leveraging the native $PARTI token and components like the Omnichain Paymaster and Bundler nodes, Particle Network ensures that users can effortlessly pay transaction fees with their token of choice, promoting broader accessibility and integration of blockchains.
Business Model
Particle Network’s business model revolves around a Layer 1 which aims to simplify and enhance user experiences across various blockchain ecosystems through Universal Accounts and chain abstraction. The platform’s primary objective is to resolve the fragmentation issues prevalent in Web3 by providing seamless integration and interaction across different blockchains – adding value to each chain instead of competing for liquidity. This vision is supported by multiple revenue-generating opportunities and strategies that capitalize on value flows through the ecosystem.
Similar to other L1, transaction fees lie at the core of Particle Network’s revenue streams. Every transaction processed on the network, whether it involves cross-chain interactions, smart contract executions, or simple transfers, incurs a fee. These fees are structured to cover the computational and operational costs of maintaining the network (nodes), ensuring its efficiency and scalability.
Another significant aspect of Particle Network’s business model is its dual staking mechanism. Users can stake the native $PARTI tokens or $BTC, which not only secures the network but also generates staking rewards. These rewards are derived from the transaction fees collected by the network and possibly from new token issuances, depending on the network’s future governance decisions. This mechanism incentivizes participation and investment in the network, boosting its security and decentralization while providing a return to the stakeholders.
It’s key to note that the $PARTI token will accrue significant value since its been consumed from every transaction that occurs by a Universal Account as part of the settlement process.
Tokenomics
$PARTI, the native token of Particle Network. The token serves as the backbone of the Particle Ecosystem for chain abstraction and powering Universal Accounts for cross-chain interactions. It also functions as a governance token within the proof-of-stake (PoS) framework of the Particle Chain, alongside supporting Universal Gas and settlements.
Token Distribution
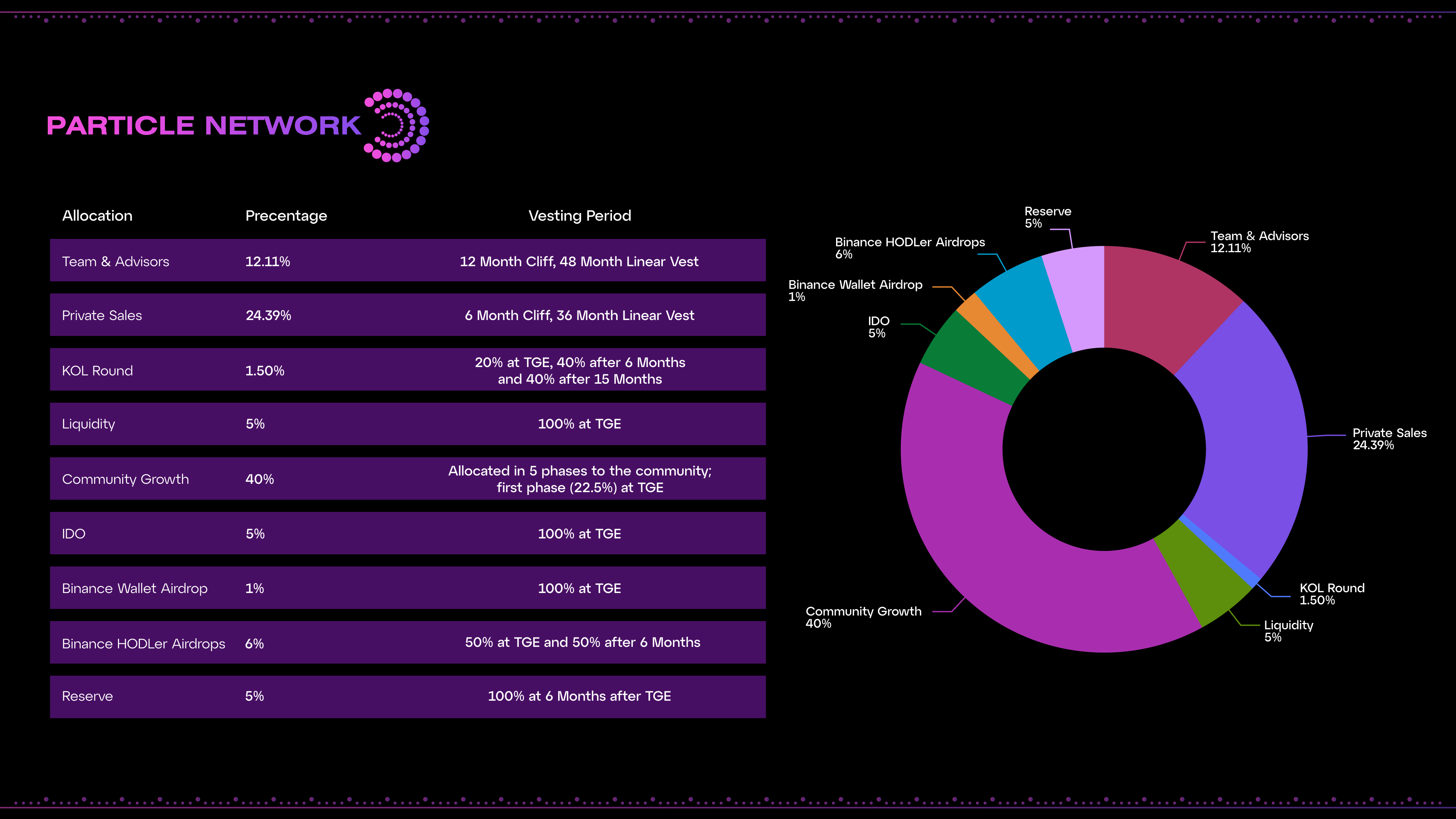
The fixed total supply of $PARTI tokens is capped at (1,000,000,000) 1 billion, with the following distribution:
Community Growth: 40% (400,000,000 tokens)
- Includes 9% (90,000,000 tokens) for initial airdrops.
- The remaining 31% (310,000,000 tokens) is to be released periodically to incentivize user adoption and engagement.
Private Sales: 24.39% (243,900,000 tokens)
- Subject to an initial lockup period, followed by a multi-year release schedule.
Team & Advisors: 12.11% (121,100,000 tokens)
- Vested over multiple years to ensure alignment with the project’s long-term objectives.
Binance HODLer Airdrops: 6% (60,000,000 tokens)
- Distributed in two separate campaigns targeting long-term BNB holders.
Liquidity: 5% (50,000,000 tokens)
- Deployed at the token generation event (TGE) to support immediate market stability and depth.
Initial DEX Offering (IDO): 5% (50,000,000 tokens)
- Allocated for $PARTI’s Binance Wallet IDO.
Reserve: 5% (50,000,000 tokens)
- Held for future strategic needs and ecosystem expansion.
KOL (Key Opinion Leader) Round: 1.5% (15,000,000 tokens)
- Partially unlocked at TGE, with the remainder released gradually over time for strategic influencers and partners.
Binance Wallet Airdrop: 1% (10,000,000 tokens)
- Allocated at TGE for targeted user onboarding via Binance Wallet.
Risks
Particle Network, like any blockchain-based system, faces a variety of risks that can impact its functionality, security, and adoption. Here are some of the key risks associated with a protocol like Particle Network.
Technical Risks
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Despite rigorous testing, smart contracts can contain bugs or vulnerabilities that may be exploited by malicious actors. These vulnerabilities can lead to loss of funds or unintended behaviors in the protocol.
- Scalability Issues: As the network grows, scalability challenges may arise. If Particle Network cannot efficiently handle an increased number of transactions, it might experience slower transaction times and higher costs, which could deter users.
- Integration Complexity: The protocol’s ability to interact with multiple blockchains adds a layer of complexity, which could lead to potential errors or inconsistencies in cross-chain transactions.
When it comes to blockchains these parameters are the most common and the first that need to be addressed by the protocol.
Security Risks
- Key Management: While the dual key management and threshold signature schemes enhance security, they also introduce complexity in key management. Any failure in these systems, such as synchronization errors or compromised key shares, could lead to security breaches.
- Dependence on External Services: The use of external data availability layers and other third-party services introduces dependency risks. Any compromise or failure of these services could impact the network’s stability and security.
- Node Compromise: With a decentralized network of nodes like Bundler Nodes and Relayer Nodes, there is a risk of node compromise. If enough nodes are compromised, it could affect the integrity of the transactions or data relayed across the network.
Security is a matter of the utmost importance regarding blockchains. A reliable and secure platform builds trust among users and investors who are the key factor of growth and success.
Adoption Risk
As part of the modular expansion, Particle Network introduces innovations and technologies that are directly connected to the technology of modular blockchains. This concept is fairly new and its adoption is still being tested by the larger user base of crypto. This narrative has gained a lot of traction with the introduction of the newest projects and it’s considered one of the most promising ones in the crypto space.
Particle Network bets on this adoption wave with a strong product offering.
Security
Particle Network places great importance on the secure management of private keys (only social logins), recognizing them as the most valuable possessions in the blockchain space. The security architecture and key management philosophy are designed to ensure the utmost protection of user assets while maintaining ease of use and accessibility.
Particle Network believes in three fundamental principles to ensure the security of its services:
- User Control: Only the user has full control over their funds. No other parties, including Particle Network or developers, can initiate the signing process or access the user’s funds.
- Safe Account Restoration: Users can safely restore their accounts even if they delete their apps or lose their phones, ensuring continued access to their assets without compromising security.
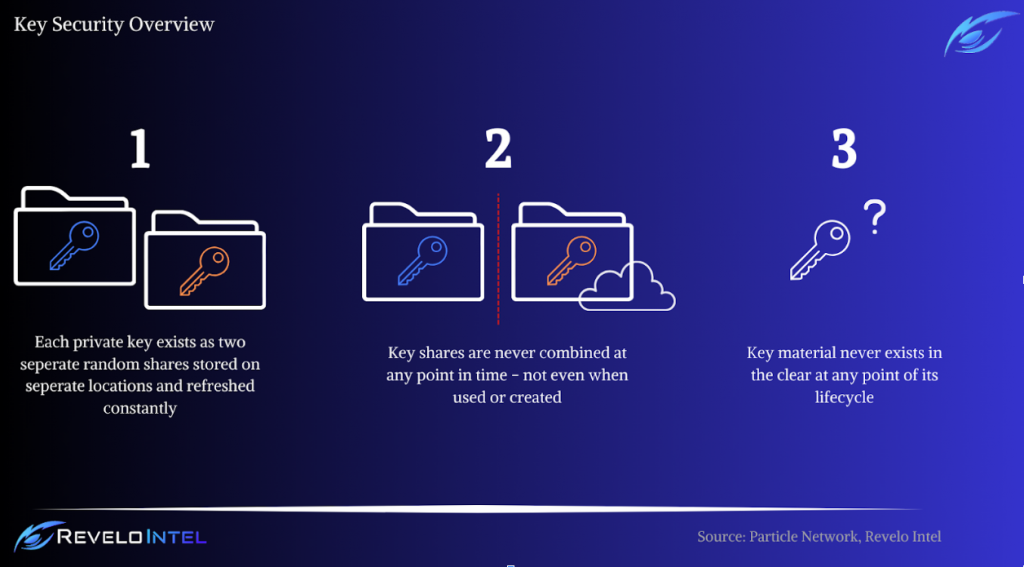
- Elimination of Single Points of Failure: Traditional private key systems are vulnerable to loss or theft. Particle Network addresses this by replacing the conventional private key with two independently created mathematical secret shares, removing any single point of failure.
Next-Gen Key Management Approach
This approach involves secure multiparty computation (MPC) for protecting and managing cryptographic keys:
- Key Division: Sensitive keys and secrets are split into two random shares and stored on separate, segregated entities. Each share is independently meaningless and reveals nothing about the full key material.
- Cryptographic Operations: All operations, including signing, derivation, and generation, are performed without combining these shares, ensuring that the complete key material or secret is never present in memory.
- Continuous Key Refresh: The system modifies key shares continuously without altering the key itself, requiring an attacker to compromise both parties simultaneously to access the key material.
Furthermore, Particle Network employs a secure MPC implementation supporting various cryptographic algorithms:
- 2-Party EdDSA: For networks like Solana.
- 2-Party ECDSA: Applicable to Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, and others.
Through this implementation, Particle Network ensures that the key management system is secure, chain-agnostic, robust, and non-custodial.
Threshold Signatures
The Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) is used for distributed key generation and signing, enhancing security by distributing the private key’s responsibilities across multiple parties. Unlike multisig which operates on-chain and is blockchain-specific, TSS operates off-chain using pure cryptography, allowing for universal support. Compared to the Shamir Secret Sharing Scheme (SSSS), TSS does not require reconstructing the private key for signing, thus eliminating a point of failure.
Infrastructure Security Architecture
To safeguard its infrastructure, Particle Network implements the highest industry standards:
- The network features end-to-end encryption with TLS, segregated public/private networks, and advanced intrusion detection systems.
- It includes a Trustee Particle Network TSS Party-2 Server and a Hardware Security Module to ensure physical and digital security measures are state-of-the-art.
Audits
Particle Network has conducted private audits with Salus Sec and public audits with Certik.
Certik’s Audit for Particle Network.
Also, there was an audit by OpenZeppelin for BTC Connect.
Particle Network BTC Smart Account Audit.
To maintain a consistent baseline of security, Particle Network gets its codebase inspected regularly. As a result, Particle Network is one of the top-ranked protocols globally on CertiK among audits that do not include tokens.
Furthermore, Particle Network maintains an ongoing bug bounty program with CertiK, which may be accessed here.
Dependencies and Access Controls
Particle Network, like many blockchain platforms, relies on various dependencies and implements access controls to ensure the security and functionality of its ecosystem.
The protocol depends on several external services, such as data availability layers (like Celestia, Avail, and NEAR DA) and other blockchain services that facilitate cross-chain interactions. The performance and reliability of these services may directly affect Particle Network’s operations.
Moreover, the network’s functionality relies on the proper operation of decentralized nodes such as Bundlers and Relayers. These nodes must work synchronously to manage cross-chain transactions, messaging, and security monitoring, making the network dependent on their continuous and fault-free operation.
Particle Network’s dual staking model, involving both its native token $PARTI and $BTC (through Babylon), introduces a dependency on the economic stability and security of these assets. Potential changes in the valuation or security assumptions of these tokens could impact the network’s consensus mechanism.
Particle also employs advanced key management techniques for WaaS and social logins, including MPC (Multi-Party Computation) and TSS (Threshold Signature Schemes), which distribute the control over private keys among multiple parties. This setup prevents a single point of failure but introduces complexity in key access and management.
Certain operations within the network, such as transaction bundling or data relaying, are restricted by Particle to nodes that fulfill specific criteria and roles. This ensures that only authorized and capable nodes participate in these critical functions, enhancing security.
Finally, Particle Network likely implements role-based access controls (RBAC) within its infrastructure to manage the permissions for network administrators and users. This helps in controlling access to administrative functions and sensitive operations, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and actions.
Team
The team of Particle Network is composed of several individuals with rich backgrounds and extensive experience in the Web3 ecosystem with significant contributions to the space. Despite being based in Singapore, Particle Network employs individuals all around the world combining experience, knowledge, and different backgrounds.
The core team includes the following members:
- Pengyu Wang – Founder & CEO | LinkedIn | Twitter
- Peter Pan – Co-Founder & CTO | Twitter
- DongXi Huang – Backend Lead | LinkedIn
- Kerf Chang – Head of Ecosystem | LinkedIn
- Ethan Francis (TABASCO) – Head of Developer Relations | LinkedIn | Twitter
- Isaac Wellner – Business Development & Partnerships | LinkedIn
- Jethro Kwan – Growth Manager | LinkedIn
- Carlos Maximiliano Cano – Senior Content Manager | LinkedIn
Project Investors
Particle Network’s latest fundraising efforts have culminated in a $25 million injection aimed at further developing its platform and technologies. This follows an earlier funding round that raised $15 million, which was led by Spartan Group and Gumi Crypto. The continued financial backing highlights the project’s growing traction and potential in the blockchain space.
The recent investment rounds have attracted a diverse group of backers. Spartan Group and Gumi Crypto led the initial significant investment, emphasizing their strategic commitment to Particle Network’s vision.
The latest funding rounds saw contributions from several prominent venture capital firms and investors, including SevenX Ventures, Morningstar Ventures, HashKey Capital, MH Ventures, UOB Venture Management, Flow Traders, ZeroSevenOne Labs, and SNZ.
Particle Network is also supported by its original backers who were instrumental in the early stages of the project. This group includes Animoca Ventures, LongHash Ventures, and Alibaba Group.
FAQ
What is Particle Network?
Particle Network is a Layer 1 blockchain platform designed to unify different blockchain networks through Universal Accounts, enabling seamless cross-chain interactions and liquidity management to solve the issue of fragmentation in the Web3 ecosystem.
How does Particle Network solve blockchain fragmentation?
Particle Network addresses fragmentation by introducing Universal Accounts that allow users to maintain a single identity and balance across multiple blockchains. This is facilitated through technologies like Universal Liquidity and Universal Gas, which simplify interactions and transactions across different networks.
What are Universal Accounts?
Universal Accounts in Particle Network are specialized smart account implementations that enable users to have a consistent address and balance across various blockchain ecosystems. These accounts simplify the management of assets and interactions across different chains.
What is Universal Liquidity?
Universal Liquidity is a feature within Particle Network that unifies liquidity across all chains. It allows for the optimistic execution of multi-chain atomic transactions, enabling users to interact with new chains without holding native tokens on those chains.
How does Universal Gas work?
Universal Gas allows users to pay transaction fees with any token from any chain, which is then converted into Particle Network’s native token, $PARTI, to settle transactions. This feature eliminates the need to manage multiple types of gas tokens, simplifying the user experience.
Can I use Particle Network right now?
No, the protocol is still in testnet and to participate in it you must acquire an invite code to use the platform. As of now, users can only use social logins and AA on Mainnent.
Can I integrate Particle Network into my existing application?
Yes, developers can integrate Particle Network’s services into existing applications using its comprehensive APIs and SDKs. This includes Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS) functionalities that support social logins and embedded wallet interfaces.
What security measures does Particle Network employ?
Particle Network utilizes advanced cryptographic techniques such as Multi-Party Computation (MPC) for secure key management (social logins) and Threshold Signature Schemes (TSS) to enhance security. It also implements decentralized validation mechanisms to secure the network and transactions.
What is the role of the $PARTI token in Particle Network?
The $PARTI token will serve multiple purposes within Particle Network, including paying for transaction fees, participating in governance decisions, and staking for network security. It acts as the primary medium of exchange and value within the ecosystem.
How can I get started with using Particle Network?
To start using Particle Network, users can create a Universal Account through the platform’s interface or integrated applications. Developers interested in building on Particle Network can access its developer documentation for detailed guides and API references to integrate Particle Network’s functionalities into their projects.
How does Particle Network handle cross-chain transaction finality and security?
Particle Network ensures cross-chain transaction finality and security using a combination of its Modular Nodes and Decentralized Messaging Network (DMN). The Modular Nodes, including Bundler and Relayer nodes, manage the execution and confirmation of transactions across different blockchains. The DMN, powered by protocols like Hyperlane, monitors and verifies the success of these transactions, ensuring reliable communication and finality across chains.
Community Links